|
Gary E. Martin
Gary Martin is an American chemist and expert in the fields of both NMR spectroscopy and medicinal chemistry. He is a distinguished fellow at the Merck Research Laboratories. He is also a photographer specializing in the capture of images of lighthouses, especially under conditions of extreme weather. Career Martin holds a B.S. in Pharmacy from the University of Pittsburgh and a Ph.D. degree in Medicinal Chemistry/Pharmaceutical Sciences from the University of Kentucky. He was a Professor of Medicinal Chemistry at the University of Houston from 1975–1989 and the director of the University of Houston NMR Facility between 1984–1989. He moved to the pharmaceutical industry in 1989 and worked at a number of pharmaceutical companies as described below. He has published more than 275 papers, invited reviews, and chapters and is a frequently invited lecturer at national and international NMR meetings. Between 1989 and 1995 he worked at Burroughs Wellcome (later GlaxoSmithKline) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilkinsburg
Wilkinsburg is a borough in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. The borough has a population of 15,930 as of the 2010 census. Wilkinsburg is part of the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. The borough was named for John Wilkins Jr., a United States Army officer who served as Quartermaster General of the United States Army from 1796 to 1802. History Prehistory and early history Historically, Wilkinsburg was located in an area on the Appalachian Plateau where various land and water transportation routes joined, which had been inhabited by Native Americans for thousands of years. Wilkinsburg was formed from the area of a valley going through the hills located east of the three rivers confluence, the Allegheny River, the Monongahela River, and the Ohio River: this natural valley allowed passage by land through the east–west barrier of the Appalachian Mountains to and from the east, whether to or from Philadelphia or other parts of the Atlantic coast, along the rivers (which eventually jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891). Pfizer develops and produces medicines and vaccines for immunology, oncology, cardiology, endocrinology, and neurology. The company has several blockbuster drugs or products that each generate more than billion in annual revenues. In 2020, 52% of the company's revenues came from the United States, 6% came from each of China and Japan, and 36% came from other countries. Pfizer was a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average stock market index from 2004 to August 2020. The company ranks 64th on the Fortune 500 and 49th on the Forbes Global 2000. History 1849–1950: Early history Pfizer was founded in 1849 by Charles Pfizer and Charles F. Erhart, two cousins who had i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopists
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century American Chemists
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius ( AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Functional Theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better model the exchange and correlation interactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residual Chemical Shift Anisotropy
Residual chemical shift anisotropy (RCSA) is the difference between the chemical shift anisotropy (CSA) of aligned and non-aligned molecules. It is normally three orders of magnitude smaller than the static CSA, with values on the order of parts-per-billion (ppb). RCSA is useful for structural determination and it is among the new developments in NMR spectroscopy. See also * Residual dipolar coupling References Further reading * * * * Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Nuclear chemistry Nuclear physics Asymmetry {{NMR-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Residual Dipolar Coupling
The residual dipolar coupling between two spins in a molecule occurs if the molecules in solution exhibit a partial alignment leading to an incomplete averaging of spatially anisotropic dipolar couplings. Partial molecular alignment leads to an incomplete averaging of anisotropic magnetic interactions such as the magnetic dipole-dipole interaction (also called dipolar coupling), the chemical shift anisotropy, or the electric quadrupole interaction. The resulting so-called ''residual'' anisotropic magnetic interactions are becoming increasingly important in biomolecular NMR spectroscopy. History and pioneering works NMR spectroscopy in partially oriented media was first discovered in 1963, and in a very fundamental paper Alfred Saupe was also able to present the essential theory to describe and understand the observable phenomena only one year later. After this initiation a flood of NMR spectra in various liquid crystalline phases was reported (see ''e.g.'' ). A second technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMBC
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (2D NMR) is a set of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) methods which give data plotted in a space defined by two frequency axes rather than one. Types of 2D NMR include correlation spectroscopy (COSY), J-spectroscopy, exchange spectroscopy (EXSY), and nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY). Two-dimensional NMR spectra provide more information about a molecule than one-dimensional NMR spectra and are especially useful in determining the structure of a molecule, particularly for molecules that are too complicated to work with using one-dimensional NMR. The first two-dimensional experiment, COSY, was proposed by Jean Jeener, a professor at the Université Libre de Bruxelles, in 1971. This experiment was later implemented by Walter P. Aue, Enrico Bartholdi and Richard R. Ernst, who published their work in 1976. Fundamental concepts Each experiment consists of a sequence of radio frequency (RF) pulses w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
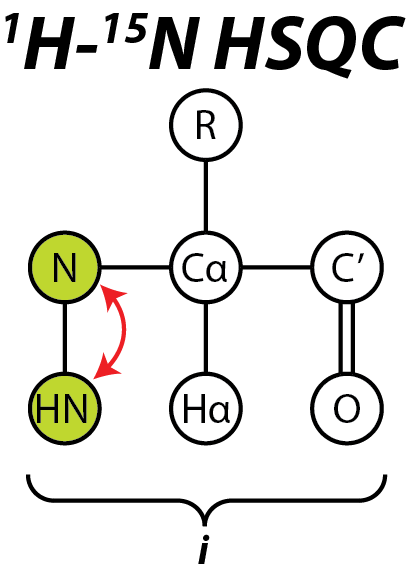
HSQC
The heteronuclear single quantum coherence or heteronuclear single quantum correlation experiment, normally abbreviated as HSQC, is used frequently in NMR spectroscopy of organic molecules and is of particular significance in the field of protein NMR. The experiment was first described by Geoffrey Bodenhausen and D. J. Ruben in 1980. The resulting spectrum is two-dimensional (2D) with one axis for proton (1H) and the other for a heteronucleus (an atomic nucleus other than a proton), which is usually 13C or 15N. The spectrum contains a peak for each unique proton attached to the heteronucleus being considered. The 2D HSQC can also be combined with other experiments in higher-dimensional NMR experiments, such as NOESY-HSQC or TOCSY-HSQC. General scheme The HSQC experiment is a highly sensitive 2D-NMR experiment and was first described in a 1H—15N system, but is also applicable to other nuclei such as 1H—13C and 1H—31P. The basic scheme of this experiment involves the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2D-NMR
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (2D NMR) is a set of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) methods which give data plotted in a space defined by two frequency axes rather than one. Types of 2D NMR include correlation spectroscopy (COSY), J-spectroscopy, exchange spectroscopy (EXSY), and nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY). Two-dimensional NMR spectra provide more information about a molecule than one-dimensional NMR spectra and are especially useful in determining the structure of a molecule, particularly for molecules that are too complicated to work with using one-dimensional NMR. The first two-dimensional experiment, COSY, was proposed by Jean Jeener, a professor at the Université Libre de Bruxelles, in 1971. This experiment was later implemented by Walter P. Aue, Enrico Bartholdi and Richard R. Ernst, who published their work in 1976. Fundamental concepts Each experiment consists of a sequence of radio frequency (RF) pulses with d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruker
Bruker Corporation is an American manufacturer of scientific instruments for molecular and materials research, as well as for industrial and applied analysis. It is headquartered in Billerica, Massachusetts, and is the publicly traded parent company of Bruker Scientific Instruments (Bruker AXS, Bruker BioSpin, Bruker Daltonics and Bruker Optics) and Bruker Energy & Supercon Technologies (BEST) divisions. In April 2010, Bruker created a Chemical Analysis Division (headquartered in Fremont, CA) under the Bruker Daltonics subsidiary. This division contains three former Varian product lines: ICPMS systems, laboratory gas chromatography (GC), and GC-triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (originally designed by Bear Instruments and acquired by Varian in 2001). In 2012, it sponsored the Fritz Feigl Prize, and since 1999 the company has also sponsored the Günther Laukien Prize. History The company was founded on September 7, 1960, in Karlsruhe, Germany as ''Bruker-Physik AG'' by five peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |