|
Gallows (band) Albums
A gallows (or less precisely scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks of grain or minerals, usually positioned in markets or toll gates. The term was also used for a projecting framework from which a ship's anchor might be raised so it is no longer sitting on the seabed, riverbed or dock; "weighing heanchor" meant raising it using this apparatus while avoiding striking the ship's hull. In modern usage the term has come to mean almost exclusively a scaffold or gibbet used for execution by hanging. Etymology The term "gallows" was derived from a Proto-Germanic word '' galgô'' that refers to a "pole", "rod" or "tree branch". With the beginning of Christianization, Ulfilas used the term ''galga'' in his Gothic Testament to refer to the cross of Christ, until the use of the Latin term (crux = cross) prevail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
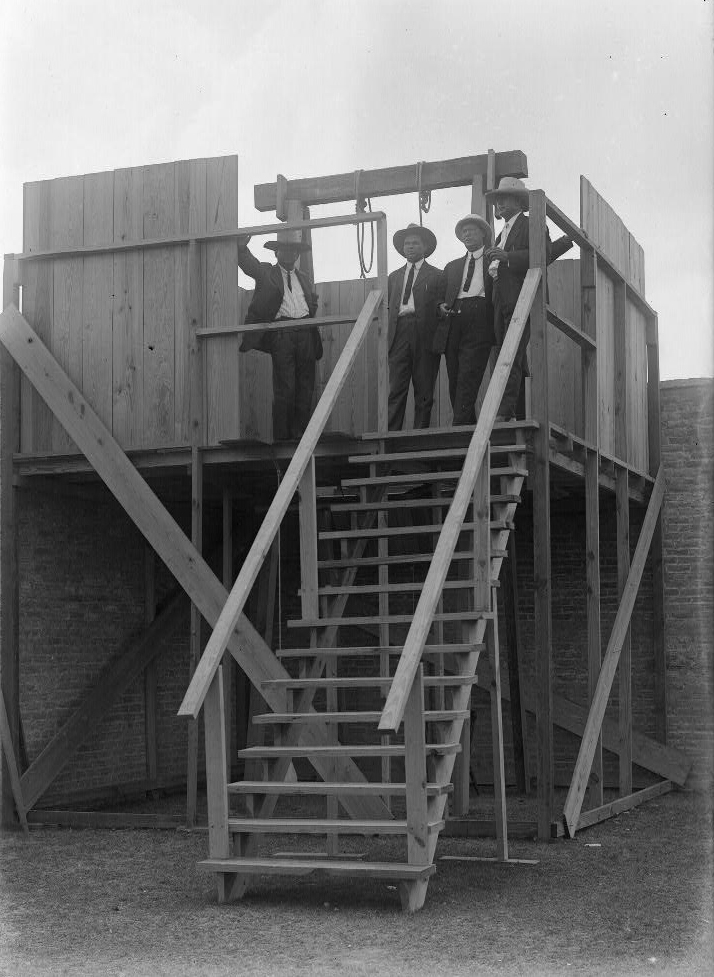
Gallows In Texas, 1916
A gallows (or scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended (i.e., hung) or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks of grain or minerals, usually positioned in markets or toll gates. The term was also used for a projecting framework from which a ship's anchor might be raised so that it is no longer sitting on the bottom, i.e., "weighing heanchor,” while avoiding striking the ship’s hull. In modern usage it has come to mean almost exclusively a scaffold or gibbet used for execution by hanging. Etymology The term "gallows" was derived from a Proto-Germanic word '' galgô'' that refers to a "pole", "rod" or "tree branch". With the beginning of Christianization, Ulfilas used the term ''galga'' in his Gothic Testament to refer to the cross of Christ, until the use of the Latin term (crux = cross) prevailed. Forms of hanging Gallows can take several f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and (in scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble Arch
The Marble Arch is a 19th-century white marble-faced triumphal arch in London, England. The structure was designed by John Nash (architect), John Nash in 1827 to be the state entrance to the cour d'honneur of Buckingham Palace; it stood near the site of what is today the three-bayed, central projection of the palace containing the well-known balcony. In 1851, on the initiative of architect and urban planner Decimus Burton, a one-time pupil of John Nash, it was relocated to its current site. Following the widening of Park Lane (road), Park Lane in the early 1960s, the site became a large traffic island at the junction of Oxford Street, Park Lane and Edgware Road, isolating the arch. Admiralty Arch, Holyhead in Wales is a similar arch, also cut off from public access, at the other end of the A5 road (Great Britain), A5. Only members of the British Royal Family, Royal Family and the King's Troop, Royal Horse Artillery are said to be permitted to pass through the arch; this happens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
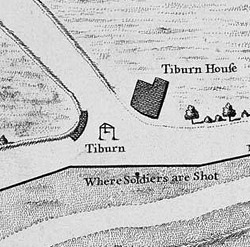
Tyburn
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. The parish, probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street), the junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For this reason, for many centuries, the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment, it having been the principal place for execution of London criminals and convicted traitors, including many religious martyrs. It was also known as 'God's Tribunal', in the 18th century. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream',Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. but Tyburn Brook should not be confused wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strangulation
Strangling is compression of the neck that may lead to unconsciousness or death by causing an increasingly hypoxic state in the brain. Fatal strangling typically occurs in cases of violence, accidents, and is one of two main ways that hanging causes death (alongside breaking the victim's neck). Strangling does not have to be fatal; limited or interrupted strangling is practised in erotic asphyxia, in the choking game, and is an important technique in many combat sports and self-defense systems. Strangling can be divided into three general types according to the mechanism used: * Hanging—Suspension from a cord wound around the neck * Ligature strangulation—Strangulation without suspension using some form of cord-like object called a garrote * Manual strangulation—Strangulation using the fingers or other extremity General Strangling involves one or several mechanisms that interfere with the normal flow of oxygen into the brain: *Compression of the carotid arteries or j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapdoor
A trapdoor is a sliding or hinged door in a floor or ceiling. It is traditionally small in size. It was invented to facilitate the hoisting of grain up through mills, however, its list of uses has grown over time. The trapdoor has played a pivotal function in the operation of the gallows, cargo ships, trains booby traps,and more recently theatre and films. History Originally, trapdoors were sack traps in mills, and allowed the sacks to pass up through the mill while naturally falling back to a closed position. Many buildings with flat roofs have hatches that provide access to the roof. On ships, hatches—usually not flush, and never called trapdoors—provide access to the deck. Cargo ships, including bulk carriers, have large hatches for access to the holds. Gallows Most 19th- and early 20th-century gallows featured a trapdoor, usually with two flaps. The victim will be placed at the join. The edge of a trapdoor farthest from the hinge accelerates faster than gravity, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John André
John André (2 May 1750/1751''Gravesite–Memorial'' Westminster Abbey webpage; accessed September 2020 – 2 October 1780) was a major in the and head of its Secret Service in America during the . He was as a by the |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical'' ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphyxiation
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can induce asphyxia, all of which are characterized by the inability of a person to acquire sufficient oxygen through breathing for an extended period of time. Asphyxia can cause coma or death. In 2015, about 9.8 million cases of unintentional suffocation occurred which resulted in 35,600 deaths. The word asphyxia is from Ancient Greek "without" and , "squeeze" (throb of heart). Causes Situations that can cause asphyxia include but are not limited to: airway obstruction, the constriction or obstruction of airways, such as from asthma, laryngospasm, or simple blockage from the presence of foreign materials; from being in environments where oxygen is not readily accessible: such as underwater, in a low oxygen atmosphere, or in a vacuum; envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutland County Museum
Rutland County Museum is located in Oakham, Rutland, in the old Riding School of the Rutland Fencible Cavalry which was built in 1794–95. The museum, opened in 1969, houses a collection of objects relating to local rural and agricultural life, social history and archaeology. Temporary exhibitions are shown alongside the permanent displays. Admission to the museum is free. Collection The Museum's original collections were those transferred to it when it was set up by the former Rutland County Council in 1967. These were the rural life collection of E G Bolton from Casterton Secondary Modern School and the mainly archaeological collection from Oakham School. Over the years the Museum has grown and it now has an extensive rural life collection which includes farm tools, tractors, wagons and a wide range of rural tradesmen's tools. In addition it also houses domestic and social history items, along with a large collection of archaeological material from around Rutland. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arson In Royal Dockyards
Arson in royal dockyards was a criminal offence in the United Kingdom and the British Empire. It was among the last offences that were punishable by execution in the United Kingdom. The crime was created by the Dockyards etc. Protection Act 1772 (12 Geo. 3 c.24) passed by the Parliament of Great Britain and was designed to protect Royal Dockyards and vessels from arson attacks. It remained one of the few capital offences after reform of the death penalty in 1861, and remained in effect even after the death penalty was permanently abolished for murder in 1969. However, it was then eliminated by the Criminal Damage Act 1971. Passage The Dockyards etc. Protection Act 1772 was passed in order to protect Royal Navy ships, dockyards, and stores from damage. At the time, ships were built of flammable oak wood and tar, and the naval yards were full of these supplies. Punishment for violating the act was a death sentence. The first section created the offence of arson in the royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)