|
Gandaridae
Gangaridai ( gr, Γανγαρίδαι; Latin: ''Gangaridae'') is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE-2nd century AD) to describe a people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these writers state that Alexander the Great withdrew from the Indian subcontinent because of the strong war elephant force of the Gangaridai. A number of modern scholars locate Gangaridai in the Ganges Delta of the Bengal region, although alternative theories also exist. Gange or Ganges, the capital of the Gangaridai (according to Ptolemy), has been identified with several sites in the region, including Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar. Names The Greek writers use the names "Gandaridae" (Diodorus), "Gandaritae", and "Gandridae" (Plutarch) to describe these people. The ancient Latin writers use the name "Gangaridae", a term that seems to have been coined by the 1st century poet Virgil. Some modern etymologies of the word Gangaridai split it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
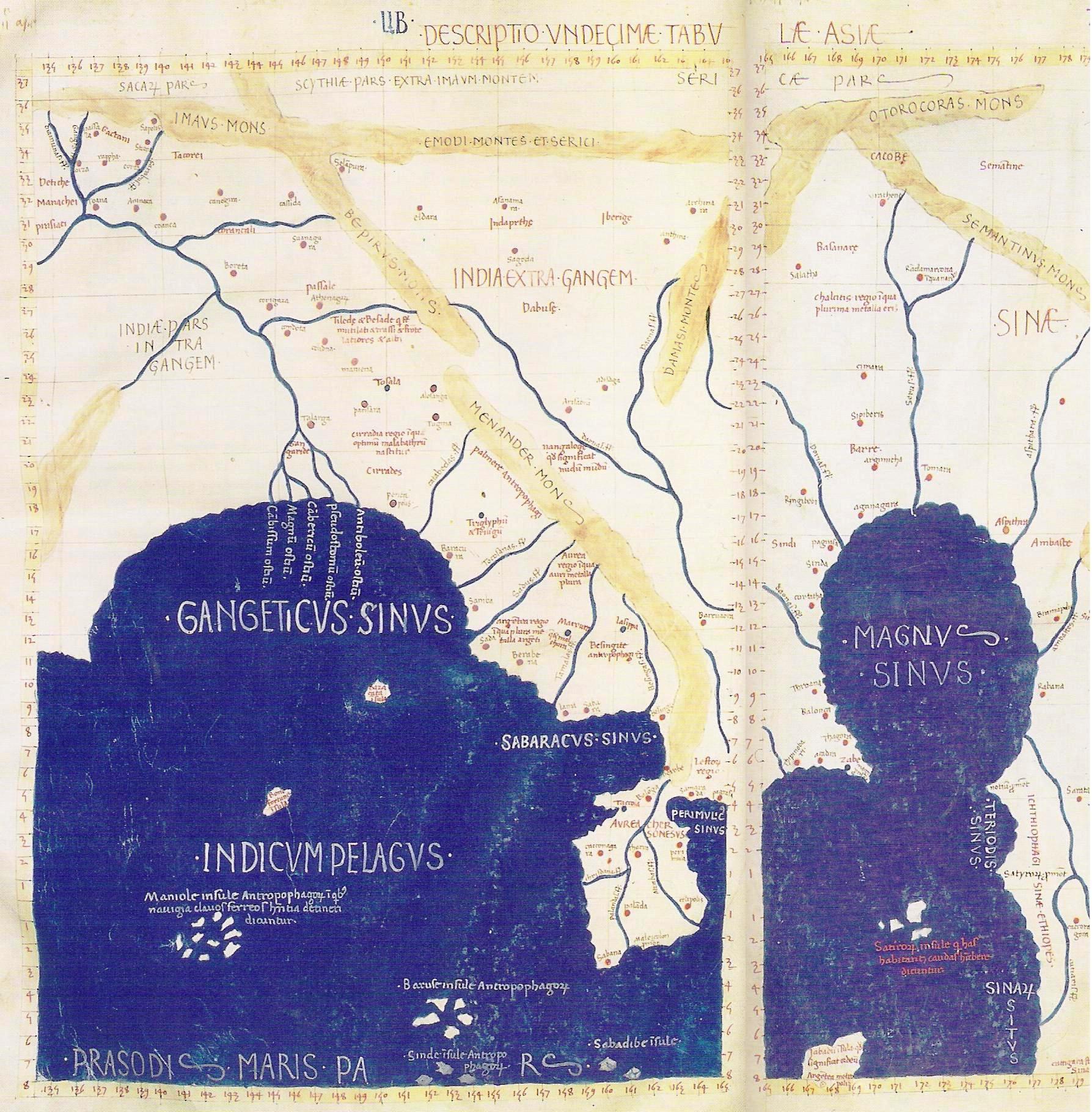
Ptolemy Asia Detail
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadriparti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch Of Chaeronea-03
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadion (unit)
The stadion (plural stadia, grc-gre, ; Romanization, latinized as stadium), also anglicized as stade, list of obsolete units of measurement, was an ancient Greek units of measurement, ancient Greek unit of length, consisting of 600 Ancient Greek feet (''podes''). Calculations According to Herodotus, one stadium was equal to 600 pous, Greek feet (''podes''). However, the length of the foot varied in different parts of the Greek world, and the length of the stadion has been the subject of argument and hypothesis for hundreds of years. An empirical determination of the length of the stadion was made by Lev Vasilevich Firsov, who compared 81 distances given by Eratosthenes and Strabo with the straight-line distances measured by modern methods, and averaged the results. He obtained a result of about . Various equivalent lengths have been proposed, and some have been named. Among them are: Which measure of the stadion is used can affect the interpretation of ancient texts. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Work
A lost work is a document, literary work, or piece of multimedia produced some time in the past, of which no surviving copies are known to exist. It can only be known through reference. This term most commonly applies to works from the classical world, although it is increasingly used in relation to modern works. A work may be lost to history through the destruction of an original manuscript and all later copies. Works—or, commonly, small fragments of works—have survived by being found by archaeologists during investigations, or accidentally by anybody, such as, for example, the Nag Hammadi library scrolls. Works also survived when they were reused as bookbinding materials, quoted or included in other works, or as palimpsests, where an original document is imperfectly erased so the substrate on which it was written can be reused. The discovery, in 1822, of Cicero's ''De re publica'' was one of the first major recoveries of a lost ancient text from a palimpsest. Another famous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxiles
Taxiles (in Greek language, Greek Tαξίλης or Ταξίλας; lived 4th century BC) was the Greece, Greek chroniclers' name for the ruler who reigned over the tract between the Indus River, Indus and the Jhelum River, Jhelum (Hydaspes) Rivers in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander the Great's expedition. His real name was Ambhi (Greek: Omphis), and the Greeks appear to have called him Taxiles or Taxilas, after the name of his capital city of Taxila, near the modern city of Attock, Pakistan.Diodorus Siculus, ''Bibliotheca''xvii. 86/ref> Life Ambhi ascended to throne of Taxila, Takshasila. He sent an embassy to Alexander the Great, Alexander along with presents consisting of 200 Talent (measurement), Talents of silver, 3,000 fat oxen and 10,000 sheep or more ( both are estimated around 600 talents of silver), 30 elephants and a force of 700 horsemen and offered for surrender. He appears to have been on hostile terms with his neighbour, Porus the Elder, Porus, who held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porus The Elder
