|
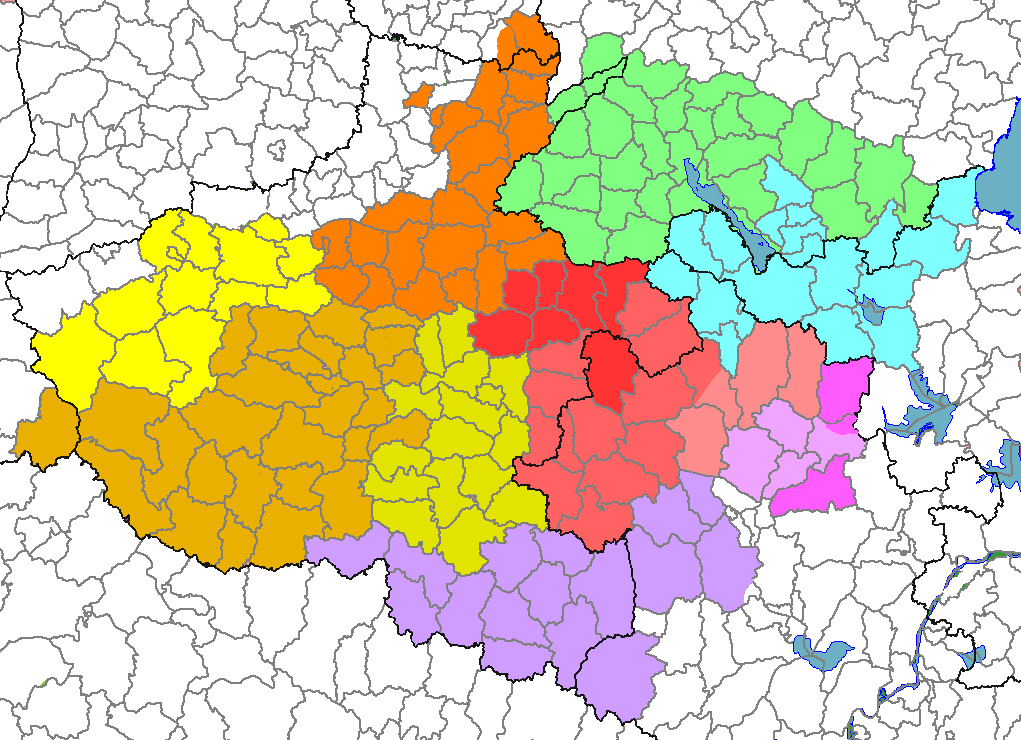
Ganyu Dialect
The Ganyu dialect () is a dialect of Mandarin Chinese. It is spoken in Ganyu District and Donghai County, in Jiangsu province of China. According to the ''Language Atlas of China'', the Ganyu dialect is a kind of Zhongyuan Mandarin, but this is disputed. Some linguists regard it as one of Central Plains Mandarin like the Xuzhou dialect because of a similar evolution of the entering tone in ancient Chinese with Central Plains Mandarin. However, some linguists think of it as a kind of Jiaoliao Mandarin because of same initial consonant system. In fact, the Ganyu dialect shares more common vocabulary with Jiaoliao Mandarin. It is a little difficult for one whose mother tongue is Central Plains Mandarin to understand Ganyu Dialect. While there are differences in how the Ganyu dialect is spoken, all forms of it are mutually intelligible. The accent of someone from northwestern Ganyu sounds more like the one of someone who was born and grew up in the neighboring area of Shandong Provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji''. Chinese characters in South Korea, which are known as ''hanja'', retain significant use in Korean academia to study its documents, history, literature and records. Vietnam once used the '' chữ Hán'' and developed chữ Nôm to write Vietnamese before turning to a romanized alphabet. Chinese characters are the oldest continuously used system of writing in the world. By virtue of their widespread current use throughout East Asia and Southeast Asia, as well as their profound historic use throughout the Sinosphere, Chinese characters are among the most widely adopted writing systems in the world by number of users. The total number of Chinese characters ever to appear in a dictionary is in the tens of thousands, though most are graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganyu District
Ganyu District () is under the administration of Lianyungang, Jiangsu province, China. It contains the province's northernmost point and is located along the Yellow Sea coast where the coastline takes a sharp turn toward the southeast, and borders the Shandong prefecture-level cities of Linyi and Rizhao to the north. Culture Unlike the rest of Northern Jiangsu, the native locals of Ganyu speak Jiaoliao Mandarin which is also native to Eastern Shandong province and most of Liaodong peninsula, instead of Jianghuai Mandarin. Demographics According to the Fifth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, there are 49 nations in Ganyu. Among all the people, the Han population accounts for 99.8% and the ethnic minority population account for 0.2%. Geography and climate Ganyu has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cwa'') influenced by the East Asian Monsoon. The winters are cold and quite dry, while the summers are hot, rainy, and humid. The normal monthly mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as an important criterion for distinguishing languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between languages can be asymmetric, with speakers of one understanding more of the other than speakers of the other understanding the first. When it is relatively symmetric, it is characterized as "mutual". It exists in differing degrees among many related or geographically proximate languages of the world, often in the context of a dialect continuum. Intelligibility Factors An individual's achievement of moderate proficiency or understanding in a language (called L2) other than their first language (L1) typically requires considerable time and effort through study and practical application if the two l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiaoliao Mandarin
Jiaoliao or Jiao–Liao Mandarin () is a primary dialect of Mandarin Chinese, spoken on the Jiaodong Peninsula, from Yantai to Qingdao, Ganyu District in northeastern Jiangsu and the Liaodong Peninsula, from Dalian to Dandong, and in Mishan, Hulin, Fuyuan & Raohe counties of Heilongjiang. Yantai, Dalian, and Weihai dialects are the standard Jiao–Liao Mandarin.Margaret Mian Yan Introduction to Chinese Dialectology 2006 - Page 62 "Jiao–Liao Mandarin Group 胶辽官话The estimated number of native speakers of this group is 28.83 million; it is divided into the following subgroups: ; (1) Qingzhou subgroup (2) Deng–Lian subgroup (3) Gai–Huan Subgroup 5. Zhongyuan Mandarin ..." Etymology Jiao is short for the Jiao River. Liao is short for the Liaodong Peninsula, and the name ''Liaodong'' means "East of the Liao River". (''Liao'' is also an abbreviation used for the city of Liaoyang.) Sub-dialects *Yantai dialect *Dalian dialect *Weifang dialect *Weih ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuzhou Dialect
The Xuzhou dialect () is a Mandarin dialect spoken in the city of Xuzhou in Jiangsu province, China. Jiangsu has two basic dialect types: that of the south, influenced by Wu, and that of the north. Beginning roughly in the area extending from Changzhou to Danyang, there is a change in the dialects spoken. From the north of Yangzhou, the dialect begins to take on the essential form of the northern Jiangsu dialect. The Xuzhou dialect is the point where the northern dialects of Jiangsu meet the dialects of Shandong. The Xuzhou dialect also reflects the influence of Shanxi, whose dialects were imported by migrants from Shanxi to Xuzhou during the Sui dynasty. Peixian, which is a region under the auspices of the city of Xuzhou, was the destination of the majority of migrants from Shanxi. There are important differences in the dialects of Xuzhou and Peixian, which show the results of the Shanxi influence. The Xuzhou dialect has the two extra initials /ȵ/ and /w̃/ compared with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Atlas Of China
The ''Language Atlas of China'' (), published in two parts in 1987 and 1989, maps the distribution of both the varieties of Chinese and minority languages of China. It was a collaborative effort by the Australian Academy of the Humanities and the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, published simultaneously in the original Chinese and in English translation. Endymion Wilkinson rated this joint venture "outstanding". A second edition was published in 2012. Classification of Chinese varieties The atlas organizes the varieties of Chinese in a hierarchy of groupings, following the work of Li Rong: * supergroups (大区 ''dàqū''): Mandarin and Min * groups (区 ''qū''): Jin, Wu, Hui, Xiang, Gan, Hakka, Yue, Pinghua and groups within Mandarin and Min * subgroups (片 ''piàn'') * clusters (小片 ''xiǎopiàn'') are only identified for some subgroups * local dialects (点 ''diǎn''): localities that were surveyed Contents The atlas contains 36 colour maps, divided into thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, Postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an Eastern China, eastern coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third smallest, but the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, fifth most populous and the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population density, most densely populated of the 23 provinces of the People's Republic of China. Jiangsu has the highest GDP per capita of Chinese provinces and second-highest GDP of Chinese provinces, after Guangdong. Jiangsu borders Shandong in the north, Anhui to the west, and Zhejiang and Shanghai to the south. Jiangsu has a coastline of over along the Yellow Sea, and the Yangtze River passes through the southern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donghai County
Donghai County () is under the administration of Lianyungang, Jiangsu province, China. It borders the prefecture-level cities of Linyi (Shandong) to the north and Xuzhou Xuzhou (徐州), also known as Pengcheng (彭城) in ancient times, is a major city in northwestern Jiangsu province, China. The city, with a recorded population of 9,083,790 at the 2020 census (3,135,660 of which lived in the built-up area ma ... to the west. The county has 300 million tons of quartz and 300,000 tons of rock crystal reserves, which is the highest in China, so it is nicknamed "the county of rock crystal". Administrative divisions In the present, Donghai County has 2 subdistricts,11 towns and 8 townships. ;2 subdistricts ;11 towns ;8 townships Climate References www.xzqh.org External links County-level divisions of Jiangsu Lianyungang {{Jiangsu-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Dialects
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language of China. Because Mandarin originated in North China and most Mandarin dialects are found in the north, the group is sometimes referred to as Northern Chinese (). Many varieties of Mandarin, such as those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the standard language (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Mandarin is by far the largest of the seven or ten Chinese dialect groups; it is spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lianyungang
Lianyungang () is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its name derives from Lian Island, the largest island in Jiangsu which lies off its coastline, and Yuntai Mountain, the highest peak in Jiangsu, a few miles from the city center, and the fact that it is a port. The name can be literally translated as the Port Connecting the Clouds. Lianyungang was home to 4,599,360 inhabitants as of the 2020 census whom 1,210,767 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of Haizhou and Lianyun counties. Lianyungang was known in the West as Haichow (Postal romanization), which means the City of Sea. Haichow was opened to foreign trade by the Qing imperial government in 1905. Geography Lianyungang is between 118°24' and 119°48' east longitude and 34°11' and 35°07' north latitude. Lianyungang covers an area of . Admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety (linguistics), variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. Under this definition, the dialects or varieties of a particular language are closely related and, despite their differences, are most often largely Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, especially if close to one another on the dialect continuum. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors, such as social class or ethnicity. A dialect that is associated with a particular social class can be termed a sociolect, a dialect that is associated with a particular ethnic group can be termed an ethnolect, and a geographical/regional dialect may be termed a regiolectWolfram, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongyuan Mandarin
Central Plains Mandarin, or ''Zhongyuan'' Mandarin (), is a variety of Mandarin Chinese spoken in the central and southern parts of Shaanxi, Henan, southwestern part of Shanxi, southern part of Gansu, far southern part of Hebei, northern Anhui, northern parts of Jiangsu, southern Xinjiang and southern Shandong. The archaic dialect in Peking opera is a form of Zhongyuan Mandarin. Among Hui people, Zhongyuan Mandarin is sometimes written with the Arabic alphabet, called Xiao'erjing ("Children's script"). Subdialects * Zheng-Kai (鄭開) region: e.g. Kaifeng (開封) dialect, Zhengzhou (鄭州) dialect * Luo-Song (洛嵩) region: e.g. Luoyang dialect (洛陽話) * Nan-Lu (南魯) region: e.g. Nanyang (南陽) dialect * Luo-Xiang (漯項) region: e.g. Zhumadian (駐馬店) dialect * Shang-Fu (商阜) region: e.g. Shangqiu (商丘) dialect, Fuyang (阜陽) dialect * Xin-Beng (信蚌) region: e.g. Xinyang (信陽) dialect, Bengbu (蚌埠) dialect * Yan-He (兗菏) region: e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)