|
Gallic Invasion Of Greece
Gallic is an adjective that may describe: * ancient Gaul (Latin: Gallia), roughly corresponding to the territory of modern France **pertaining to the Gauls **Roman Gaul (1st century BC to 5th century) **Gallic Empire (260–273) **Frankish Gaul (5th to 8th centuries) ** A Latinism for France, the French people, and their customs * Gallic epoch, an obsolete epoch of the Cretaceous * pertaining to gall, a formation induced by a parasite in plants, **hence the name gallic acid, for a phenolic compound found in these formations 'Gallic' is also a proper noun naming the following ships: * , a paddle wheel steamship * , a cargo steamship See also * Gaulish * Gallican * Galician (other) * Gaelic (other) * Gallium Gallium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by France, French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in boron group, group 13 of the periodic table and is similar t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy ( Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and into the Balkans, leading to war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settled in Anatolia, becoming known as Galatians. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Gaul
Roman Gaul refers to GaulThe territory of Gaul roughly corresponds to modern-day France, Belgium and Luxembourg, and adjacient parts of the Netherlands, Switzerland and Germany. under provincial rule in the Roman Empire from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD. History During the Republic The Roman Republic's influence began in southern Gaul. By the mid-2nd century BC, Rome was trading heavily with the Greek colony of Massalia, Massilia (modern Marseille) and entered into an alliance with them, by which it agreed to protect the town from local Gauls, including the nearby Aquitani and from sea-borne Carthaginians and other rivals, in exchange for land that it wanted in order to build a road to Hispania, to assist in troop movements to its provinces there. The Mediterranean settlements on the coast continued to be threatened by the powerful Gallic tribes to the north and in 122 BC the Roman general Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (consul 122 BC), Gnaeus Domitius Ahenoba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Empire
The Gallic Empire or the Gallic Roman Empire are names used in modern historiography for a breakaway part of the Roman Empire that functioned ''de facto'' as a separate state from 260 to 274. It originated during the Crisis of the Third Century, when a series of Roman military leaders and aristocrats declared themselves emperors and took control of Gaul and adjacent provinces without attempting to conquer Italy or otherwise seize the central Roman administrative apparatus. The Gallic Empire was established by Postumus in 260 in the wake of barbarian invasions and instability in Rome, and at its height included the territories of Germania, Gaul, Britannia, and (for a time) Hispania. After Postumus' assassination in 269 it lost much of its territory, but continued under a number of emperors and usurpers. It was retaken by Roman emperor Aurelian after the Battle of Châlons in 274. History Origins The Roman Crisis of the Third Century continued as the Emperor Valerian was defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of Gaul i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Epoch
The Gallic epoch is an obsolete epoch of the Mesozoic Era's Cretaceous, the latter being a geologic period and system that spans 79 million years from the end of the Jurassic Period million years ago ( mya) to the beginning of the Paleogene Period mya. The Gallic epoch encompasses the Barremian, Aptian, Albian, Cenomanian and Turonian faunal stages. In the system of the International Commission on Stratigraphy, the Gallic corresponds to the later part of the Early Cretaceous epoch and the early part of the Late Cretaceous. See also * List of geochronologic names This is a list of official and unofficial names for time spans in the geologic timescale and units of chronostratigraphy. Since many of the smallest subdivisions of the geologic timescale were in the past defined on regional lithostratigraphic unit ... Cretaceous geochronology {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gall
Galls (from the Latin , 'oak-apple') or ''cecidia'' (from the Greek , anything gushing out) are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to benign tumors or warts in animals. They can be caused by various parasites, from viruses, fungi and bacteria, to other plants, insects and mites. Plant galls are often highly organized structures so that the cause of the gall can often be determined without the actual agent being identified. This applies particularly to some insect and mite plant galls. The study of plant galls is known as cecidology. In human pathology, a gall is a raised sore on the skin, usually caused by chafing or rubbing. Causes of plant galls Insects and mites Insect galls are the highly distinctive plant structures formed by some herbivorous insects as their own microhabitats. They are plant tissue which is controlled by the insect. Galls act as both the habitat a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
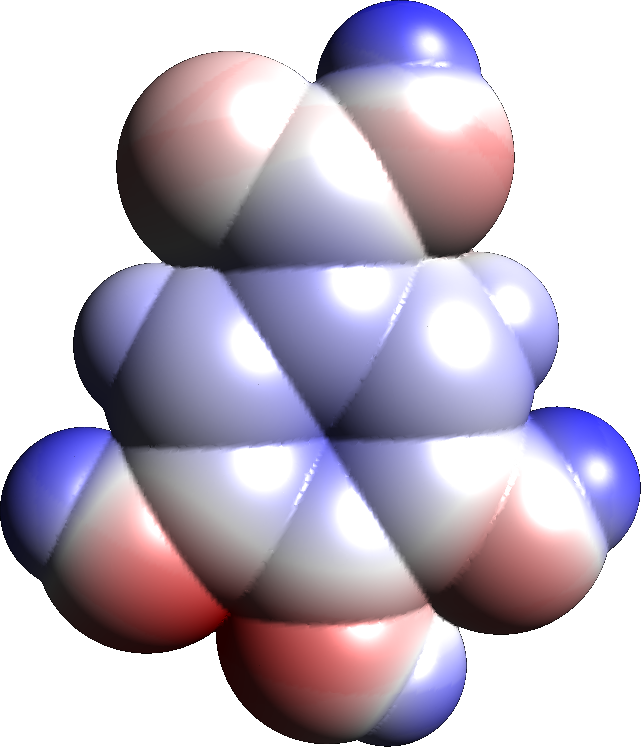
Gallic Acid
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6 H2( OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates". Isolation and derivatives Gallic acid is easily freed from gallotannins by acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, gallic acid converts to rufigallol. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively. Biosynthesis Gallic acid is formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase to produce 3,5-didehydroshikimate. This latter compound aromatizes. Reactions Oxidation and oxidative coupling Alkaline solutions of gallic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the west bank of the Rhine). In a wider sense, it also comprises varieties of Celtic that were spoken across much of central Europe ("Noric language, Noric"), parts of the Balkans, and Anatolia ("Galatian language, Galatian"), which are thought to have been closely related. The more divergent Lepontic language, Lepontic of Northern Italy has also sometimes been subsumed under Gaulish. Together with Lepontic and the Celtiberian language, Celtiberian spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, Gaulish helps form the geographic group of Continental Celtic languages. The precise linguistic relationships among them, as well as between them and the modern Insular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallican (other)
Gallican may refer to: * Gallican Church (), a term referring to the Catholic Church in France * Église gallicane, a Catholic denomination founded in 1869 by Hyacinthe Loyson * Gallicanism, a doctrince that civil authority over the Catholic Church is comparable to that of the Pope * Gallican Psalter or , one of Jerome's Latin translations of the book pf Psalms * Gallican Rite, a 1st-millennium Christian liturgy and other ritual practices in Western Christianity ** Gallican chant, the liturgical plainchant repertory of the Gallican rite * Gallican, a largely obsolete synonym of ''Gallic'', referring to: ** France, a country in Western Europe *** French people, the majority demographic group of France *** French language, the majority language of France * Gallican, a largely obsolete synonym of ''Gaulish'', referring to: ** Gaul, ancient nation encompassing modern-day France and parts of surrounding countries *** Gauls, the principal people of Gaul *** Gaulish language, spoken b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galician (other)
Galician may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Galicia (Spain) ** Galician language ** Galician people ** Gallaeci, a large Celtic tribal federation who inhabited Gallaecia (currently Galicia (Spain) * Something of, from, or related to Galicia (Eastern Europe) Galicia ()"Galicia" '' SS ''Galician'' a liner later renamed the HMHS ''Glenart Castle''
See also * Galicia (other) * Halychian (di ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |