|
Gedaliah Son Of Pashhur
Gedaliah, son of Pashhur, is a man described in the Book of Jeremiah of the Hebrew Bible, Judaism's Tanakh, and Christianity's Old Testament. He is described as one of the political opponents of Jeremiah, one of those who appealed to King Zedekiah to have Jeremiah executed because of his prophecies that Jerusalem and the Temple would be destroyed by the Babylonians due to the wickedness of the Jews: 1 And Shephatiah the son of Mattan, and Gedaliah the son of Pashhur, and Jucal the son of Shelemiah, and Pashhur the son of Malchiah, heard the words that Jeremiah spoke unto all the people, saying: 2 Thus saith the LORD: He that remaineth in this city shall die by the sword, by the famine, and by the pestilence; but he that goeth forth to the Chaldeans shall live, and his life shall be unto him for a prey, and he shall live. 3 Thus saith the LORD: This city shall surely be given into the hand of the army of the king of Babylon, and he shall take it.' 4 Then the princes said unto the k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah ( he, ספר יִרְמְיָהוּ) is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, and the second of the Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. The superscription at chapter Jeremiah 1:1–3 identifies the book as "the words of Jeremiah son of Hilkiah". Of all the prophets, Jeremiah comes through most clearly as a person, ruminating to his scribe Baruch about his role as a servant of God with little good news for his audience. His book is intended as a message to the Jews in exile in Babylon, explaining the disaster of exile as God's response to Israel's pagan worship: the people, says Jeremiah, are like an unfaithful wife and rebellious children, their infidelity and rebelliousness made judgment inevitable, although restoration and a new covenant are foreshadowed. Authentic oracles of Jeremiah are probably to be found in the poetic sections of chapters 1 –25, but the book as a whole has been heavily edited and added to by the prophet's f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BCE. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of Akkad" (''Māt Akkadī'' in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older state of Assyria to the north and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi ( fl. c. 1792–1752 BCE middle chronology, or c. 1696–1654 BCE, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom. Like Assyria, the Babylonian state retained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Archaeology
Biblical archaeology is an academic school and a subset of Biblical studies and Levantine archaeology. Biblical archaeology studies archaeological sites from the Ancient Near East and especially the Holy Land (also known as Palestine, Land of Israel and Canaan), from biblical times. Biblical archaeology emerged in the late 19th century, by British and American archaeologists, with the aim of confirming the historicity of the Bible. Between the 1920s, right after World War I, when Palestine came under British rule and the 1960s, biblical archaeology became the dominant American school of Levantine archaeology, led by figures such as William F. Albright and G. Ernest Wright. The work was mostly funded by churches and headed by theologists. From the late 1960s, biblical archaeology was influenced by processual archaeology ("New Archaeology") and faced issues that made it push aside the religious aspects of the research. This has led the American schools to shift away from bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Jerusalem Post
''The Jerusalem Post'' is a broadsheet newspaper based in Jerusalem, founded in 1932 during the British Mandate of Palestine by Gershon Agron as ''The Palestine Post''. In 1950, it changed its name to ''The Jerusalem Post''. In 2004, the paper was bought by Mirkaei Tikshoret, a diversified Israeli media firm controlled by investor Eli Azur. In April 2014, Azur acquired the newspaper ''Maariv''. The newspaper is published in English and previously also printed a French edition. Originally a left-wing newspaper, it underwent a noticeable shift to the political right in the late 1980s. From 2004 editor David Horovitz moved the paper to the center, and his successor in 2011, Steve Linde, pledged to provide balanced coverage of the news along with views from across the political spectrum. In April 2016, Linde stepped down as editor-in-chief and was replaced by Yaakov Katz, a former military reporter for the paper who previously served as an adviser to former Prime Minister Naftali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compound, or simply al-Aqsa Mosque (, ''al-Masjid al-Aqṣā'', lit. 'The Furthest Mosque'), * ''Where Heaven and Earth Meet'', page 13: "Nowadays, while oral usage of the term Haram persists, Palestinians tend to use in formal texts the name Masjid al-Aqsa, habitually rendered into English as 'the Aqsa Mosque'" * * * * PEF Survey of Palestine, 1883, volume III Jerusalem, p.119: "The Jamia el Aksa, or 'distant mosque' (that is, distant from Mecca), is on the south, reaching to the outer wall. The whole enclosure of the Haram is called by Moslem writers Masjid el Aksa, 'praying-place of the Aksa,' from this mosque." * Yitzhak Reiter: "This article deals with the employment of religious symbols for national identities and national narratives by us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of David (Silwan)
Wadi Hilweh is a neighborhood in the Palestinian Arab village of Silwan, intertwined with an Israeli settlement. The Silwan area of East Jerusalem was annexed by Israel following the 1967 Six-Day War and 1980 Jerusalem Law, an action not recognized internationally. The international community regards Israeli settlements as illegal under international law, although Israel disputes this. The Wadi Hilweh neighborhood stretches over historical Jerusalem's so-called Southeast Hill, extending down from the southern city walls of the Old City. According to tradition, Silwan originated at the time of Saladin in the twelfth century on Ras al-Amud, on the southwest slope of the Mount of Olives, then in the early twentieth century it expanded across the Kidron Valley (known to locals as ''Wadi Sitti Maryam'' or the Valley of St. Mary), eventually incorporating all of the Southeast Hill. Modern history Late Ottoman period The area immediately outside the walls of Jerusale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ir David Foundation
Ir David Foundation or City of David Foundation, commonly known as Elad l'ad( he, אלע"ד, an acronym for "אל עיר דוד", meaning "to the City of David") is a Jerusalem-based, Israeli settler association which aims to strengthen the Jewish connection to Jerusalem, and renew the Jewish community in the City of David, which is also part of the neighborhood of Silwan. The foundation works to achieve its goals by tourism, education, archaeological excavations and obtaining homes in the area to establish a Jewish presence. Background "Ir David" - or the City of David is the name given to a site beyond the southern edge of Jerusalem's Temple Mount and Old City, with the Tyropoeon Valley on its west, the Hinnom valley to the south, and the Kidron Valley on the east. Modern Jewish settlement on the ridge began in the City of David began in 1873–1874, when the Meyuchas family, a Jewish rabbinical and merchant family that had lived in Jerusalem since their expulsion from Spain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
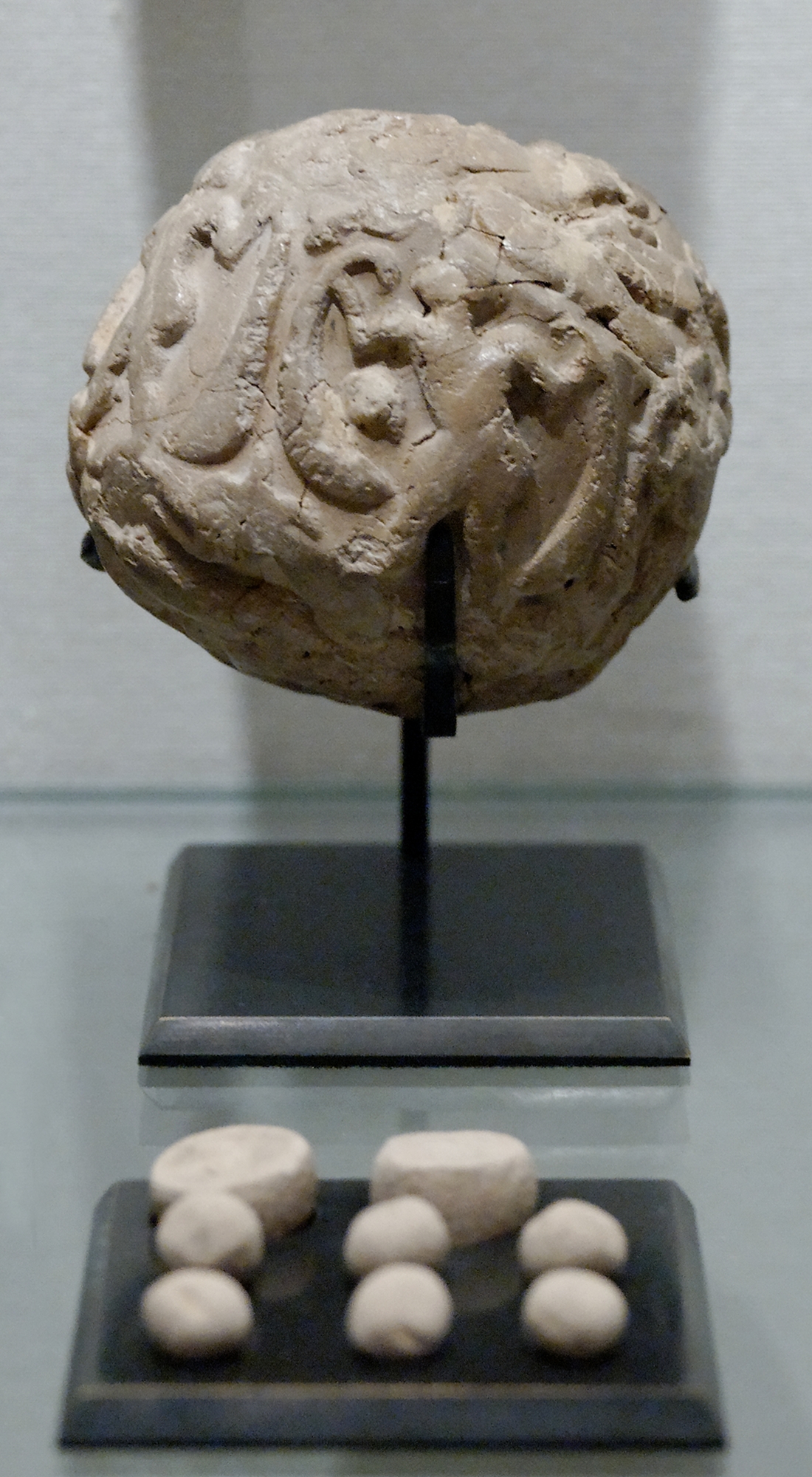
Bulla (seal)
A bulla (Medieval Latin for "a round seal", from Classical Latin ''bulla'', "bubble, blob"; plural bullae) is an inscribed clay or soft metal (such as lead or tin) or bitumen or wax token used in commercial and legal documentation as a form of authentication and for tamper-proofing whatever is attached to it (or, in the historical form, contained in it). In their oldest attested form, as used in the ancient Near East and the Middle East of the 8th millennium BC onwards, bullae were hollow clay balls that contained other smaller tokens that identified the quantity and types of goods being recorded. In this form, bullae represent one of the earliest forms of specialization in the ancient world, and likely required skill to create. From about the 4th millennium BC onwards, as communications on papyrus and parchment became widespread, bullae evolved into simpler tokens that were attached to the documents with cord, and impressed with a unique sign (i.e., a seal) to provide the same kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eilat Mazar
Eilat Mazar ( he, אילת מזר; 10 September 195625 May 2021) was an Israeli archaeologist. She specialized in Jerusalem and Phoenician archaeology. She was also a key person in Biblical archaeology noted for her discovery of the Large Stone Structure, which she surmised to be the palace of King David. Biography Eilat Mazar was born on 10 September 1956. She was the granddaughter of pioneering Israeli archaeologist Benjamin Mazar, who served as president of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. She obtained a Bachelor of Arts from that same institution, before joining the excavation team of Yigal Shiloh in 1981 and working there for four years. She was granted a Doctor of Philosophy from Hebrew University in 1997. Her thesis was written on the culture of Phoenicia, based on the excavations she undertook in Achziv. Mazar had one daughter from her first marriage, which ended in divorce. Her second marriage was to Yair Shoham, who was also an archaeologist. They remained ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple In Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. According to the Hebrew Bible, the Solomon's Temple, First Temple was built in the 10th century BCE, during the reign of Solomon over the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel. It stood until , when it was destroyed during the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), Babylonian siege of Jerusalem. Almost a century later, the First Temple was replaced by the Second Temple, which was built after the Neo-Babylonian Empire was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire. While the Second Temple stood for a longer period of time than the First Temple, it was likewise destroyed during the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), Roman siege of Jerusalem in 70 CE. Projects to build the hypothetical "Third Temple" have not co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; Hebrew: ''Mīqrā''), is the Biblical canon, canonical collection of Hebrew language, Hebrew scriptures, including the Torah, the Nevi'im, and the Ketuvim. Different branches of Judaism and Samaritanism have maintained different versions of the canon, including the 3rd-century Septuagint text used by Second-Temple Judaism, the Syriac language Peshitta, the Samaritan Torah, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and most recently the 10th century medieval Masoretic Text, Masoretic text created by the Masoretes currently used in modern Rabbinic Judaism. The terms "Hebrew Bible" or "Hebrew Canon" are frequently confused with the Masoretic text, however, this is a medieval version and one of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)