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Ancient India, Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only mentioned in Greek sources. Credited to have been a legendary warrior with exceptional skills, Porus unsuccessfully fought against Alexander the Great in the Battle of the Hydaspes (326 BC).Fuller, pg 198 In the aftermath, an impressed Alexander not only reinstated him as his satrap but also granted him dominion over lands to the south-east extending until the Hyphasis (Beas River, Beas).p. xl, Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, J, Woronoff & I. SpenceArrian Anabasis of Alexander, V.29.2 Porus reportedly died sometime between 321 and 315 BC. Sources The only contemporary information available on Porus and his kingdom is from Greek sources, whereas Indian sources do not mention him. These Greek sources differ consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirement of William P. Sisler in 2017, the university appointed as Director George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and Latin literature designed to make the text accessible to the broadest possible audience by presenting the original Greek or Latin text on each left-hand page, and a fairly literal translation on the facing page. The General Editor is Jeffrey Henderson, holder of the William Goodwin Aurelio Professorship of Greek Language and Literature at Boston University. History The Loeb Classical Library was conceived and initially funded by the Jewish-German-American banker and philanthropist James Loeb (1867–1933). The first volumes were edited by Thomas Ethelbert Page, W. H. D. Rouse, and Edward Capps, and published by William Heinemann, Ltd. (London) in 1912, already in their distinctive green (for Greek text) and red (for Latin) hardcover bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Henry Oldfather
Charles Henry Oldfather (13 June 1887 – 20 August 1954) was an American professor of history of the ancient world, specifically at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. He was born in Tabriz, Persia. Parentage Oldfather's parents, Jeremiah and Felicia, had been missionaries in Persia for 19 years; they emigrated to the United States of America when their child was aged two years, his father having been born within Farmsberg, Ohio in 1842 and his mother in Covington, Indiana. Life Oldfather received a bachelor's degree from Hanover School. He was a schoolteacher during 1906 and 1907, involved in some form of business activities that year to the following, and returned to teaching during the period 1912–1914. His involvement with teaching at university level commenced with his appointment as Classics professor at Hanover College in Indiana in 1914, succeeded by Wabash College, also in Indiana, between 1916 and 1926. After that year he became professor of Greek and ancient history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieronymus Of Cardia
Hieronymus of Cardia ( el, Ἱερώνυμος ὁ Καρδιανός, 354?–250 BC) was a Greek general and historian from Cardia in Thrace, and a contemporary of Alexander the Great (356–323 BC). After the death of Alexander he followed the fortunes of his friend and fellow-countryman Eumenes. He was wounded and taken prisoner by Antigonus, who pardoned him and appointed him superintendent of the asphalt beds in the Dead Sea. He was treated with equal friendliness by Antigonus's son Demetrius, who made him polemarch of Thespiae, and by Antigonus Gonatas, at whose court he died at the purported age of 104. He wrote a history of the Diadochi and their descendants, encompassing the period from the death of Alexander to the war with Pyrrhus (323–272 BC), which is one of the chief authorities used by Diodorus Siculus (xviii.–xx.) and also by Plutarch in his life of Pyrrhus. He made use of official papers and was careful in his investigation of facts. The simplicity of his st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |