|
Gaia Sausage
The Gaia Sausage or Gaia Enceladus is the remains of a dwarf galaxy (the Sausage Galaxy, or Gaia-Enceladus-Sausage, or Gaia-Sausage-Enceladus) that merged with the Milky Way about 8–11 billion years ago. At least eight globular clusters were added to the Milky Way along with 50 billion solar masses of stars, gas and dark matter. It represents the last major merger of the Milky Way. Etymology The "Gaia Sausage" is so-called because of the characteristic sausage shape of the population in a chart of velocity space, in particular a plot of radial (\boldsymbol_r) versus azimuthal velocity (\boldsymbol_\theta) of stars (See spherical coordinate system), using data from the Gaia Mission. The stars that have merged with the Milky Way have orbits that are highly elongated. The outermost points of their orbits are around 20 kiloparsecs from the Galactic Center at what is called the "halo break". These stars had previously been seen in Hipparcos data and identified as ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulated Gaia-Enceladus Debris
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance tuning or optimizing, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functioning, as in economics. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply not e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
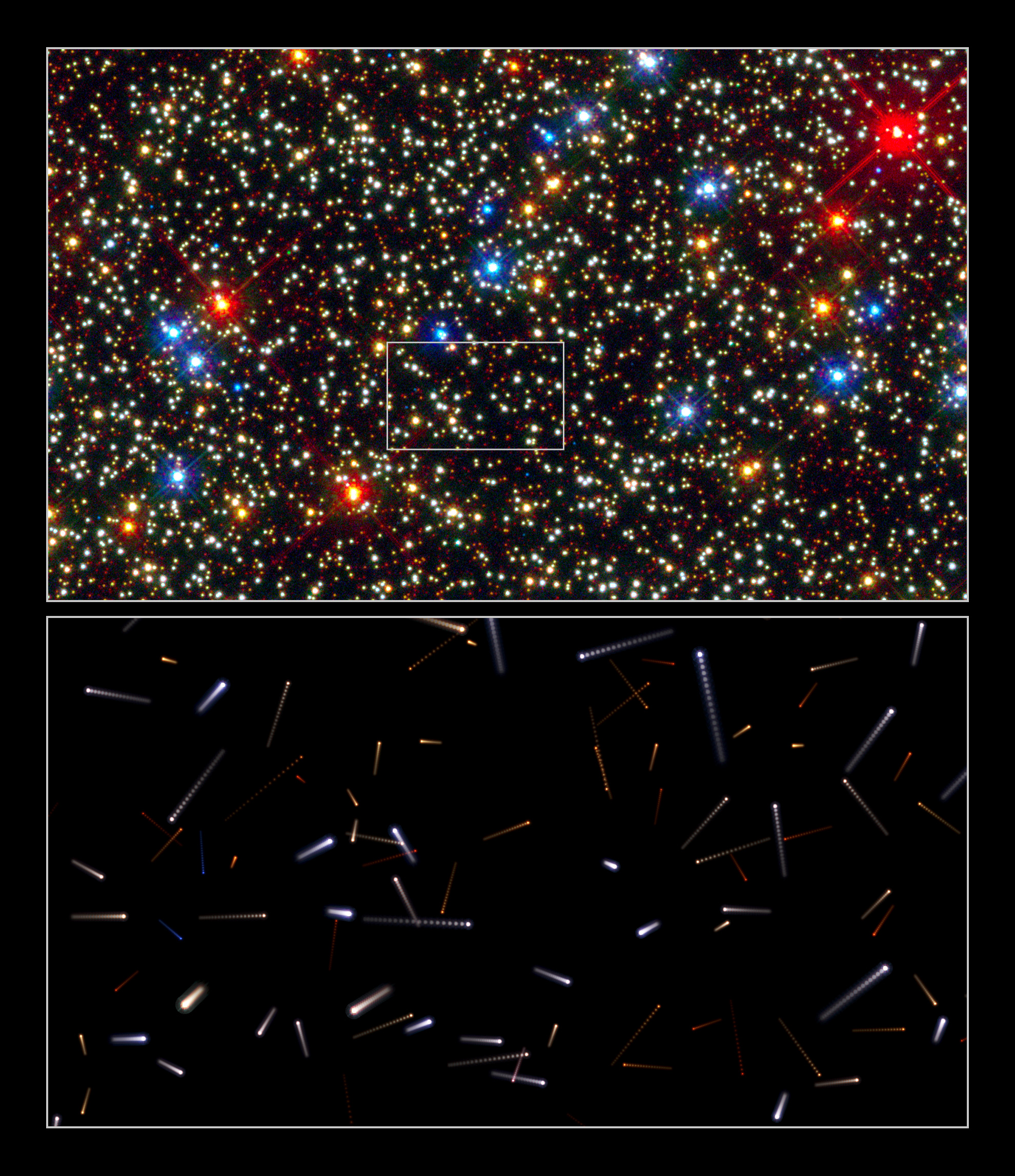
NGC 2298
NGC 2298 is a globular cluster in the southern constellation of Puppis. Discovered by James Dunlop on May 30, 1826, it is probably a former member of the disputed Canis Major Dwarf galaxy. The cluster is being disrupted by the galactic tide, trailing a long tidal tail A tidal tail is a thin, elongated region of stars and interstellar gas that extends into space from a galaxy. Tidal tails occur as a result of galactic tide forces between interacting galaxies. Examples of galaxies with tidal tails include the .... References External links * NGC 2298at Wikisky at Astrosurf NGC 2298at Deepskypedia * Globular clusters Puppis 2298 {{star-cluster-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J1124+4535
J11 may refer to: Vehicles Aircraft * Fiat J 11, an Italian sesquiplane fighter in service with the Swedish Air Force * Junkers J 11, a German ground-attack aircraft * Shenyang J-11, a Chinese jet fighter Automobiles * James Comet J11, an English motorcycle * Nissan Qashqai J11, a Japanese SUV Locomotives * GSR Class J11, an Irish steam locomotive * LNER Class J11, a class of British steam locomotives Ships * , a ''Halcyon''-class minesweeper of the Royal Navy * , a ''Visby''-class destroyer of the Swedish Navy Other uses * County Route J11 (California) * DEC J-11, a microprocessor chip set * Gyroelongated pentagonal pyramid In geometry, the gyroelongated pentagonal pyramid is one of the Johnson solids (). As its name suggests, it is formed by taking a pentagonal pyramid and "gyroelongating" it, which in this case involves joining a pentagonal antiprism to its base. ..., a Johnson solid (J11) See also * JII (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M32p
M32p is a hypothesized former galaxy that was incorporated into the Andromeda Galaxy. It was a sister galaxy to the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, previously the third or fourth largest galaxy in the Local Group, and was merged into the larger Andromeda Galaxy an estimated 2 billion years ago. The merger is thought to have created the thick disc and contributed the majority of the halo stars of Andromeda and caused its burst of star formation at the time of the merger. The former galaxy may be associated with the Andromeda satellite galaxy Messier 32 (M32), which may be the remains of its dense core. M32's unusual characteristics of dense compactness and burst of star formation 2 