|
Gender-based Medicine
Sex differences in medicine include sex-specific diseases or conditions which occur only in people of one sex due to underlying biological factors (for example, prostate cancer in males or uterine cancer in females); sex-related diseases, which are diseases that are more common to one sex (for example, breast cancer and systemic lupus erythematosus which occur predominantly in females); and diseases which occur at similar rates in males and females but manifest differently according to sex (for example, peripheral artery disease). Sex differences should not be confused with gender differences. The US National Academy of Medicine recognizes sex differences as biological at the chromosomal and anatomical levels, whereas gender differences are based on self-representation and other factors including biology, environment and experience. That said, both biological and behavioural differences influence human health, and may do so differentially. Such factors can be inter-related and diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structure and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models. Overview Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific xenobiotic/chemical after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. In humans, the female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The female reproductive tract includes the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and childbirth, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus or womb accommodates the embryo which develops into the fetus. The uterus also produces secretions which help the transit of sperm to the fallopian tubes, where sperm fertilize ova (egg cells) produced by the ovaries. The external sex organs are also known as the ''genitals'' and these are the organs of the vulva including the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening. During the menstrual cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
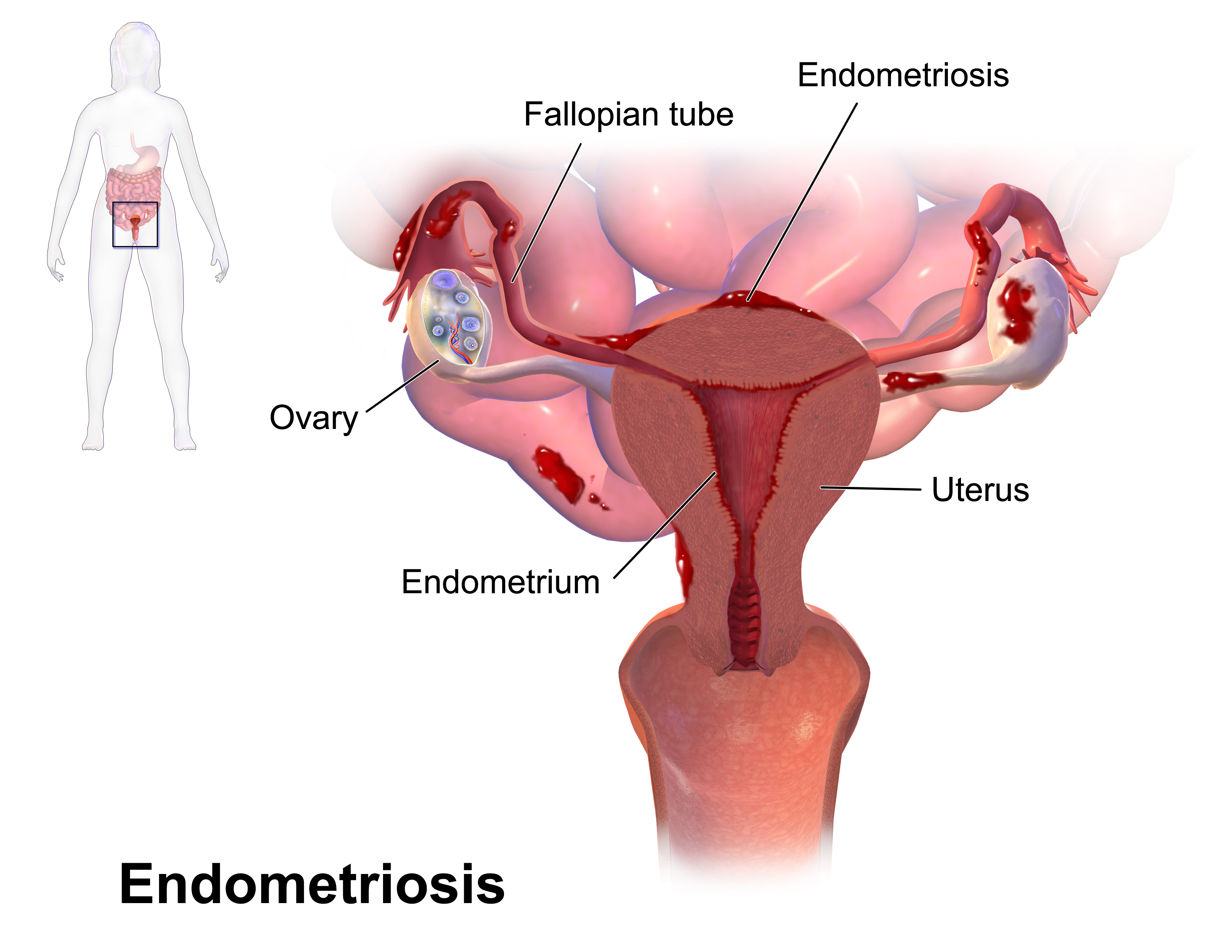
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body. Some symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. Nearly half of those affected have chronic pelvic pain, while in 70% pain occurs during menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse is also common. Infertility occurs in up to half of affected individuals. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms and 85% of those seen with infertility in a tertiary center have no pain. Endometriosis can have both social and psychological effects. The cause is not entirely clear. Risk factors include having a family history of the condition. The areas of endometriosis bleed each month (menstrua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The NCI conducts and supports research, training, health information dissemination, and other activities related to the causes, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer; the supportive care of cancer patients and their families; and cancer survivorship. NCI is the oldest and has the largest budget and research program of the 27 institutes and centers of the NIH ($6.9 billion in 2020). It fulfills the majority of its mission via an extramural program that provides grants for cancer research. Additionally, the National Cancer Institute has intramural research programs in Bethesda, Maryland, and at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research at Fort Detrick in Frederick, Maryland. The NCI receives more than in funding each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female
Female (Venus symbol, symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ovum, ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the Sperm, male gamete during sexual reproduction. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes, unlike isogamy where they are the same size. The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. In species that have males and females, Sex-determination system, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Female characteristics vary between different species with some species having pronounced Secondary sex characteristic, secondary female sex characteristics, such as the presence of pronounced mammary glands in mammals. In humans, the word ''female'' can also be used to refer to gender i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender Role
A gender role, also known as a sex role, is a social role encompassing a range of behaviors and attitudes that are generally considered acceptable, appropriate, or desirable for a person based on that person's sex. Gender roles are usually centered on conceptions of masculinity and femininity, although there are exceptions and variations. The specifics regarding these gendered expectations may vary among cultures, while other characteristics may be common throughout a range of cultures. In addition, gender roles (and perceived gender roles) vary based on a person's race or ethnicity. Gender roles influence a wide range of human behavior, often including the clothing a person chooses to wear, the profession a person pursues, the personal relationships a person enters, and how they behave within those relationships. Although gender roles have evolved and expanded, they traditionally keep women in the "private" sphere, and men in the "public" sphere. Various groups, most notab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive System
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring. Reproductive System 2001 Body Guide powered by Adam Animals In mammals, the major organs of the reproductive system include the external |
Sex-linked
Sex linked describes the sex-specific patterns of inheritance and presentation when a gene mutation (allele) is present on a sex chromosome (allosome) rather than a non-sex chromosome ( autosome). In humans, these are termed X-linked recessive, X-linked dominant and Y-linked. The inheritance and presentation of all three differ depending on the sex of both the parent and the child. This makes them characteristically different from autosomal dominance and recessiveness. There are many more X-linked conditions than Y-linked conditions, since humans have several times as many genes on the X chromosome than the Y chromosome. Only females are able to be carriers for X-linked conditions; males will always be affected by any X-linked condition, since they have no second X chromosome with a healthy copy of the gene. As such, X-linked recessive conditions affect males much more commonly than females. In X-linked recessive inheritance, a son born to a carrier mother and an unaffected fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic (genetics)
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized egg. Genetic mosaics may often be confused with chimerism, in which two or more genotypes arise in one individual similarly to mosaicism. In chimerism, though, the two genotypes arise from the fusion of more than one fertilized zygote in the early stages of embryonic development, rather than from a mutation or chromosome loss. Genetic mosaicism can result from many different mechanisms including chromosome nondisjunction, anaphase lag, and endoreplication. Anaphase lagging is the most common way by which mosaicism arises in the preimplantation embryo. Mosaicism can also result from a mutation in one cell during development, in which case the mutation will be passed on only to its daughter cells (and will be present only in certain adult ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-inactivation
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated in a particular embryonic cell is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism (its cell line). The result is that the choice of inactivated X chromosome in all the cells of the organism is a random distribution, often with about half the cells having the paternal X chromos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |