|
Galeata
Galeata ( rgn, Gagliêda) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Forlì-Cesena in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southwest of Forlì. Galeata borders the following municipalities: Civitella di Romagna, Predappio, Premilcuore, Rocca San Casciano, Santa Sofia. History Galeata's origins are connected to the old Umbrian town of ''Mevaniola'', captured by the Romans in 266 BC. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the settlement was moved to the modern Galeata. The latter's fortunes in the Middle Ages stemmed from the creation of the powerful Abbey of Sant'Ellero (Hilary of Galeata), which administrated for centuries the nearby territories, with an army and fortresses of its own. In the early 15th century, Galeata became part of the Florentine possessions, belonging to the Grand Duchy of Tuscany until 1860. It was part of the Province of Florence until 1923, when it was moved to the province of Forlì. Main sights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilary Of Galeata
Saint Hilary of Galeata (Italian: ''Sant'Ilaro'' or ''Sant'Ellero''; 476 – 15 May 558) is venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. His feast day is 15 May. ΜΕΓΑΣ ΣΥΝΑΞΑΡΙΣΤΗΣ. According to tradition, he was born in in 476, and he decided to dedicate himself to the life of a at the age of twelve. He left his home, and traveled across the towards |
Civitella Di Romagna
Civitella di Romagna ( rgn, Zivitèla) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Forlì-Cesena in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southwest of Forlì. Civitella di Romagna borders the following municipalities: Cesena, Galeata, Meldola, Predappio, Santa Sofia, Sarsina Sarsina ( rgn, Sêrsna) is an Italian town situated in the province of Forlì-Cesena, Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy. Its territory is included in the Tuscan-Romagnolo Apennines. History Ancient Sarsina or Sassina was a town of the Umbri. Capt .... References External links Official website Cities and towns in Emilia-Romagna {{EmiliaRomagna-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premilcuore
Premilcuore ( rgn, Premaicur) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Forlì-Cesena in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southwest of Forlì. History Following a local tradition, the town was founded in the year 215 by a Roman centurion named "Marcelliano", who took refuge with some soldiers in the valley of Rabbi river. First mentioned in 1124, it was part of the Province of Florence, in Tuscany, until 1923. Geography Located at the borders of Romagna with Tuscany, Premilcuore is a little hill town of the Apennine Mountains, below the Alpe di San Benedetto and Falterona mountains. It borders the municipalities of Galeata, Portico e San Benedetto, Rocca San Casciano, San Godenzo ( FI), and Santa Sofia. It counts the hamlet (''frazione'') of Ponte Fantella. Demographics Colors= id:lightgrey value:gray(0.9) id:darkgrey value:gray(0.7) id:sfondo value:rgb(1,1,1) id:barra value:rgb(0.6,0.7,0.8) ImageSize = wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocca San Casciano