billion years ago would be explained by this theory as a remnant of an earlier large galaxy, given its unlikeness to other similarly sized elliptical galaxies. It was described in 2018 by scientists at the University of Michigan , mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth" , former_name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri (ω Cen, NGC 5139, or Caldwell 80) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of , it is the largest-known globular cluster in the Milky Way at a diameter of roughly 150 light-years. It is estimated to contain approximately 10 million stars, and a total mass equivalent to 4 million solar masses, making it the most massive-known globular cluster in the Milky Way. Omega Centauri is very different from most other galactic globular clusters to the extent that it is thought to have originated as the core remnant of a disrupted dwarf galaxy. Observation history In 150 AD, Greco-Roman writer and astronomer Ptolemy catalogued this object in his ''Almagest'' as a star on the horse's back, "Quae est in principio scapulae". German cartographer Johann Bayer used Ptolemy's data to designate this object "Omega Centauri" with his 1603 publication of ''Uranometria''. Usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoceros Ring
The Monoceros Ring ''(monoceros: Greek for 'unicorn')'' is a long, complex, ring of stars that wraps around the Milky Way three times. This is proposed to consist of a stellar stream torn from the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy by tidal forces as part of the process of merging with the Milky Way over a period of billions of years, although this view has long been disputed. The ring contains 100 million solar masses and is 200,000 light years long. The stream of stars was first reported in 2002 by astronomers conducting the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. In the course of investigating this ring of stars, and a closely spaced group of globular clusters similar to those associated with the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy, they discovered the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy. Dispute In 2006, a study using 2MASS data cast doubts on the nature of the "Ring", arguing that the data suggests that the ring is actually part of the warped galactic disc of the Milky Way. However, observations using the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Of Streams
The Field of Streams is a patch of sky where several stellar streams are visible and crisscross. It was discovered by Vasily Belokurov and Daniel Zucker's team in 2006 by analyzing the Sloan Digital Sky Survey II (SDSS-II) data. The team named the area ''Field of Streams'' because of so many crisscrossing trails of stars. The Sagittarius Stream of the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (SagDEG) dominates the ''Field''. It has a split trail within the area of the Field of Streams, because SagDEG has wrapped around the Milky Way Galaxy multiple times, which has resulted in overlapping trails. The forking of the trail has made it possible to infer the organization of dark matter in the inner halo of the Milky Way Galaxy, resulting in the determination that it is distributed in a round spherical manner, as opposed to the expected flattened spheroid. The shape of the streams also implies that the dark matter is very cold, due to the thin trails, and persisting existence. Also appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Halo
A galactic halo is an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy which extends beyond the main, visible component. Several distinct components of galaxies comprise the halo: * the stellar halo * the galactic corona (hot gas, i.e. a plasma) * the dark matter halo The distinction between the halo and the main body of the galaxy is clearest in spiral galaxies, where the spherical shape of the halo contrasts with the flat disc. In an elliptical galaxy, there is no sharp transition between the other components of the galaxy and the halo. A halo can be studied by observing its effect on the passage of light from distant bright objects like quasars that are in line of sight beyond the galaxy in question. Components of the galactic halo Stellar halo The stellar halo is a nearly spherical population of field stars and globular clusters. It surrounds most disk galaxies as well as some elliptical galaxies of type cD. A low amount (about one percent) of a galaxy's stellar mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thick Disk
The thick disk is one of the structural components of about 2/3 of all disk galaxies, including the Milky Way. It was discovered first in external edge-on galaxies. Soon after, it was proposed as a unique galactic structure in the Milky Way, different from the thin disk and the halo in the 1983 article by Gilmore & Reid. It is supposed to dominate the stellar number density between above the galactic plane and, in the solar neighborhood, is composed almost exclusively of older stars. Its stellar chemistry and stellar kinematics (composition and motion of it stars) are also said to set it apart from the thin disk. Compared to the thin disk, thick disk stars typically have significantly lower levels of metals—that is, the abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium. The thick disk is a source of early kinematic and chemical evidence for a galaxy's composition and thus is regarded as a very significant component for understanding galaxy formation. With the availabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Disk
The thin disk is a structural component of spiral and S0-type galaxies, composed of stars, gas and dust. It is the main non-centre (e.g. galactic bulge) density, of such matter. That of the Milky Way is thought to have a scale height of around in the vertical axis perpendicular to the disk, and a scale length of around in the horizontal axis, in the direction of the radius. For comparison, the Sun is out from the center. The thin disk contributes about 85% of the stars in the Galactic plane and 95% of the total disk stars. It can be set apart from the thick disk of a galaxy since the latter is composed of older population stars created at an earlier stage of the galaxy formation and thus has fewer heavy elements. Stars in the thin disk, on the other hand, are created as a result of gas accretion at the later stages of a galaxy formation and are on average more metal-rich. The thin disk contains stars with a wide range of ages and may be divided into a series of sub-populations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as a convenient short term for ''"all elements except hydrogen and helium"''. This word-use is distinct from the conventional chemical or physical definition of a metal as an electrically conducting solid. Stars and nebulae with relatively high abundances of heavier elements are called "metal-rich" in astrophysical terms, even though many of those elements are nonmetals in chemistry. The presence of heavier elements hails from stellar nucleosynthesis, where the majority of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium in the Universe (''metals'', hereafter) are formed in the cores of stars as they evolve. Over time, stellar winds and supernovae deposit the metals into the surrounding environment, enriching the interstellar medium and providing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * circular orbit: ''e'' = 0 * elliptic orbit: 0 < ''e'' < 1 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



-blank.png)
