|
Gambier, Ohio
Gambier is a village in Knox County, Ohio, United States. The population was 2,391 at the 2010 census. Gambier is the home of Kenyon College. A major feature is a gravel path running the length of the village, referred to as "Middle Path". This path has become a piece of Gambier's history, as it is used by college students and residents alike as a way through the community. History Gambier was laid out in 1824. The village was named after one of Kenyon College's early benefactors, Lord Gambier. In the 1960s, Japanese writer Junzo Shono spent several years in Gambier, culminating in the writing of the book ''A Sojourn in Gambier'', which would prove to be quite popular in Japan. In May 2020, the Village of Gambier became the first municipality in Knox County to establish anti-discrimination legislation for LGBTQ+ people. Geography Gambier is located along the Kokosing River. According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all land. Demograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village (United States)
In the United States, the meaning of village varies by geographic area and legal jurisdiction. In many areas, "village" is a term, sometimes informal, for a type of administrative division at the local government level. Since the Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits the federal government from legislating on local government, the states are free to have political subdivisions called "villages" or not to and to define the word in many ways. Typically, a village is a type of municipality, although it can also be a special district or an unincorporated area. It may or may not be recognized for governmental purposes. In informal usage, a U.S. village may be simply a relatively small clustered human settlement without formal legal existence. In colonial New England, a village typically formed around the meetinghouses that were located in the center of each town.Joseph S. Wood (2002), The New England Village', Johns Hopkins University Press Many of these colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
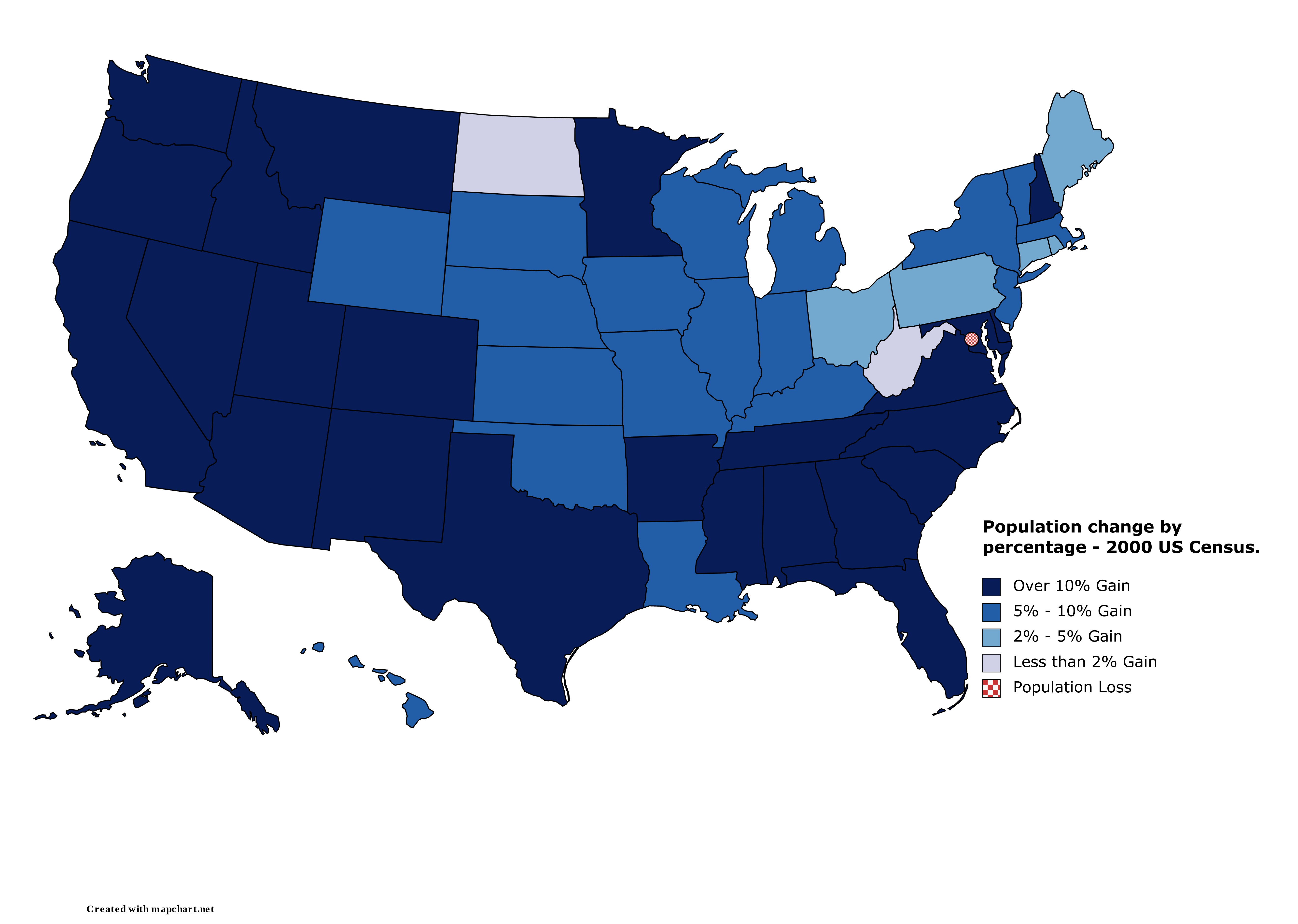
2010 United States Census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators serving to spot-check randomly selected neighborhoods and communities. As part of a drive to increase the count's accuracy, 635,000 temporary enumerators were hired. The population of the United States was counted as 308,745,538, a 9.7% increase from the 2000 census. This was the first census in which all states recorded a population of over half a million people as well as the first in which all 100 largest cities recorded populations of over 200,000. Introduction As required by the United States Constitution, the U.S. census has been conducted every 10 years since 1790. The 2000 U.S. census was the previous census completed. Participation in the U.S. census is required by law of persons living in the United States in Title 13 of the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philander Chase
Philander Chase (December 14, 1775 – September 20, 1852) was an Episcopal Church bishop, educator, and pioneer of the United States western frontier, especially in Ohio and Illinois. Early life and family Born in Cornish, New Hampshire to one of the town's founders, Dudley Chase, and his wife Allace Corbett, Philander Chase was the youngest of fourteen children, and ultimately survived all his siblings. His ancestors had been Puritans who fled to New England. His father, a deacon at their local Congregational church, wanted one of his five sons to become a minister. As had three of his brothers (who however, had no inclinations toward ministry), Philander enrolled at Dartmouth College. As a student, Chase became acquainted with the Book of Common Prayer and became a lay reader in the Episcopal Church. After graduating in 1795, he worked as a lay reader in various New England towns while studying for ordination. Thus, he helped establish Trinity Church in his hometown. He st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret L
