|
Gao Cheng
Gao Cheng (; 521–549), courtesy name Zihui (子惠), formally Prince Wenxiang of Bohai (勃海文襄王), later further posthumously honored by Northern Qi as Emperor Wenxiang (文襄皇帝) with the temple name Shizong (世宗), was the paramount official of the Xianbei-led Chinese Eastern Wei dynasty, a branch successor state of the Northern Wei. He was Gao Huan's oldest son, and because his father wielded actual power during Emperor Xiaojing's reign, Gao Cheng also received increasingly great authority, and after his father's death in 547 took over the reign of the state. He was considered capable but frivolous and arrogant, as well as lacking in sexual discretion. In 549, he was assassinated by his servant Lan Jing (蘭京), and his younger brother Gao Yang took over the control over the Eastern Wei regime. Background Gao Cheng was born in 521, when his father Gao Huan was still a courier of documents between the Northern Wei capital Luoyang and the old capital Pingche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gao (surname)
Gao () is an East Asian surname of Chinese origin that can be literally translated as "high" or "tall". There are approximately 16 million living people with this surname. Some places, such as Taiwan, usually romanise this family name into "Kao". In Hong Kong, it is romanized to "Ko". In Macau, it is romanized to "Kou". In English, it is romanized to "Kauh". In 2019 it was the 19th most common surname in Mainland China. The Korean surname, "Ko (Korean surname), Ko" or "Koh", is derived from and written with the same Chinese character (高). Romanisation and pronunciation Origin According to ''Lüshi Chunqiu'', the earliest figure with the Gao surname was Gao Yuan (高元) who created dwellings in antiquity. Zhuanxu, the grandson of the Yellow Emperor, was also known as Gao Yang (高陽). Another origin of Gao is the Jiang (surname 姜), Jiang (姜) surname. According to the Song dynasty encyclopedia ''Tongzhi (encyclopedia), Tongzhi'', an early ancestor was Gao Xi (高傒) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xiaozhuang Of Northern Wei
Emperor Xiaozhuang of Northern Wei (, 507–531; r. 528-530), personal name Yuan Ziyou (), courtesy name Yanda (彥達), was an emperor of China of the Xianbei-led Northern Wei dynasty. He was placed on the throne by General Erzhu Rong, who refused to recognize the young emperor, Yuan Zhao, who Empress Dowager Hu had placed on the throne after she poisoned her son Emperor Xiaoming. During his reign, General Erzhu largely controlled the military and acted in a violent manner, leading Emperor Xiaozhuang to believe that he would usurp the throne. In 530, Emperor Xiaozhuang ambushed General Erzhu and killed him in the palace, but his cousin Erzhu Shilong and nephew Erzhu Zhao subsequently captured and killed Xiaozhuang. Early life Yuan Ziyou was born in 507, during the reign of his cousin Emperor Xuanwu, as the third son of the highly regarded imperial prince, Emperor Xuanwu's uncle Yuan Xie the Prince of Pengcheng. His mother was Yuan Xie's wife Princess Li Yuanhua, the daughter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wu Of Liang
Emperor Wu of Liang () (464 – 12 June 549), personal name Xiao Yan (蕭衍), courtesy name Shuda (叔達), childhood name Lian'er (練兒), was the founding emperor of the Chinese Liang dynasty, during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. His reign, until its end, was one of the most stable and prosperous among the Southern dynasties. He came from the same Xiao clan of Lanling (蘭陵蕭氏) that ruled the preceding Southern Qi dynasty, but from a different branch. Emperor Wu established universities and extended the Confucian civil service exams, demanding that sons of nobles (士族) study. He was well read himself and wrote poetry and patronized the arts. Although for governmental affairs he was Confucian in values, he embraced Buddhism as well. He himself was attracted to many Indian traditions. He banned the sacrifice of animals and was against execution. It was said that he received the Buddhist precepts during his reign, earning him the nickname ''The Bodhisattva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was preceded by the Southern Qi dynasty and succeeded by the Chen dynasty. The rump state of Western Liang existed until it was conquered in 587 by the Sui dynasty. Rule During the Liang dynasty, in 547 a Persian embassy paid tribute to the Liang, amber was recorded as originating from Persia by the ''Book of Liang''. In 548, Hou Jing Prince of Henan started a rebellion with Xiao Zhengde the Prince of Linhe, nephew and a former heir of Emperor Wu of Liang and installed Xiao Zhengde as emperor. In 549, Hou sacked Jiankang, deposed and killed Xiao Zhengde, seized the power and put Emperor Wu effectively under house arrest. He dismissed the armies opposed to him in the name of Emperor Wu. In 550 Emperor Wu died, Hou created Emperor Wu's third son Crown Prince G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the Yellow River civilization, birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far East, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating natural disasters in China, floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hou Jing
Hou Jing (; died June 552), courtesy name Wanjing (萬景), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician. He was a general of Northern Wei, Eastern Wei, and Liang, and briefly, after controlling the Liang imperial regime for several years, usurped the Liang throne, establishing a state of Han. He was soon defeated by the Liang prince Xiao Yi, the prince of Xiangdong, and was killed by his own associates while in flight. He is one of the most reviled figures in ancient Chinese history, known for his extreme cruelty to enemies and civilians. Early life and career It is not known when Hou Jing was born, but it was known that he was from Huaishuo Garrison (懷朔鎮) -- one of the garrisons that Northern Wei established on the northern border to defend against Rouran attacks. He appeared to be ethnically Chinese, but the matter of his ethnicity is not conclusive. When he was young, he was one of a group of friends who associated with Gao Huan, who often spent time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is also applied to the entirety of China proper. Henan is a birthplace of Han Chinese civilization, with over 3,200 years of recorded history and remained China's cultural, economic and political center until approximately 1,000 years ago. Henan Province is home to many heritage sites, including the ruins of Shang dynasty capital city Yin and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the Eight Great Ancient Capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. The practice of tai chi also began here in Chen Jia Gou Village (Chen style), as did the later Yang and Wu styles. Although the name of the province () means "south of the ellowriver.", approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River, also known as the Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhengzhou
Zhengzhou (; ), also spelt Zheng Zhou and alternatively romanized as Chengchow, is the capital and largest city of Henan Province in the central part of the People's Republic of China. Located in north-central Henan, it is one of the National Central Cities in China, the centre of Central Plains area, and serves as the political, economic, technological, and educational center of the province. The Zhengzhou metropolitan area (including Zhengzhou and Kaifeng) is the core area of the Central Plains Economic Zone. The city lies on the southern bank of the Yellow River. Zhengzhou is a major hub of China's national transportation network, with railways connecting Zhengzhou to Europe and an international airport. Zhengzhou is a and a State-list Famous Historical and Culture City. As of 2020, there are two World Cultural Heritage Sites in Zhengzhou. The Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange (ZCE) is China's first futures exchange. Zhengzhou Airport Economy Zone is China's first Airport E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Erzhu Ying'e
Empress Erzhu (514–556) was an empress of the Xianbei-led Northern Wei dynasty of China. She was the wife of Emperor Xiaozhuang and a daughter of the paramount general Erzhu Rong. She later became a concubine of Northern Wei and Eastern Wei's paramount general Gao Huan. In historical texts, she's often referred to by her final title of Princess Dowager of Pengcheng (彭城太妃). To distinguish her from Erzhu Zhao's daughter who married Yuan Ye, she's also referred to as Elder Lady Erzhu (大尔朱氏); while Yuan Ye's wife is referred to as Young Lady Erzhu (小尔朱氏). Background Lady Erzhu's father Erzhu Rong had been a hereditary chief of the Qihu (契胡) tribe, a branch of the Xiongnu, located at Xiurong (秀容, in modern Shuozhou, Shanxi), and during the agrarian rebellions during Emperor Xiaoming's reign had become increasingly powerful as a military general. Sometime during Emperor Xiaoming's reign, she became Emperor Xiaoming's concubine with the rank of ''Pin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
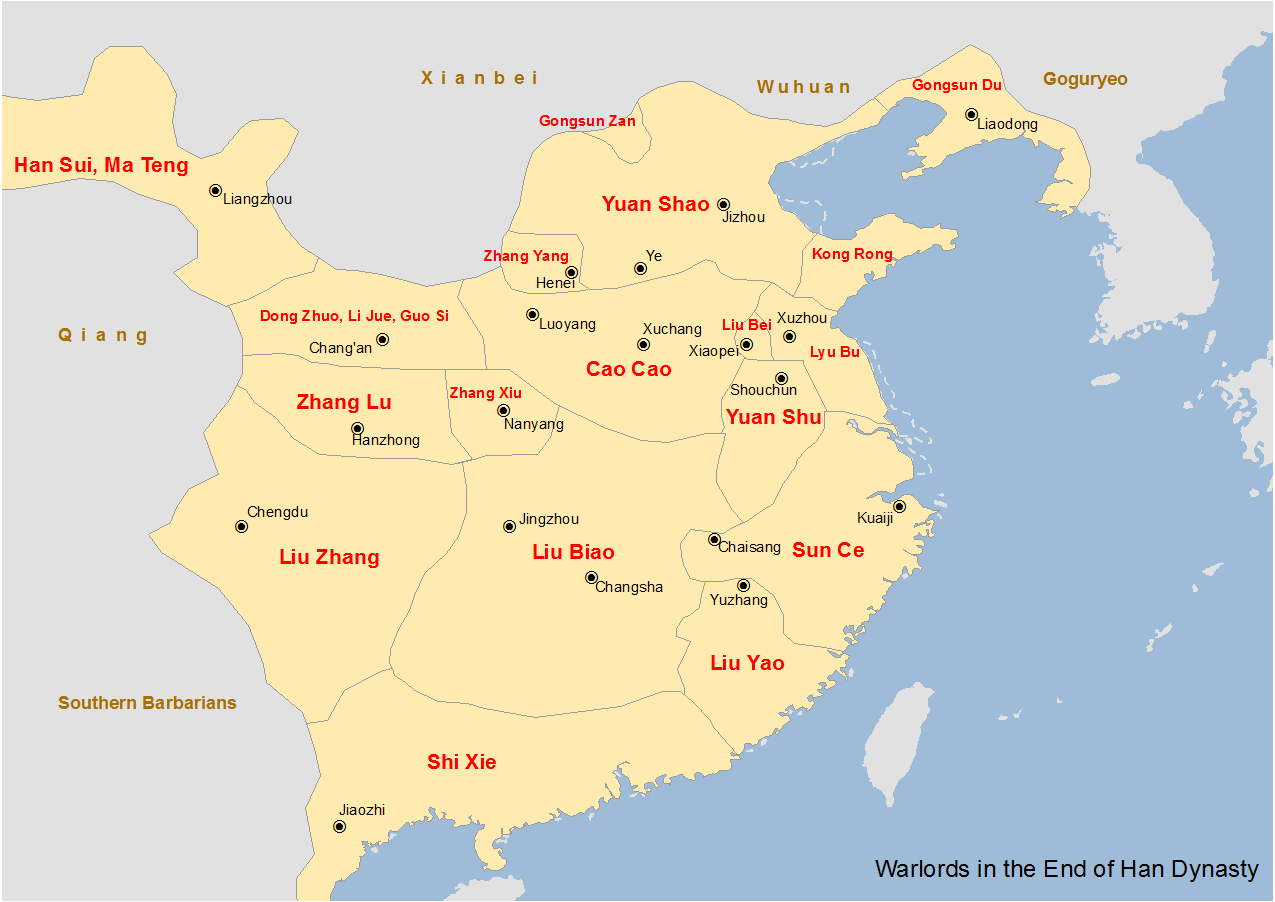
Gao You
Gao You (–212) was a Chinese historian, philosopher, and politician during the Eastern Han dynasty under its last emperor and the warlord Cao Cao. Life Gao You was born in Zhuo Commandery ''Zhuōjùn''; present-day Zhuozhou, Hebei). around AD168. He studied with one of the area's preëminent scholars at the time, Lu Zhi. Lu was known for his work with texts concerning Chinese rituals and for his assistance in compiling the '' History of the Eastern Han'' ''Dōngguān Hànjì''). His other students included Liu Bei, the future king of Shu, and Gongsun Zan, another regional warlord of the era.. Gao's schooling was interrupted by the Yellow Turban Rebellion in AD184. Gao was working in Xuchang in the Capital Construction Office in AD205 when he received his first post as magistrate of Puyang in the Eastern Commandery ''Dōngjùn''). This was about south of the location of the present county-level city of Puyang in Henan. He later held some other mid-level appointments u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concubine
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive. Concubinage was a formal and institutionalized practice in China until the 20th century that upheld concubines' rights and obligations. A concubine could be freeborn or of slave origin, and their experience could vary tremendously according to their masters' whim. During the Mongol conquests, both foreign royals and captured women were taken as concubines. Concubinage was also common in Meiji Japan as a status symbol, and in Indian society, where the intermingling of castes and religions was frowned upon and a taboo, and concubinage could be practiced with women with whom marriage was considered undesirable, such as those from a lower caste and Muslim women who wouldn't be accepted in a Hindu household and Hindu women who wouldn't be accepted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ye, China
Ye or Yecheng () was an ancient Chinese city located in what is now Linzhang County, Handan, Hebei province and neighbouring Anyang, Henan province. Ye was first built in the Spring and Autumn period by Duke Huan of Qi, and by the time of the Warring States period the city belonged to the state of Wei. During the Han dynasty, Ye was the seat of Wei Commandery and an important regional center. Ye was a political and economic center of China during the Three Kingdoms Period and Northern Dynasties. It served as the military headquarters of the warlords Yuan Shao and Cao Cao in the last years of the Eastern Han Dynasty. As the years of war had destroyed the inner city of Ye, Cao Cao set about rebuilding the city in the mold of an imperial capital. He initiated a number of works in Ye, digging canals in and around the city to improve irrigation and drainage, building the Hall of Civil Splendour (文昌殿) which was to become the centerpiece of Ye's palace complex, and erecting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)