|
Gaspard De La Nuit
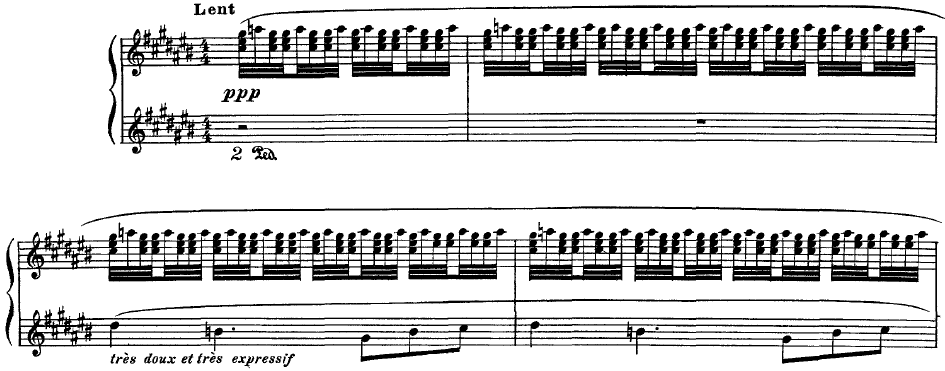
''Gaspard de la nuit'' (subtitled ''Trois poèmes pour piano d'après Aloysius Bertrand''), M. 55 is a suite of piano pieces by Maurice Ravel, written in 1908. It has three movements, each based on a poem or ''fantaisie'' from the collection '' Gaspard de la Nuit – Fantaisies à la manière de Rembrandt et de Callot'' completed in 1836 by Aloysius Bertrand. The work was premiered in Paris, on January 9, 1909, by Ricardo Viñes. The piece is famous for its difficulty, partly because Ravel intended the Scarbo movement to be more difficult than Balakirev's '' Islamey''. Because of its technical challenges and profound musical structure, Scarbo is considered one of the most difficult solo piano pieces in the standard repertoire. The manuscript currently resides in the Harry Ransom Center of the University of Texas at Austin. Etymology The name " Gaspard" is derived from its original Persian form, denoting "the man in charge of the royal treasures": "Gaspard of the Night" o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suite (music)
A suite, in Western classical music and jazz, is an ordered set of instrumental or orchestral/concert band pieces. It originated in the late 14th century as a pairing of dance tunes and grew in scope to comprise up to five dances, sometimes with a prelude, by the early 17th century. The separate movements were often thematically and tonally linked. The term can also be used to refer to similar forms in other musical traditions, such as the Turkish fasıl and the Arab nuubaat. In the Baroque era, the suite was an important musical form, also known as ''Suite de danses'', ''Ordre'' (the term favored by François Couperin), '' Partita'', or ''Ouverture'' (after the theatrical "overture" which often included a series of dances) as with the orchestral suites of Christoph Graupner, Telemann and J.S. Bach. During the 18th century, the suite fell out of favour as a cyclical form, giving way to the symphony, sonata and concerto. It was revived in the later 19th century, but in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premières Mesures
Premières () is a former commune in the Côte-d'Or department in eastern France. On 28 February 2019, it was merged into the new commune of Collonges-et-Premières. Population See also * *Premiere
A première, also spelled premiere, is the debut (first public presentation) of a play, film, dance, or musical composition.
A work will often have many premières: a world première (the first time it is shown anywhere in t ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-flat Minor
E-flat minor is a minor scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature consists of six flats. Its relative key is G-flat major (or enharmonically F-sharp major) and its parallel key is E-flat major. Its enharmonic equivalent, D-sharp minor, contains the same number of sharps. The E-flat natural minor scale is: : Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The E-flat harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: : : Music in E-flat minor In the 24 canonic keys, most of the composers preferred E-flat minor, while Johann Sebastian Bach, Sergei Lyapunov, and Manuel Ponce preferred D-sharp minor. In Book 1 of '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'' by Bach, Prelude No. 8 is written in E-flat minor while the following fugue is written in D-sharp minor. In Book 2, both movements are in D-sharp minor. Haydn's Piano Trio No. 41, H. XV.31 in two movements, composed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Éditions Durand
Éditions Durand are a music publishing company of French origin, among the most important in the field of classical music, which includes three previously independent publishers: * Éditions Durand — the oldest of the three companies — established in 1869 by Auguste Durand and Louis Schönewerk. * Éditions Salabert established in 1878 by Édouard Salabert * Éditions Eschig established in 1907 by Max Eschig. History The Éditions Durand, a family business from 1869 to 1982, had as successive directors from its foundation on December 30, 1869 to 2000: * Auguste Durand (1830-1909) from 1869 to his death in 1909, with the German Louis Schönewerk (1814-18???) as a partner from 1869 to 1891, during which period the company was called Éditions Durand-Schönewerk & Cie, before changing its corporate name on 19 November 1891 to Éditions A. Durand & Fils, when Auguste's son Jacques, became associated with the company * Jacques Durand (1865-1928) son of the former, from 1909 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar (music)
In musical notation, a bar (or measure) is a segment of time corresponding to a specific number of beats in which each beat is represented by a particular note value and the boundaries of the bar are indicated by vertical bar lines. Dividing music into bars provides regular reference points to pinpoint locations within a musical composition. It also makes written music easier to follow, since each bar of staff symbols can be read and played as a batch. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the time signature. In simple time, (such as ), the top figure indicates the number of beats per bar, while the bottom number indicates the note value of the beat (the beat has a quarter note value in the example). The word ''bar'' is more common in British English, and the word ''measure'' is more common in American English, although musicians generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflets Dans L'eau
Claude Debussy's ''Reflets dans l'eau'' ("Reflections in the Water") is the first of three piano pieces from his first volume of ''Images'', which are frequently performed separately. It was written in 1905. As with much of Debussy's work, it is referred to as Impressionistic, meaning that it expresses emotions and senses by making use of non-functional harmony and ambiguous key signatures, its tonality being mainly non-diatonic and usually having a sense of modality. Musical analysis ''Reflets dans l'eau'' opens in a slow tempo (''andantino molto'') (which is repeated through much of the piece) while the right hand is playing a set of chords to accompany the melody. It shares the main characteristics of French music of this period, similar to works by Ravel such as ''Jeux d'eau''. The piece has several brief melody statements and climaxes that are more glimpses of music than full ideas, which is typical of Debussy's middle and late piano works. Writing "images", Debussy was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnes (Debussy)
''Nocturnes'', L 98 (also known as ''Trois Nocturnes'' or Three Nocturnes) is an impressionist orchestral composition in three movements by the French composer Claude Debussy, who wrote it between 1892 and 1899. It is based on poems from ''Poèmes anciens et romanesques'' (Henri de Régnier, 1890). Composition "Three Scenes at Twilight" Based on comments in various Debussy letters and in Léon Vallas's biography, it has generally been assumed that composition of the ''Nocturnes'' began in 1892 under the title ''Trois Scènes au Crépuscule'' ("Three Scenes at Twilight"), an orchestral triptych. However, the lack of actual manuscripts makes it impossible to determine whether such works were truly related to the ''Nocturnes''. ''Trois Scènes au Crépuscule'' was inspired by ten poems by Henri de Régnier entitled ''Poèmes anciens et romanesques'' (published in 1890). Régnier was a symbolist poet, and his poems contain vivid imagery and dreamlike associations of ideas. In a let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionism in music, Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Born to a family of modest means and little cultural involvement, Debussy showed enough musical talent to be admitted at the age of ten to France's leading music college, the Conservatoire de Paris. He originally studied the piano, but found his vocation in innovative composition, despite the disapproval of the Conservatoire's conservative professors. He took many years to develop his mature style, and was nearly 40 when he achieved international fame in 1902 with the only opera he completed, ''Pelléas et Mélisande (opera), Pelléas et Mélisande''. Debussy's orchestral works include ''Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune'' (1894), ''Nocturnes (Debussy), Nocturnes'' (1897–18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeux D'eau (Ravel)
''Jeux d'eau'' () is a piece for solo piano The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a musica ... by Maurice Ravel, composed in 1901 and given its first public performance the following year. The title is variously translated as "Fountains", "Playing Water" or literally "Water Games". At the time of writing ''Jeux d'eau'', Ravel was a student of Gabriel Fauré, to whom the piece is dedicated. The work is in a single movement, typically lasting between four and half and six minutes in performance. Background and first performances In 1901 Maurice Ravel was aged 26 and had yet to make an impression on the French musical scene. He had failed to win any prizes as a student at the Paris Conservatoire and was expelled on that account. As a former student he was permitted to attend the clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undine
Undines (; also ondines) are a category of elemental beings associated with water, stemming from the alchemical writings of Paracelsus. Later writers developed the undine into a water nymph in its own right, and it continues to live in modern literature and art through such adaptations as Danish Hans Christian Andersen's " The Little Mermaid" and the '' Undine'' of Friedrich de la Motte Fouqué. Etymology The term ''Undine'' first appears in the alchemical writings of Paracelsus, a Renaissance alchemist and physician. It derives from the Latin word ''unda'', meaning "wave", and first appears in Paracelsus' '' A Book on Nymphs, Sylphs, Pygmies, and Salamanders, and on the Other Spirits'', published posthumously in 1566. ''Ondine'' is an alternative spelling, and has become a female given name. Elementals Paracelsus believed that each of the four classical elements – earth, water, air and fire – is inhabited by different categories of elemental spirits, liminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are typically tied to a specific place or landform, and are usually depicted as maidens. They were not necessarily immortal, but lived much longer than human beings. They are often divided into various broad subgroups, such as the Meliae (ash tree nymphs), the Dryads (oak tree nymphs), the Naiads (freshwater nymphs), the Nereids (sea nymphs), and the Oreads (mountain nymphs). Nymphs are often featured in classic works of art, literature, mythology, and fiction. Since the Middle Ages, nymphs have been sometimes popularly associated or even confused with fairies. Etymology The Greek word has the primary meaning of "young woman; bride, young wife" but is not usually associated with deities in particular. Yet the etymology of the noun rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneirology
Oneirology (; from Greek ''ὄνειρον'', ''oneiron'', "dream"; and -''λογία'', -''logia'', "the study of") is the scientific study of dreams. Current research seeks correlations between dreaming and current knowledge about the functions of the brain, as well as understanding of how the brain works during dreaming as pertains to memory formation and mental disorders. The study of oneirology can be distinguished from dream interpretation in that the aim is to quantitatively study the process of dreams instead of analyzing the meaning behind them. History In the 19th century, two advocates of this discipline were the French sinologists Marquis d' Hervey de Saint Denys and Alfred Maury. The field gained momentum in 1952, when Nathaniel Kleitman and his student Eugene Aserinsky discovered regular cycles. A further experiment by Kleitman and William C. Dement, then another medical student, demonstrated the particular period of sleep during which electrical brain activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_cover_-_Project_Gutenberg_eText_18752.jpg)