Margaret is a female first name, derived via French () and Latin () from grc, μαργαρίτης () meaning "pearl". The Greek is borrowed from Persian. Margaret has been an English name since the 11th century, and remained popular throughout the Middle Ages. It became less popular between the 16th century and 18th century, but became more common again after this period, becoming the second-most popular female name in the United States in 1903. Since this time, it has become less common, but was still the ninth-most common name for women of all ages in the United States as of the 1990 census. Margaret has many diminutive forms in many different languages, including Maggie, Madge, Daisy, Margarete, Marge, Margo, Margie, Marjorie, Meg, Megan, Rita, Greta, Gretchen, and Peggy. Name variants Full name * ( Irish) * ( Irish) * ( Dutch), (German), (Swedish) * ( English) Diminutives * ( English) * ( English) First half * (French) * (Welsh) Second half * ( En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty Line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for the average adult.Poverty Lines – Martin Ravallion, in The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd Edition, London: Palgrave Macmillan The cost of housing, such as the rent for an apartment, usually makes up the largest proportion of this estimate, so economists track the real estate market and other housing cost indicators as a major influence on the poverty line. Individual factors are often used to account for various circumstances, such as whether one is a parent, elderly, a child, married, etc. The poverty threshold may be adjusted annually. In practice, like the definition of poverty, the official or common understanding of the poverty line is significantly higher in developed countries than in developing countries. In October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000 United States Census
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 census. This was the twenty-second federal census and was at the time the largest civilly administered peacetime effort in the United States. Approximately 16 percent of households received a "long form" of the 2000 census, which contained over 100 questions. Full documentation on the 2000 census, including census forms and a procedural history, is available from the Integrated Public Use Microdata Series. This was the first census in which a state – California – recorded a population of over 30 million, as well as the first in which two states – California and Texas – recorded populations of more than 20 million. Data availability Microdata from the 2000 census is freely available through the Integrated Public Use Microdata S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race And Ethnicity In The United States Census
Race and ethnicity in the United States census, defined by the federal Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the United States Census Bureau, are the self-identified categories of race or races and ethnicity chosen by residents, with which they most closely identify, and indicate whether they are of Hispanic or Latino origin (the only categories for ethnicity). The racial categories represent a social-political construct for the race or races that respondents consider themselves to be and, "generally reflect a social definition of race recognized in this country." OMB defines the concept of race as outlined for the U.S. census as not "scientific or anthropological" and takes into account "social and cultural characteristics as well as ancestry", using "appropriate scientific methodologies" that are not "primarily biological or genetic in reference." The race categories include both racial and national-origin groups. Race and ethnicity are considered separate and dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokosing River
The Kokosing River (''ko-KO-sing'') is a tributary of the Walhonding River, 57.2 miles (92.1 km) long, in east-central Ohio in the United States. Via the Walhonding, Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 482 square miles (1248 km²). Etymologically, "Kokosing" translates roughly to "River of Little Owls." The Kokosing River rises in Morrow County, northeast of Mount Gilead, and initially flows southwardly. It turns eastwardly near Chesterville and flows through Knox and Coshocton Counties, passing the communities of Mount Vernon, Gambier and Howard. In western Coshocton County the Kokosing joins the Mohican River to form the Walhonding River, about 2 miles (3 km) northwest of Nellie.DeLorme (1991). ''Ohio Atlas & Gazetteer''. Yarmouth, Maine: DeLorme. Upstream of Mount Vernon, the Kokosing collects its largest tributary, the North Branch Kokosing River, which rises in Morrow County an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBT
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity. The LGBT term is an adaptation of the initialism ', which began to replace the term ''gay'' (or ''gay and lesbian'') in reference to the broader LGBT community beginning in the mid-to-late 1980s. When not inclusive of transgender people, the shorter term LGB is still used instead of LGBT. It may refer to anyone who is non-heterosexual or non-cisgender, instead of exclusively to people who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. To recognize this inclusion, a popular variant, ', adds the letter ''Q'' for those who identify as queer or are questioning their sexual or gender identity. The initialisms ''LGBT'' or ''GLBT'' are not agreed to by everyone that they are supposed to include. History of the term The first widely used term, '' homosexu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBT Anti-discrimination Laws In The United States
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights in the United States are among the most socially, culturally, and legally permissive and advanced in the world, with public opinion and jurisprudence on the issue changing significantly since the late 1980s. In 1962, all 50 states criminalized same-sex sexual activity, but by 2003 all remaining laws against same-sex sexual activity were invalidated in Lawrence v. Texas. Beginning with Massachusetts in 2004, LGBT Americans had won the right to marry in all 50 states by 2015. Additionally, in many states and municipalities, LGBT Americans are explicitly protected from discrimination in employment, housing, and access to public accommodations. Many LGBT rights in the United States have been established by the United States Supreme Court, which has invalidated a state law banning protected class recognition based upon homosexuality, struck down sodomy laws nationwide, struck down Section 3 of the Defense of Marriage Act, made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junzo Shono
was a Japanese novelist. A native of Osaka, he began writing novels after World War II. He won the 1954 Akutagawa Prize for his book ''Purusaido Shokei'' (''Poolside Scene''). Shōno's other award-winning books include ''Seibutsu'' (''Still Life''), for which he won the Shinchosha literary prize, ''Yube no Kumo'' (''Evening Clouds''), which was awarded the 1965 Yomiuri Prize, and ''Eawase'' (''Picture Cards'') which took the Noma literary prize. Biography Shōno lived for one year in the United States in the late 1950s on a fellowship from the Rockefeller Foundation at Kenyon College in Ohio. He later published a book, ''Gambia Taizaiki'' about his experiences at Kenyon. Shōno was made a member of the Japan Art Academy in 1978. He died of natural causes at his home in Kawasaki Kawasaki ( ja, 川崎, Kawasaki, river peninsula, links=no) may refer to: Places *Kawasaki, Kanagawa, a Japanese city **Kawasaki-ku, Kawasaki, a ward in Kawasaki, Kanagawa **Kawasaki City Todorok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |