|
Gajam Anjaiah
Gajam Anjaiah, an Indian master handloom designer, who is widely recognised in the handloom industry for his innovations and developments of Tie and Dye handloom products along with Telia Rumal technique of weaving based on Ikat tie-dye process. He received Padma Shri from Government of India under Art category in 2013. He is known for his excellence in traditional handloom design works, such as Puttapaka Sarees in Tie and dye skill, that is the traditional art of designing on paper and then transferring it on to cloth. His dedication to the Handloom Industry has kept the Indian tradition of weaving alive, brought livelihood to the weavers and gave exclusive/unique designed handloom products to the people in India. Early life and family He was born on 16 May 1955, in a Padmashali community in Puttapaka village, Narayanpur mandal in Nalgonda district, Telangana to Narasimha, also a textile designer, who is credited with bringing Telia Rumal to his community from Chirala. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nalgonda District, Telangana
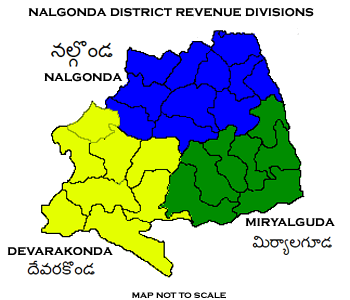
Nalgonda district is a district in the Telangana state of India. Nalgonda district has the highest number of mandals in the state with 31 mandals. The district shares boundaries with Suryapet, Rangareddy, Yadadri and Nagarkurnool districts and with the state boundary of Andhra Pradesh. Etymology Nalgonda is derived from two Telugu words Nalla (Black) & Konda (Hills) i.e. ''Black Hills''. History Nalgonda was earlier referred to as Neelagiri, the name given by some local rulers and the name was changed to ''Nallagonda'' only after its conquest by Allauddin Bahaman Shah, the founder of Bahmani Sultanate . The district had a major role in the Telangana Rebellion. Geography The district is spread over an area of . Demographics Census of India, the district has a population of 1,618,416. According to the 2011 census, 81.75% of the population spoke Telugu, 11.91% Lambadi and 5.51% Urdu as their first language. The Krishna River, Musi River, Aleru, Peddavagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telia Rumal
Telia Rumal is a method for the oil treatment of yarn. It originated from Chirala in Andhra Pradesh. At Chirala, in the Prakasam district of Andhra Pradesh where the craft started, the weavers had virtually stopped making Telia Rumals. People who acquired skill in this dying art took the lead to introduce this in Puttapaka village of Nalgonda district in Telangana. Recently Puttapaka Telia Rumal was accorded with Geographical indication (GI) tag. History These rumals were patronised by Nizams of Hyderabad, who commissioned elaborate pieces. Gajam Govardhana popularized the tradition and revived the art of telia rumal which was then dying. today his contributions to revival of Telia Rumal has brought this sustainable, natural process of art to an international level. Process It is an art of Ikat ''Ikat'' (in Indonesian languages means "bind") is a dyeing technique originating from Indonesia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Nalgonda District
A person (plural, : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal obligation, legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telugu People
Telugu people ( te, తెలుగువారు, Teluguvāru), or Telugus, or Telugu vaaru, are the largest of the four major Dravidian ethnolinguistic groups in terms of population. Telugus are native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and the Yanam district of Puducherry. A significant number of Telugus also reside in the surrounding Indian states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Gujarat, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, and Odisha, as well in the union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Telugus claim descent from the Andhras, from whom the Telugus inherit their ethnonym. Telugu is the fourth most spoken language in India and the 15th most spoken language in the world. Andhra was mentioned in the Sanskrit epics such as Aitareya Brahmana (by some estimates c. 800 BCE). According to Aitareya Brahmana of the Rigveda, the Andhras left North India from the banks of river Yamuna and migrated to South India. They are mentioned at the time of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sant Kabir Award
Sant Kabir Award is an Indian Government award conferred to outstanding weavers who have made valuable contribution in keeping alive the handloom heritage. It was established for dedication in building up linkages between the past, present and future through dissemination of knowledge on traditional skills and designs by Ministry of Textiles, Government of India. The award was christened in the memory of sant Kabir, a 15th-century mystic poet and sant of India. The award is presented by the President of India, along with Shilp Guru Awards and National Awards to Master Craftspersons and master weavers, introduced in 1965. Overview Every year, two stages of selection process will be constituted to finalize the winning entry. First stage of selection will be done at the level of respective Zonal Directors. Final selection will be done by Apex selection committee of Development Commissioner(Handlooms). Award consists of one mounted gold coin, one shawl and a citation. In addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirala
Chirala (), (, Telugu) a city in Bapatla district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a municipality and the headquarters of Chirala mandal in Chirala revenue division. , it had a population of above 170,000. Chirala is the most populated city in Bapatla Lok Sabha Parliamentary Constituency. Etymology The city was also known as ''Kshirapuri'', (, Telugu) which translates as ''the town of milk''.The city was carved out of Sudhanagaram, original name of Patha Chirala, that was granted to Chirala Anantharaju by Goparaju Ramanna, Minister of the Kakatiya king, Ganapati Deva, during Saka 1067 (1145 AD) as mentioned in the records obtained from the Madras Oriental Library. His descendant, Chirala Venkata Krishnudu, leased out the present Chirala area for raising a new township. Thus, present-day Chirala was born on 1604 AD. Independence Movement- Chirala Perala Movement Chirala name was carved in Independence struggle The then British government has laid taxes which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padmashali
Padmasali (also spelt as Padmashali, Padmasale) is a Hindu caste residing in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu. Their traditional occupation is weaving. Etymology The term ''Padmasali'' is derived from two words ''Padma'' and ''Sali'', The Padma means lotus and Sali means weaver. The word Padma referring to the myth of the thread was a lotus which sprang from the navel of Vishnu. History The Padmasalis are part of the wider community of Telugu weavers, who are known as " Sale" or "Saliya". Historically, they were also referred to by other castes as "Julai". The Padmasalis follow their mythological origins and ''Puranas'' such as ''Kulapurana'' and ''Markandeya Purana''. The Padmasalis and the Devangas, who are another caste of weavers, were originally a single caste in ancient times and followed Vaishnavism. The caste then split due to differences in faith, with the Devangas being influenced by Lingayatism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handloom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same. Etymology and usage The word "loom" derives from the Old English ''geloma'', formed from ''ge-'' (perfective prefix) and ''loma'', a root of unknown origin; the whole word ''geloma'' meant a utensil, tool, or machine of any kind. In 1404 "lome" was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. By 1838 "loom" had gained the additional meaning of a machine for interlacing thread. Weaving Weaving is done by intersecting the longitudinal threads, the warp, i.e. "that which is thrown across", with the transverse threads, the weft, i.e. "that which is woven". The major components of the loom are the warp beam, heddles, harnesses or shafts (as few as two, four is common, sixteen not unheard of), s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
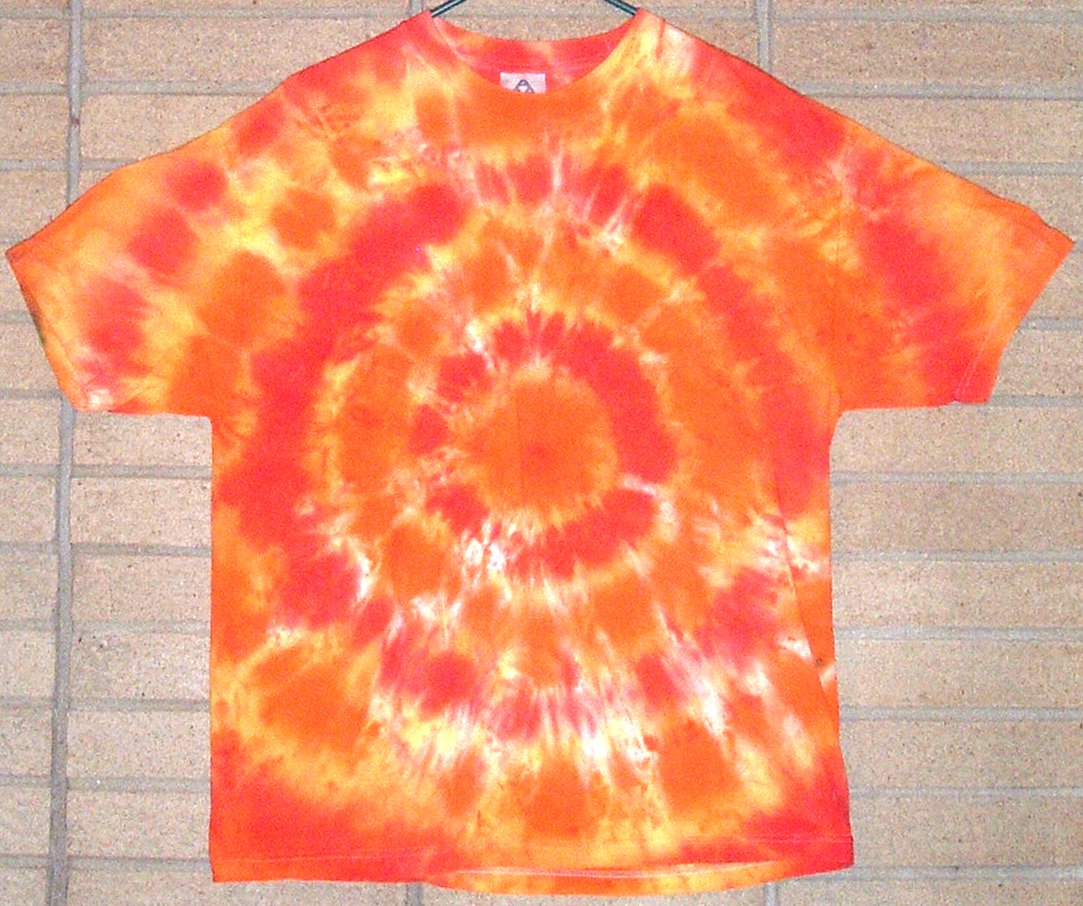
Tie And Dye
Tie-dye is a term used to describe a number of resist dyeing techniques and the resulting dyed products of these processes. The process of tie-dye typically consists of folding, twisting, pleating, or crumpling fabric or a garment, before binding with string or rubber bands, followed by the application of dye or dyes. The manipulations of the fabric before the application of dye are called resists, as they partially or completely prevent ('resist') the applied dye from coloring the fabric. More sophisticated tie-dye may involve additional steps, including an initial application of dye before the resist, multiple sequential dyeing and resist steps, and the use of other types of resists (stitching, stencils) and discharge. Unlike regular resist-dyeing techniques, modern tie-dye is characterized by the use of bright, saturated primary colors and bold patterns. These patterns, including the spiral, mandala, and peace sign, and the use of multiple bold colors, have become clichéd sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puttapaka Saree
Puttapaka Sari is a saree made in Puttapaka village, Samsthan Narayanpuram mandal in Nalgonda district, India. It is known for its unique Puttapaka tie and dye style of sarees. The Weave The ikat is warp-based unlike most other ikats designed predominantly on weft. The labour-intensive double ikat arp and weftis their strength. The warp design requires linear tying of the silk yarn strands. The unique design focus is on symmetry without undermining aesthetics. It closely resembles Sambalpuri saree. Tehliya Rumal Tehliya Rumal an oily handkerchief made in Puttapaka which was awarded with GI tag. Telia Rumal is a unique tie and dye technique that uses oil for the treatment of the yarn that helps it retain softness and has a distinct smell of gingelly oil. Cottage industry The community of weavers involved are Puttapaka Padmashalis. The weavers sell their sarees for Rs.2000 locally. Noted handloom designer, Gajam Anjaiah is known for the Puttapaka designs. But the Puttapaka sarees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)


