|
Galagoides Demidovii
The western dwarf galagos are a group of three species of strepsirrhine primates, native to western and central Africa. They are classified in the genus ''Galagoides'' of the family Galagidae. The eastern dwarf galagos (''P. cocos, P. granti, P. orinus, P. rondoensis,'' and ''P. zanzibaricus'') have been moved to their own genus, ''Paragalago'', based on genetic evidence and differences in vocalization. The two genera are not sister taxa and thus may have evolved their small sizes via parallel evolution. They are separated by the East African Rift. The first genus to be introduced to scientific literature was ''Galago'' by Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire. The genus was based on a smaller species from West Africa. Later, the genus ''Galagoides'' was introduced by Sir Andrew Smith in 1833. Smith wanted to differentiate the dwarf (''Gd. demidovii'') and the lesser galagos from the 'true galagos.' ''Otolemur'' was later introduced to indicate the greater galago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
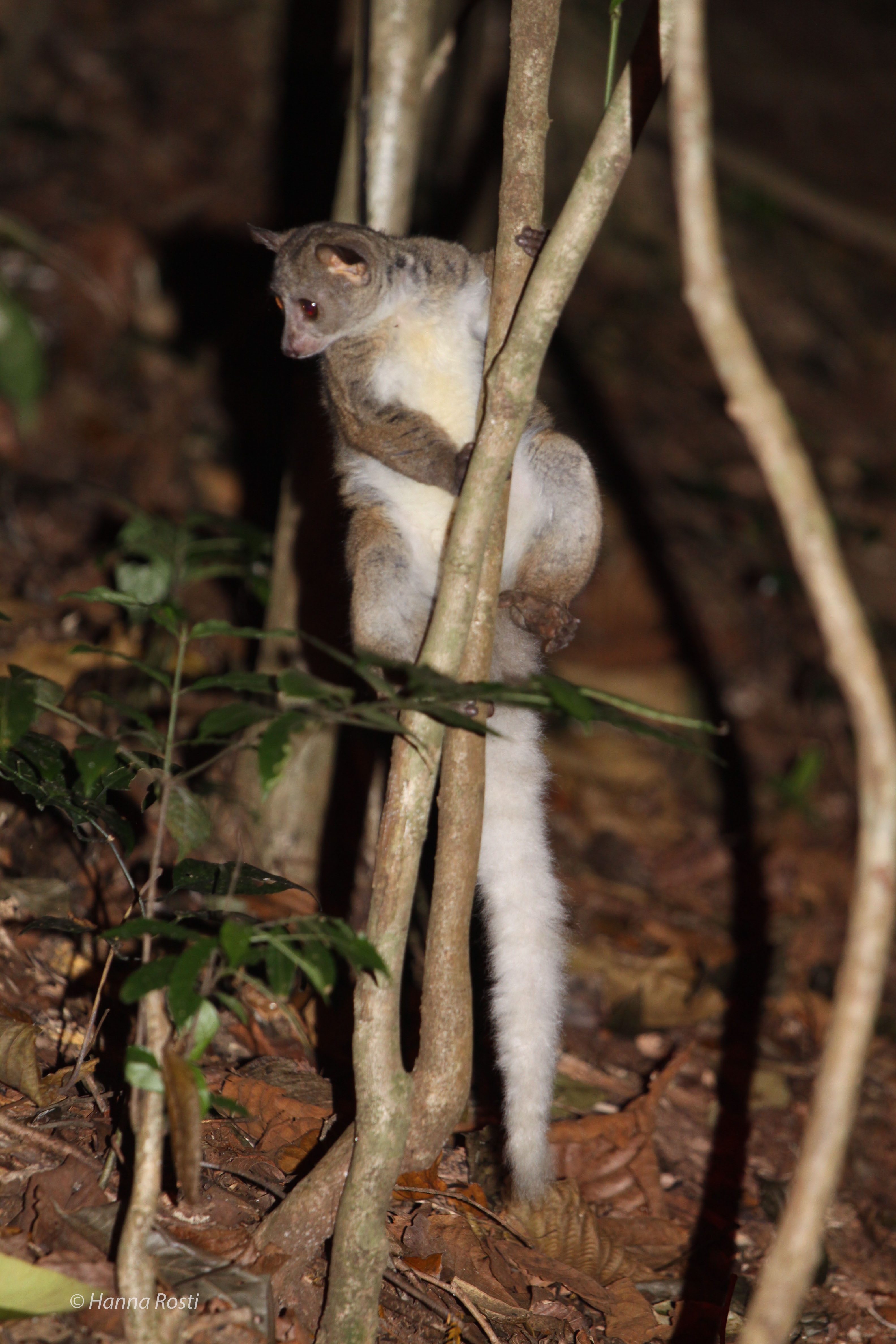
Prince Demidoff's Bushbaby
Prince Demidoff's bushbaby (''Galagoides demidovii''), also known as Prince Demidoff's galago, is a species of primate in the family Galagidae. It is native to parts of tropical West and Central Africa. Description Prince Demidoff's bushbaby grows to a head-and-body length of , with a tail of . The head is narrow with a pointed muzzle and variable colouring round the eyes. The upper parts are reddish-brown, the underparts are paler and the tail is not bushy. Distribution and habitat The species is found in Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Mali, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, possibly Kenya, and possibly Malawi. Habitats include both primary and secondary forest as well as swampy forests, mangrove areas, gallery forests and mixed habitats in the Upper Guinean forest zone. It is adaptable and tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
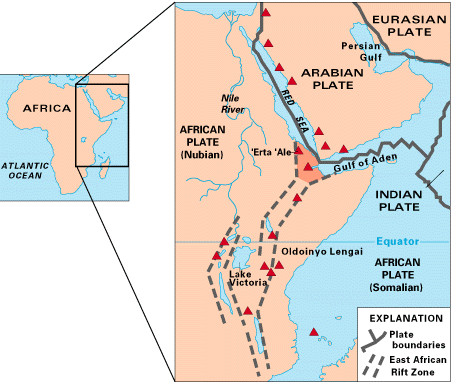
East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor. A narrow zone, the rift is a developing divergent tectonic plate boundary where the African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate, at a rate of 6-7 mm per year. The rift system consists of three microplates, the Victoria Microplate to the north, and the Rovuma and Lwandle microplates to the south. The Victoria Microplate is rotating anti-clockwise with respect to the African plate. Its rotation is caused by the configuration of mechanically weaker and stronger lithospheric regions in the EARS. Extent A series of distinct rift basins, the East African Rift System extends over thousands of kilometers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Andrew Smith (zoologist)
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primates Of Africa
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have large brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galagos
Galagos , also known as bush babies, or ''nagapies'' (meaning "night monkeys" in Afrikaans), are small nocturnal primates native to continental, sub-Sahara Africa, and make up the family Galagidae (also sometimes called Galagonidae). They are considered a sister group of the Lorisidae. According to some accounts, the name "bush baby" comes from either the animal's cries or its appearance. The Ghanaian name ''aposor'' is given to them because of their firm grip on branches. In both variety and abundance, the bush babies are the most successful strepsirrhine primates in Africa, according to the African Wildlife Foundation. Taxonomic classification and phylogeny Galagos are currently grouped into six genera. ''Euoticus'' is a basal sister taxon to all the other galagids. The 'dwarf' galagids recently grouped under the genus ''Galagoides'' have been found, based on genetic data, and supported by analysis of vocalisations and morphology, to actually consist of two clades, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas's Bushbaby
Thomas's bushbaby (''Galagoides thomasi'') is a species of primate in the family Galagidae. It is found in Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Kenya, Nigeria, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t .... References Thomas's bushbaby Mammals of Angola Mammals of Burundi Mammals of Cameroon Mammals of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Mammals of Equatorial Guinea Mammals of Gabon Mammals of Kenya Mammals of Rwanda Mammals of Tanzania Mammals of Uganda Mammals of Zambia Fauna of Central Africa Mammals of West Africa Thomas's bushbaby Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{primate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Coquerel
Jean Charles Coquerel (2 December 1822 – 12 April 1867) was a French navy surgeon, algologist, and entomologist. Coquerel collected insects in Madagascar and neighbouring islands. A number of these were described after his death by Léon Fairmaire in his ''Notes sur les Coléopteres recueillis par Charles Coquerel a Madagascar et sur les côtes d'Afrique'' (1869). During his lifetime Coquerel wrote a number of articles and books, including an appendix on insects in Auguste Vinson's ''Voyage à Madagascar au couronnement de Radama II'' (1865). A number of animals are named after him, including the Coquerel's coua (''Coua coquereli'' Grandidier, 1867), the Coquerel's sifaka (''Propithecus coquereli'' Milne-Edwards, 1867), and the Coquerel's giant mouse lemur (''Mirza coquereli'' Grandidier, 1867), each of these species is endemic to Madagascar. Coquerel's insect collection is in the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle The French National Museum of Natural History, known in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolemur
The greater galagos or thick-tailed bushbabies are three species of strepsirrhine primates. They are classified in the genus ''Otolemur'' in the family Galagidae. Historical classification and species discovery The diversity of galago species has historically been grossly underestimated. In 1931, only 5 species were recognized, 4 in the genus ''Galago'' and 1 in ''Euoticus'', and only one species that would later be placed in the genus ''Otolemur''. In 1979, the genus ''Otolemur'' was separated from ''Galago''. By 1986, eleven species were recognized with revamped systemic classification including ''Otolemur crassicaudatus'' and ''Otolemur garnettii''. Additionally, ''O. crassidautus'' and ''O. monteiri'' were recognized as separate species instead of ''O. monteiri'' as a nested subspecies. By 2001, 23 species were recognized. Classification by vocalization has particularly become prevalent and helpful as a tool in understanding of these species. All ''Otolemur'' species exhibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (15 April 177219 June 1844) was a French naturalist who established the principle of "unity of composition". He was a colleague of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and expanded and defended Lamarck's evolutionary theories. Geoffroy's scientific views had a transcendental flavor (unlike Lamarck's materialistic views) and were similar to those of German morphologists like Lorenz Oken. He believed in the underlying unity of organismal design, and the possibility of the transmutation of species in time, amassing evidence for his claims through research in comparative anatomy, paleontology, and embryology. He is considered as a predecessor of the evo-devo evolutionary concept. Life and early career Geoffroy was born at Étampes (in present-day Essonne), and studied at the Collège de Navarre, in Paris, where he studied natural philosophy under M. J. Brisson. He then attended the lectures of Daubenton at the College de France and Fourcroy at the Jardin des Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galago
Galagos , also known as bush babies, or ''nagapies'' (meaning "night monkeys" in Afrikaans), are small nocturnal primates native to continental, sub-Sahara Africa, and make up the family Galagidae (also sometimes called Galagonidae). They are considered a sister group of the Lorisidae. According to some accounts, the name "bush baby" comes from either the animal's cries or its appearance. The Ghanaian name ''aposor'' is given to them because of their firm grip on branches. In both variety and abundance, the bush babies are the most successful strepsirrhine primates in Africa, according to the African Wildlife Foundation. Taxonomic classification and phylogeny Galagos are currently grouped into six genera. ''Euoticus'' is a basal sister taxon to all the other galagids. The 'dwarf' galagids recently grouped under the genus ''Galagoides'' have been found, based on genetic data, and supported by analysis of vocalisations and morphology, to actually consist of two clades, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and parallel evolution at the amino acid sequence level. ''Mol. Biol. Evol.'' 14, 527-36. Parallel vs. convergent evolution Given a particular trait that occurs in each of two lineages descended from a specified ancestor, it is possible in theory to define parallel and convergent evolutionary trends strictly, and distinguish them clearly from one another. However the criteria for defining convergent as opposed to parallel evolution often are unclear in practice, so that arbitrary diagnosis is common in some cases. When two species are similar in a particular character, evolution is defined as parallel if the ancestors shared that similarity; if they did not, the evolution of that character in those species is defined as convergent. However, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Smith (zoologist)
Sir Andrew Smith (3 December 1797 – 11 August 1872) was a British surgeon, explorer, ethnologist and zoologist. He is considered the father of zoology in South Africa having described many species across a wide range of groups in his major work, ''Illustrations of the Zoology of South Africa''. Smith was born in Hawick, Roxburghshire. He qualified in medicine at the University of Edinburgh obtaining an M.D. degree in 1819, having joined the Army Medical Services in 1816. South Africa 1820–1837 In 1820 he was ordered to the Cape Colony and was sent to Grahamstown to supervise the medical care of European soldiers and soldiers of the Cape Corps. He was appointed the Albany district surgeon in 1822 and started the first free dispensary for indigent patients in South Africa. He led a scientific expedition into the interior and was able to indulge in his interests of natural history and anthropology. On several occasions, he was sent by governors on confidential missions to vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)
