|
General Aircraft GAL.33 Cagnet
The General Aircraft GAL.33 Cagnet was a British light trainer aircraft designed by General Aircraft Ltd which flew from 1939 to 1941. Only one example was constructed. Design The Cagnet was a two-seat pusher propeller aircraft. The side-by-side seating was in an open cockpit just ahead of the strut-mounted inline engine. The low cantilever wings featured a gull shape, with twin booms mounted, one at each wing's bend point. A horizontal stabilizer and elevator ran between twin fins with rudders, one at the end of each boom. The fixed landing gear used a nosewheel. First flight was in 1939; the aircraft bore the serial number ''T46''. General Aircraft proposed the Cagnet as a basic trainer. It was tested as a Flying Observation post trainer by the Royal School of Army Co-operation from February through June 1940 (with military serial number A serial number is a unique identifier assigned incrementally or sequentially to an item, to ''uniquely'' identify it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a landbridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's third-most-populous island after Java in Indonesia and Honshu in Japan. The term "Great Britain" is often used to refer to England, Scotland and Wales, including their component adjoining islands. Great Britain and Northern Ireland now constitute the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trainer Aircraft
A trainer is a class of aircraft designed specifically to facilitate flight training of pilots and aircrews. The use of a dedicated trainer aircraft with additional safety features—such as tandem flight controls, forgiving flight characteristics and a simplified cockpit arrangement—allows pilots-in-training to safely advance their skills in a more forgiving aircraft. Civilian pilots are normally trained in a light aircraft, with two or more seats to allow for a student and instructor. Tandem and side by side The two seating configurations for trainer aircraft are: pilot and instructor side by side, or in tandem, usually with the pilot in front and the instructor behind. The side-by-side seating configuration has the advantage that pilot and instructor can see each other's actions, allowing the pilot to learn from the instructor and the instructor to correct the student pilot. The tandem configuration has the advantage of being closer to the normal working environment that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Aircraft Ltd
General Aircraft Limited was a British aircraft manufacturer from its formation in 1931 to amalgamation with Blackburn Aircraft in 1949 to become Blackburn and General. Its main products were military gliders and light transport aircraft. History On 27 February 1931, General Aircraft Limited (GAL) was formed to undertake production of aircraft using the 'monospar' wing designs of the Mono-spar Company Ltd. Both firms were headed by Helmut J. Stieger, the Swiss inventor of the technique. GAL produced about 28 examples of the Monospar series of twin-engined light transport aircraft at Croydon Aerodrome between 1932 and 1934. In October 1934, both companies were re-capitalised by investment group British Pacific Trust, and were re-formed in a new company also named General Aircraft Limited. Also included in the new company were the assets of National Flying Services Ltd, the owner of London Air Park, plus adjoining industrial premises built in 1917 by Whitehead Aircraft Ltd. In e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pusher Propeller
In an aircraft with a pusher configuration (as opposed to a tractor configuration), the propeller(s) are mounted behind their respective engine(s). Since a pusher propeller is mounted behind the engine, the drive shaft is in compression in normal operation. Pusher configuration describes this specific (propeller or ducted fan) thrust device attached to a craft, either aerostat (airship) or aerodyne (aircraft, WIG, paramotor, rotorcraft) or others types such as hovercraft, airboat and propeller-driven snowmobiles. "Pusher configuration" also describes the layout of a fixed-wing aircraft in which the thrust device has a pusher configuration. This kind of aircraft is commonly called a pusher. Pushers have been designed and built in many different layouts, some of them quite radical. History The rubber-powered "Planophore", designed by Alphonse Pénaud in 1871, was an early successful model aircraft with a pusher propeller. Many early aircraft (especially biplanes) were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ;Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is supported at only one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilever can be formed as a beam, plate, truss, or slab. When subjected to a structural load at its far, unsupported end, the cantilever carries the load to the support where it applies a shear stress and a bending moment. Cantilever construction allows overhanging structures without additional support. In bridges, towers, and buildings Cantilevers are widely found in construction, notably in cantilever bridges and balconies (see corbel). In cantilever bridges, the cantilevers are usually built as pairs, with each cantilever used to support one end of a central section. The Forth Bridge in Scotland is an example of a cantilever truss bridge. A cantilever in a traditionally timber framed building is called a jetty or forebay. In the southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Boom
A twin-boom aircraft is characterised by two longitudinal booms (extended nacelle-like bodies). The booms may contain ancillary items such as fuel tanks and/or provide a supporting structure for other items. Typically, twin tailbooms support the tail surfaces, although on some types such as the Rutan Model 72 Grizzly the booms run forward of the wing. The twin-boom configuration is distinct from twin-fuselage designs in that it retains a central fuselage. Design The twin-boom configuration is distinct from the twin fuselage type in having a separate, short fuselage housing the pilot and payload. It has been adopted to resolve various design problems with the conventional empennage for aircraft in different roles. Engine mounting For a single engine with a propeller in the pusher configuration or a jet engine, a conventional tail requires the propeller or exhaust to be moved far aft, requiring either a very long driveshaft or jet pipe and thus reducing propulsive efficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabiliser, is a small lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplanes. Not all fixed-wing aircraft have tailplanes. Canards, tailless and flying wing aircraft have no separate tailplane, while in V-tail aircraft the vertical stabiliser, rudder, and the tail-plane and elevator are combined to form two diagonal surfaces in a V layout. The function of the tailplane is to provide stability and control. In particular, the tailplane helps adjust for changes in position of the centre of pressure or centre of gravity caused by changes in speed and attitude, fuel consumption, or dropping cargo or payload. Tailplane types The tailplane comprises the tail-mounted fixed horizontal stabiliser and movable elevator. Besides its planform, it is characterised by: *Number of tailplanes - from 0 ( tailless or canard) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Aircraft Test Serials
United Kingdom aircraft test serials are used to externally identify aircraft flown within the United Kingdom without a full Certificate of Airworthiness. They can be used for testing experimental and prototype aircraft or modifications, pre-delivery flights for foreign customers and are sometimes referred to as "B" class markings. 1930s An initial set of markings was introduced in 1929, each company was allocated a letter to which would follow a number, sometimes with a hyphen or a gap between. For example, A was allocated to the Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft and ''A 1'' was used in March 1930 on an Armstrong Whitworth Starling. Sometimes Hawker and Vickers would also add the letters PV to the markings to indicate a private venture (that is a type in development not paid for by the Air Ministry). 1940s The presentation was changed to look like a military serial for security reasons during the Second World War. For example, the prototype de Havilland Mosquito was allocated test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Military Aircraft Serials
United Kingdom military aircraft serial numbers are aircraft registration numbers used to identify individual military aircraft in the United Kingdom (UK). All UK military aircraft are allocated and display a unique registration number. A unified registration number system, maintained initially by the Air Ministry (AM), and its successor the Ministry of Defence (MoD), is used for aircraft operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF), Fleet Air Arm (FAA), and Army Air Corps (AAC). Military aircraft operated by government agencies and civilian contractors (for example QinetiQ) are also assigned registration numbers from this system. When the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was formed in 1912, its aircraft were identified by a letter/number system related to the manufacturer. The prefix 'A' was allocated to balloons of No.1 Company, Air Battalion, Royal Engineers, the prefix 'B' to aeroplanes of No.2 Company, and the prefix 'F' to aeroplanes of the Central Flying School.Bruce 1956, p.922 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
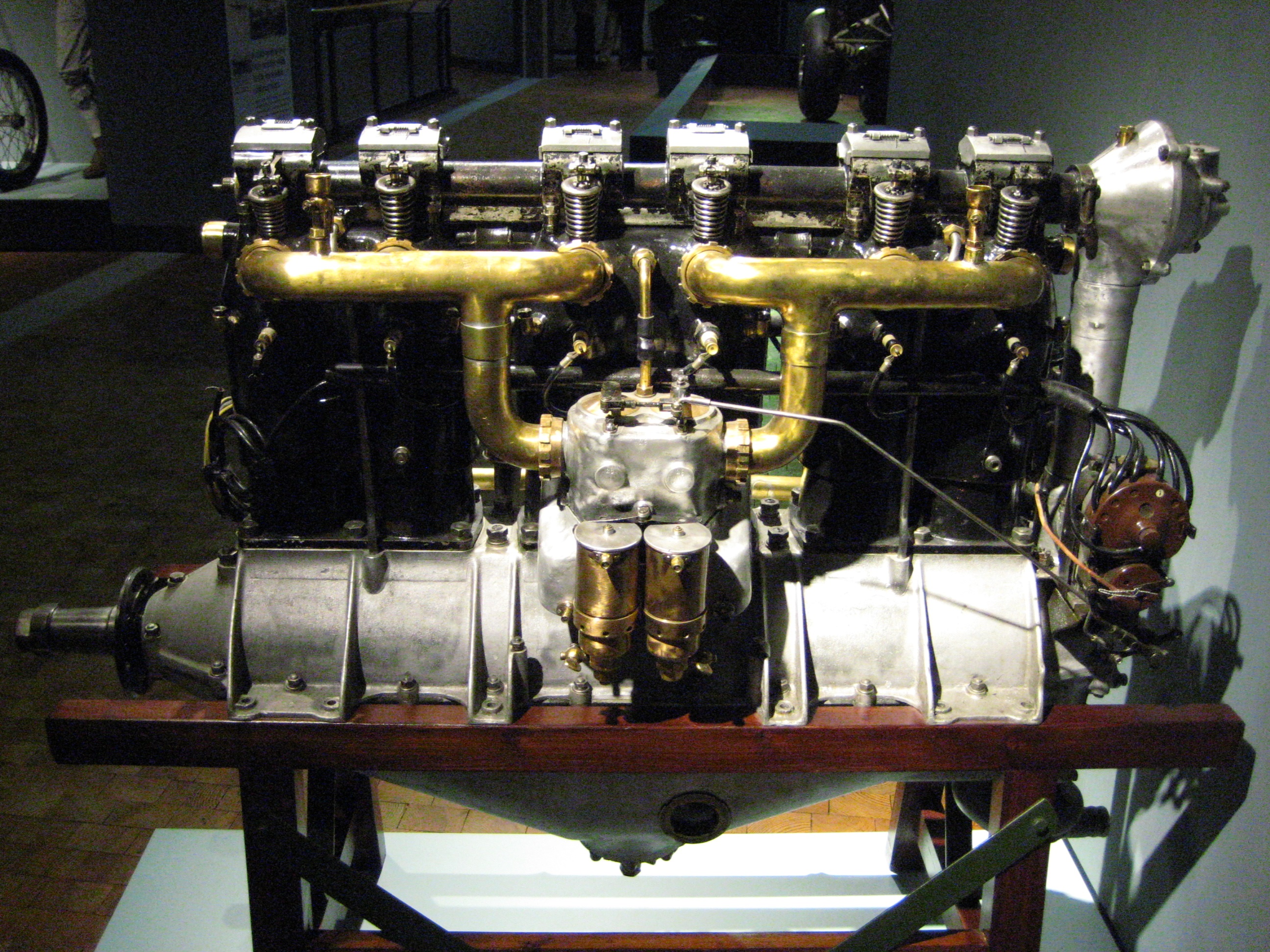
Blackburn Cirrus Minor
The Blackburn Cirrus Minor is a British four-cylinder, inverted, in-line air-cooled aero-engine that was designed and built by the Cirrus Engine Section of Blackburn Aircraft Limited in the late 1930s. Design and development The Cirrus Minor started life as a clean-sheet replacement for the original Cirrus and Hermes series of light aircraft engines. Design was led by Technical Director C. S. Napier, son of Montague Napier, and was already under way when in 1934 Cirrus-Hermes Engineering was taken over by the Blackburn Aeroplane & Motor Company and moved to Brough in Yorkshire."A New Small Engine", ''Flight'', 28 February 1935, pp.218-9."The 'Cirrus Major'", ''Flight'', 13 June 1935. Supplement. Napier remained Technical Director and, while he completed the development and initial sales of the Cirrus Minor and its larger stablemate the Cirrus Major, Blackburn kept Cirrus Hermes Engineering as a separate company (though without the hyphen in its name). Although completely new d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |