|
Gautseshen
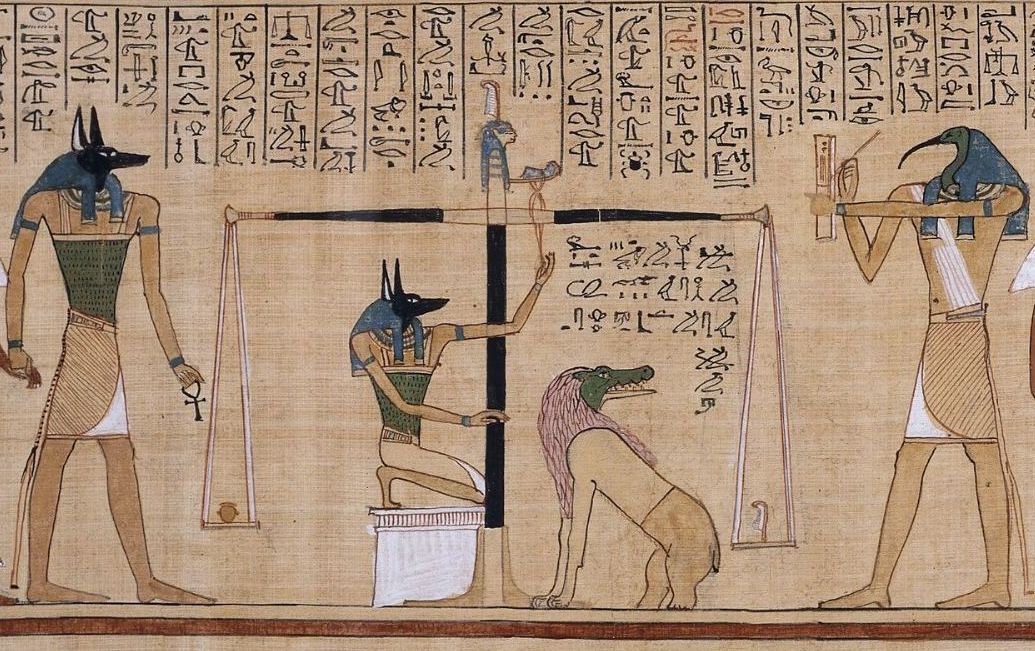
Gautseshen (her name means 'bouquet of lotuses') was an ancient Egyptian priestess, the singer of Montu. She lived during the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt. Description Her father was Menkheperre, High Priest of Amun; her mother was Princess Isetemkheb, a daughter of Pharaoh Psusennes I. Two of her brothers, Pinedjem II and Smendes II became High Priests of Amun. Gautseshen married Tjanefer, the Fourth, later Third Prophet of Amun. They had two sons, Pinedjem, later Fourth Prophet, and Menkheperre, Third Prophet of Amun. She was buried at Bab el-Gasus, where most of her family members were buried. Her coffins and funerary papyrus are now in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. The papyrus is a beautifully illustrated copy of the ''Book of the Dead,'' which shows the changes in funerary texts during the 21st dynasty, when the solar cult and that of Osiris Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of ferti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menkheperre
Menkheperre, son of Pharaoh Pinedjem I by wife Duathathor-Henuttawy (daughter of Ramesses XI by wife Tentamon), was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes in ancient Egypt from 1045 BC to 992 BC and ''de facto'' ruler of the south of the country., p.207 Biography Menkheperre's eldest full brother Masaharta followed their father Pinedjem I as High Priest. He was followed by another brother, Djedkhonsuefankh, after whose death, in the 25th year of Smendes I, Menkheperre became High Priest. With his elder half-brother ruling at Tanis as Pharaoh Psusennes I, Menkheperre's power, like that of Masaharta, must have been somewhat curtailed. Menkheperre took as his throne name the title of "First prophet of Amun", just as his great-grandfather Herihor had, perhaps an indication of this diminished role, though he kept the cartouche unlike his successors in the temple., p.207 Menkheperre married his niece Isetemkheb, daughter of his brother Psusennes I and wife Wiay. Their children were: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjanefer
Tjanefer (fl. 1008 BCE) was an ancient Egyptian priest during the reign of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt. Description His father was Nesipaherenmut, the Fourth Prophet of Amun, and his mother was Isetemheb. According to the ''Karnak Priestly Annals'', Tjanefer served as the Fourth Prophet of Amun in the 40th regnal year of Psusennes I ( 1008 BCE). He was later promoted to Third Prophet, as it is mentioned in a papyrus found in his tomb at Bab el-Gasus (today in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo). He married Gautseshen, the daughter of High Priest Menkheperre Menkheperre, son of Pharaoh Pinedjem I by wife Duathathor-Henuttawy (daughter of Ramesses XI by wife Tentamon), was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes in ancient Egypt from 1045 BC to 992 BC and ''de facto'' ruler of the south of the country. ... and Princess Isetemkheb. They had two sons, Pinedjem, later Fourth Prophet, and Menkheperre, Third Prophet of Amun.Dodson & Hilton, pp.200-201, 207-209 References Further r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab El-Gasus
Bab el-Gasus ( arz, باب الجسس, bāb el-gasus, lit=Gate of the Priests [Spies] p. 17: "Daressy’s moniker ‘Tomb of the Priests’ likely finds its origins in the local traditions of Sheikh abd el Gurnah. Indeed, this phrase could be translated directly from the dialectal form of Arabic in use by Gurnawi workmen, resulting in the local designation of the tomb as ‘Bab el-Gasawsa’, which literally means ‘Gate of the Priests’, as Egyptians traditionally see pharaonic tombs as ‘gates’ into the netherworld. This Arabic phrase was probably wrongly interpreted by Herbert Winlock, who recorded it as ‘Bab el-Gasus’, which in fact means ‘Gate of the Spies’. It is perhaps for this reason that the expression was corrected to ‘Bab el-Kusus’, certainly by scholars familiar with the Cairene form of Arabic, and eventually adapting it to the typical Gurnawi pronunciation and spelling with a -g, instead of -k, resulting in the name ‘Bab el-Gusus’."), also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |