|
Gallowayella Weberi
''Gallowayella weberi'' is a species of corticolous and saxicolous (bark- and rock-dwelling), foliose lichen in the family Teloschistaceae. Found in the eastern United States, it is a small lichen with a smooth yellow to orange upper surface and a contrasting white lower surface. Taxonomy The lichen was first formally described as a new species in 2003 by the lichenologists Sergey Kondratyuk and Ingvar Kärnefelt, who named it ''Xanthoria weberii''. The type specimen was collected in Grimes County, Texas in 1970. It was found by William Alfred Weber in woodlands dominated by '' Quercus stellata'' (Post Oak), where it was abundant on oak trees in both dusty roadside locations and urban areas. The spelling with two "i"s was erroneous, and it was corrected to ''weberi'' in a subsequent publication. After a couple more proposed generic transfers, to ''Oxneria'' and later to ''Xanthomendoza'', Kondratyuk, Kärnefelt, and their colleagues finally reclassified the taxon in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
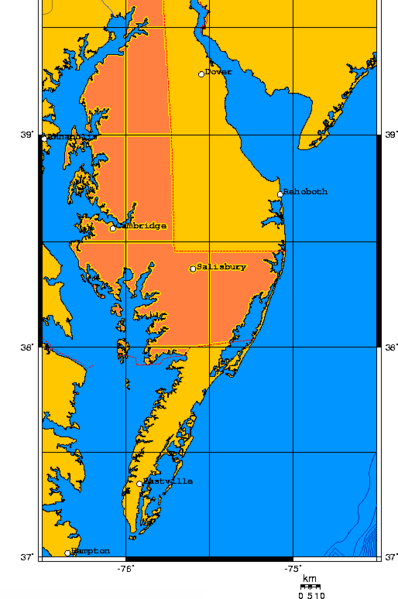
Delmarva
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. The peninsula is long. In width, it ranges from near its center, to at the isthmus on its northern edge, to less near its southern tip of Cape Charles. It is bordered by the Chesapeake Bay on the west, Pocomoke Sound on the southwest, and the Delaware River, Delaware Bay, and the Atlantic Ocean on the east. Etymology In older sources, the peninsula between Delaware Bay and Chesapeake Bay was referred to variously as the Delaware and Chesapeake Peninsula or simply the Chesapeake Peninsula. The toponym ''Delmarva'' is a clipped compound of Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia ( official abbreviation ''VA''), which in turn was modeled after Delmar, a border town named after two of those states. While Delmar was founded and named in 1859, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's Linnaean taxonomy, system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard de Jussieu, Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propagule
In biology, a propagule is any material that functions in propagating an organism to the next stage in its life cycle, such as by dispersal. The propagule is usually distinct in form from the parent organism. Propagules are produced by organisms such as plants (in the form of seeds or spores), fungi (in the form of spores), and bacteria (for example endospores or microbial cysts). In disease biology, pathogens are said to generate infectious propagules, the units that transmit a disease. These can refer to bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protists, and can be contained within host material. For instance, for influenza, the infectious propagules are carried in droplets of host saliva or mucus that are expelled during coughing or sneezing. In horticulture, a propagule is any plant material used for the purpose of plant propagation. In asexual reproduction, a propagule is often a stem cutting. In some plants, a leaf section or a portion of root can be used. In sexual reproduction, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soralia
Soredia are common reproductive structures of lichens. Lichens reproduce asexually by employing simple fragmentation and production of soredia and isidia. Soredia are powdery propagules composed of fungal hyphae wrapped around cyanobacteria or green algae. These can be either scattered diffusely across the surface of the lichen's thallus Thallus (plural: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. Many of these organisms ..., or produced in localized structures called soralia. Fungal hyphae make up the basic body structure of lichen. The soredia are released through openings in the upper cortex of the lichen structure. After their release, the soredia disperse to establish the lichen in a new location. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Lichenology {{lichen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizine
In lichens, rhizines are multicellular root-like structures, arising mostly from the lower surface. A lichen with rhizines is termed rhizinate, while a lichen lacking rhizines is termed erhizinate. Rhizines serve only to anchor the lichen to their substrate; they do not absorb nutrients as do plant roots. Characteristics of the rhizines are used to identify lichens, for example: whether they are dense or sparse, whether they are uniformly distributed or clumped in specific areas, and whether they are straight or branched. Only foliose lichens may possess rhizines, not crustose or fruticose lichens, which lack a lower cortex. Rhizohyphae are a type of attachment structure on some lichens. Rhizohyphae are more slender than rhizines and are one cell thick in diameter. Rhizohyphae often occur as a felt-like hyphal mass. See also *Rhizoid Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla (lichenology)
The medulla is a horizontal layer within a lichen thallus. It is a loosely arranged layer of interlaced hyphae below the upper cortex and photobiont A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Galloway, D.J. (1992). Flora of Australia - ''Lichen Glossary'' The medulla generally has a cottony appearance. It is the widest layer of a heteromerous lichen thallus. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Lichenology {{lichen-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebouxia
''Trebouxia'' is a unicellular green alga.Silverside, A. J. (2009). Retrieved from http://www.bioref.lastdragon.org/Chlorophyta/''Trebouxia''.html It is a photosynthetic organism that can exist in almost all habitats found in polar, tropical, and temperate regions.Erokhina, L. G., Shatilovich, A. V., Kaminskaya, O. P., & Gilichinskii, D. A. (2004). Spectral Properties of the Green Alga ''Trebouxia'', a Phycobiont of Cryptoendolithic Lichens in the Antarctic Dry Valley. Microbiology,73(4), 420-424. doi:10.1023/b:mici.0000036987.18559Lukesova, A., & Frouz, J. (2007). Soil and Freshwater Micro-Algae as a Food Source for Invertebrates in Extreme Environments. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments,265-284. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7_14Seckbach, J. (2007). Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments. Dordrecht: Springer. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7Seckbach, J. (2002). Symbiosis: Mechanisms and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Alga
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to properly include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae. Many species live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds. A few other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula . Isomers include various quinone derivatives. The term anthraquinone however refers to the isomer, 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is a building block of many dyes and is used in bleaching pulp for papermaking. It is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite. Synthesis There are several current industrial methods to produce 9,10-anthraquinone: # The oxidation of anthracene. Chromium(VI) is the typical oxidant. # The Friedel-Crafts reaction of benzene and phthalic anhydride in presence of AlCl3. o-Benzoylbenzoic acid is an intermediate. This reaction is useful for produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortex (botany)
In botany, a cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a vascular plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortex is composed mostly of large thin-walled parenchyma cells of the ground tissue system and shows little to no structural differentiation. The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Plants Stems and branches In the three dimensional structure of herbaceous stems, the epidermis, cortex and vascular cambium form concentric cylinders around the inner cylindrical core of pith. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts, giving them a green color. They can therefore produce simple carbohydrates through photosynthesis. In woody plants, the cortex is located between the periderm (bark) and the vascular tissue (phloem, in particular). It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