Rocca San Casciano ( rgn, La Ròca or ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Forlì-Cesena in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southwest of Forlì. Geography Rocca San Casciano borders the following municipalities: Dovadola, Galeata, Modigliana, Portico e San Benedetto, Predappio, Premilcuore and Tredozio. Festa del Falò Rocca San Casciano is popular in the area for its ''Festa del Falò'' ("Bonfires Feast"), which is believed to originate from Celtic Pagan rites. It is documented that bonfires have been lit near the Montone River ever since the 12th century; later the event became associated with St. Joseph's Day (19 March). San Donnino in soglio is famous History Rocca San Casciano is created in the 1200 Events By place Europe * Spring – Boniface I, marquis of Montferrat, sends envoys to Venice, Genoa and other city-states to negotiate a contract for transport to the Levant. Meanwhile, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-45 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 395 to 476, where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern provinces, with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were ''de facto'' independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts as an administrative expediency. The Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna was formally dissolved by Justinian in 554. The Eastern imperial court survived until 1453. Though the Empire had seen periods with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
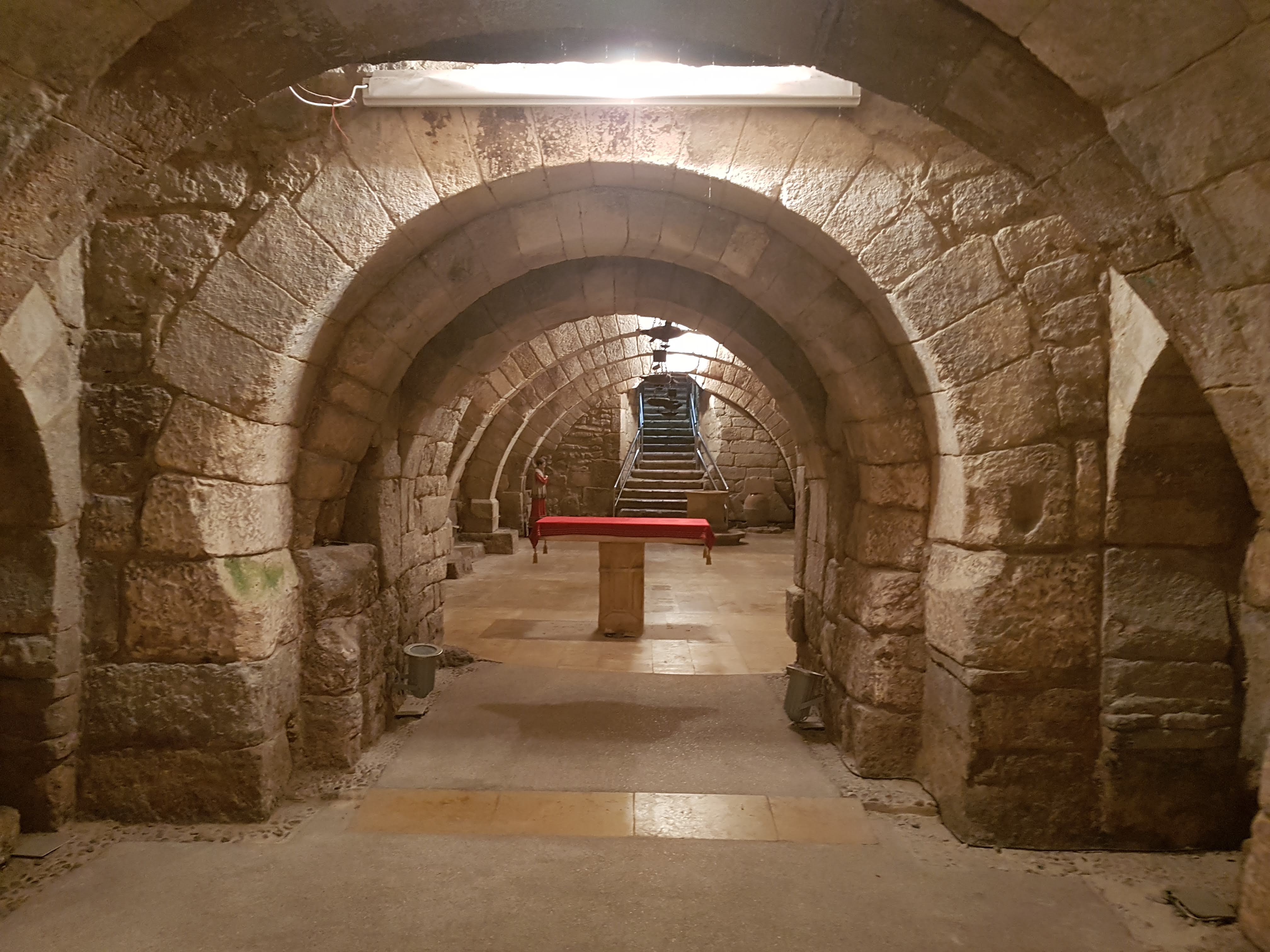
Crypt
A crypt (from Latin ''crypta'' "vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics. Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a church, such as at the Abbey of Saint-Germain en Auxerre, but were later located beneath chancel, naves and transepts as well. Occasionally churches were raised high to accommodate a crypt at the ground level, such as St Michael's Church in Hildesheim, Germany. Etymology The word "Crypt" developed as an alternative form of the Latin "vault" as it was carried over into Late Latin, and came to refer to the ritual rooms found underneath church buildings. It also served as a vault for storing important and/or sacred items. The word "Crypta", however, is also the female form of ''crypto'' "hidden". The earliest known origin of both is in the Ancient Greek '' κρύπτω'' (krupto/krypto), the first person singular indicative of the verb "to conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbytery (architecture)
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
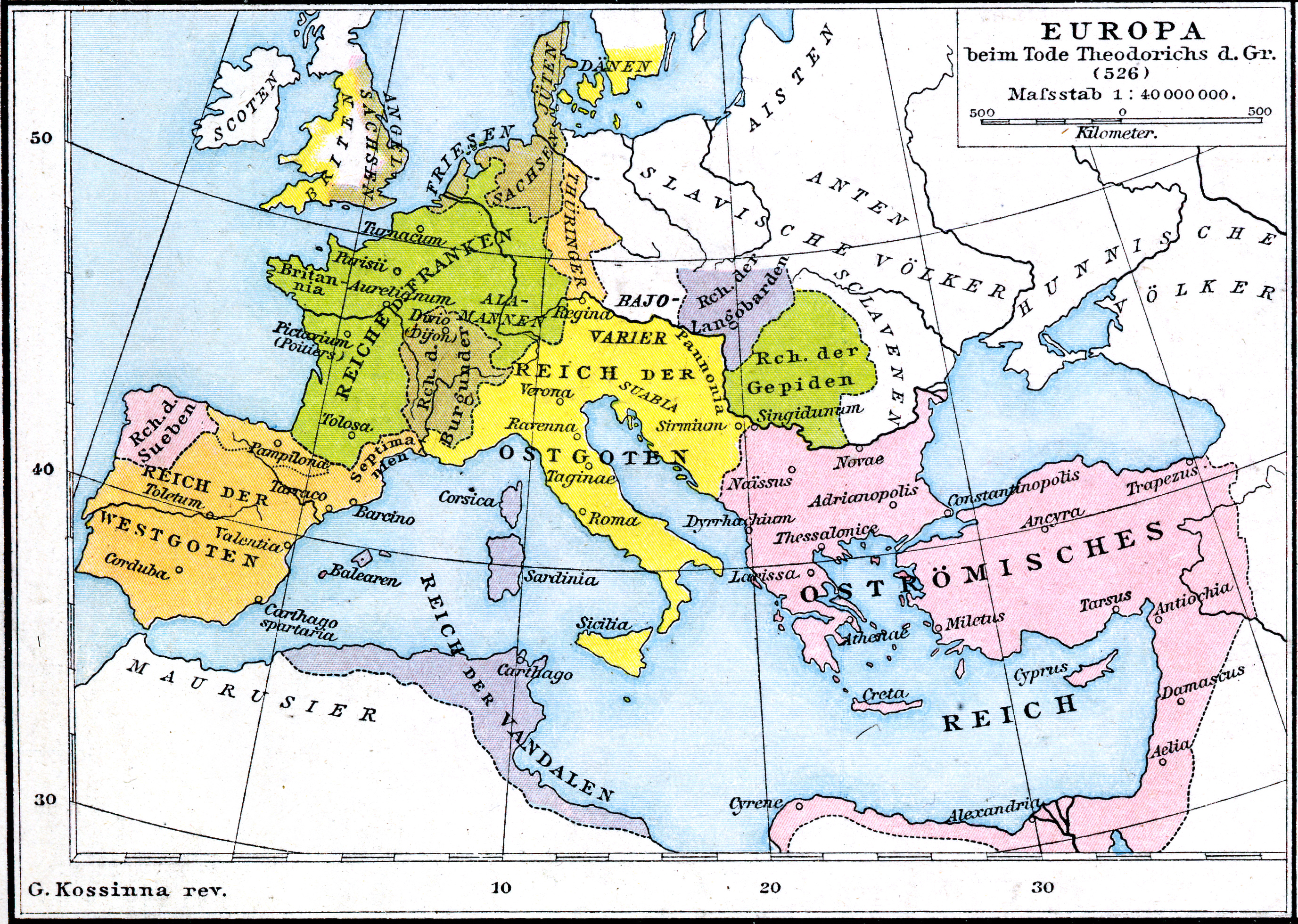
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Forlì
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''province'' has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city". While some provinces were produced artificially by colonial powers, others were formed around local groups with their own ethnic identities. Many have their own powers independent of central or federal authority, especially in Canada and Pakistan. In other countries, like China or France, provinces are the creation of central government, with very little autonomy. Etymology The English word ''province'' is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French , which itself comes from the Latin word , which referred to the sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Florence
The province of Florence ( it, provincia di Firenze) was a province in the northeast of Tuscany region of Italy. The city or ''comune'' of Florence was both the capital of the Province of Florence, and of the Region of Tuscany. It had an area of and a population of 1,012,180 as of 31 December 2014. The territory of the province was the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance. In 2015 the province was replaced by the Metropolitan City of Florence. Geography The Province of Florence was bordered by the Province of Bologna in the north, the Province of Ravenna and Forlì-Cesena in the north-east, the provinces of Prato, Pistoia, Pisa and Lucca in the west; the Province of Siena in the south and the Province of Arezzo in the east and southeast. Much of the province lied in the plain of the Arno river. Government List of presidents of the province of Florence References External links Photo gallery: Province of Florence— ''licensed photos''. . Florence Florence ( ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population of the Grand Duchy was about 1,815,000 inhabitants. Having brought nearly all Tuscany under his control after conquering the Republic of Siena, Cosimo I de' Medici, was elevated by a papal bull of Pope Pius V to Grand Duke of Tuscany on August 27, 1569. The Grand Duchy was ruled by the House of Medici until the extinction of its senior branch in 1737. While not as internationally renowned as the old republic, the grand duchy thrived under the Medici and it bore witness to unprecedented economic and military success under Cosimo I and his sons, until the reign of Ferdinando II, which saw the beginning of the state's long economic decline. It peaked under Cosimo III. Francis Stephen of Lorraine, a cognatic de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |