|
Gadabuursi Script
The Gadabuursi alphabet, also known as the Borama alphabet (Borama: ), at is an alphabetic script for the Somali language. It was devised around 1933 by of the Gadabuursi clan. History [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
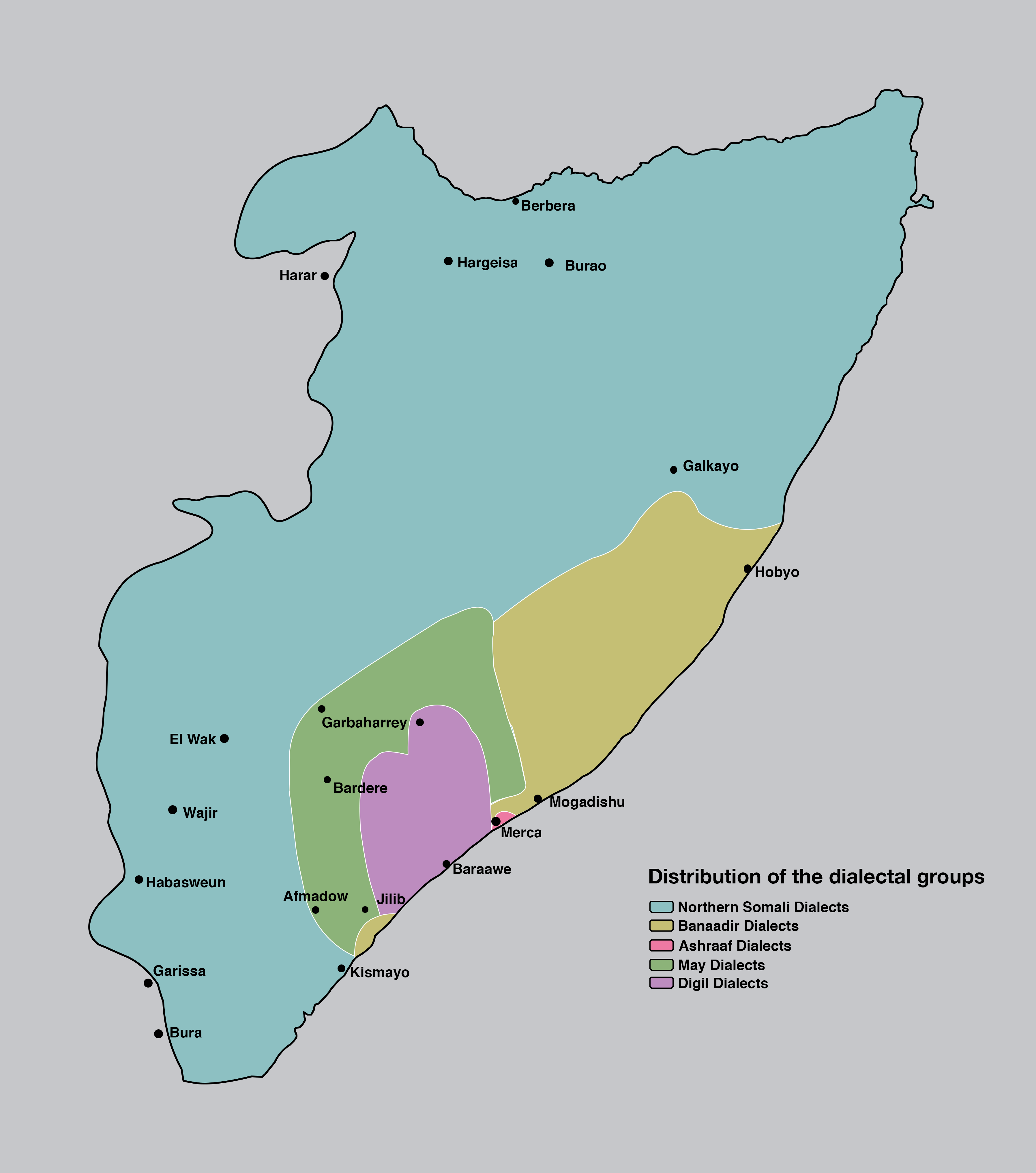
Somali Language
Somali (Latin script: ; Wadaad writing, Wadaad: ; Osmanya: ππ ππππππ ) is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch. It is spoken as a mother tongue by Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora. Somali is an official language in Somalia and Ethiopia, and a national language in Djibouti as well as in northeastern Kenya. The Somali language is written officially with the Somali Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet although the Arabic alphabet and several Somali scripts like Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and the Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama script are informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134β156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of verses (pl.: , sing.: , cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final prophet, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine messages starting with those revealed to Adam, including the Torah, the Psalms and the Gospel. The word ''Quran'' occurs so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaddare Script
The Kaddare alphabet is a writing script created to transcribe Somali, a Cushitic language in the Afroasiatic language family. History The orthography was invented in 1952 by a Sufi Sheikh, named Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare. A phonetically robust writing system, the technical commissions that appraised the Kaddare script concurred that it was a very accurate orthography for transcribing Somali. Form The Kaddare script uses both upper and lower case letters, with the lower case represented in cursive. Many characters are transcribed without having to lift the pen. Several of Kaddare's letters are similar to those in the Osmanya script, while others bear a resemblance to Brahmi. As there are no dedicated characters for long vowels, a vowel is made long by simply writing it twice. See also *Somali orthography *Borama *Osmanya The Osmanya script ( so, Farta Cismaanya πππππ ππππππππ), also known as Far Soomaali (πππ πππ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadabuursi Somali Script
The Gadabuursi script also known as the Borama alphabet (Borama: ), is a writing script for the Somali language. It was devised around 1933 by Sheikh Abdurahman Sh. Nur of the Gadabuursi clan. History Though not as widely known as Osmanya, the other major orthography for transcribing Somali, Borama has produced a notable body of literature mainly consisting of qasidas.I.M. Lewis (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134β156. A quite accurate phonetic writing system, the Borama script was principally used by Nuur and his circle of associates in his native city of Borama. See also * Kaddare *Osmanya *Somali orthography Notes References *I.M. Lewis (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmanya Script
The Osmanya script ( so, Farta Cismaanya πππππ ππππππππ), also known as Far Soomaali (πππ ππππππ, "Somali writing") and, in Arabic, as ''al-kitΔbah al-ΚΏuthmΔnΔ«yah'' (Ψ§ΩΩΨͺΨ§Ψ¨Ψ© Ψ§ΩΨΉΨ«Ω Ψ§ΩΩΨ©; "Osman writing"), is a writing script created to transcribe the Somali language. It was invented between 1920 and 1922 by Osman Yusuf Kenadid, the son of Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid and brother of Sultan Ali Yusuf Kenadid of the Sultanate of Hobyo. History While Osmanya gained reasonably wide acceptance in Somalia and quickly produced a considerable body of literature, it proved difficult to spread among the population mainly due to stiff competition from the long-established Arabic script as well as the emerging Somali Latin alphabet developed by a number of leading scholars of Somali, including Musa Haji Ismail Galal, B. W. Andrzejewski and Shire Jama Ahmed. As nationalist sentiments grew and since the Somali l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadaad's Writing
''Wadaad'' writing, also known as ''Wadaad'' Arabic ( so, Far Wadaad), is the traditional Somali adaptation of written Arabic, as well as the Arabic script as historically used to transcribe the Somali language.Lewis, p.139-140 Originally, it referred to an ungrammatical Arabic featuring some words in Somali, with the proportion of Somali vocabulary terms varying depending on the context. Alongside standard Arabic, ''wadaad'' writing was used by Somali religious men ''(wadaado)'' to record ''xeer'' (customary law) petitions and to write ''qasidas.''Singh, p.59 It was also used by merchants for business and letter writing. Over the years, various Somali scholars improved and altered the use of the Arabic script for conveying Somali. This culminated in the 1950s with the Galal alphabet, which substantially modified letter values and introduced new letters for vowels. History The Arabic script was introduced to Somalia in the 13th century by Sheikh Yusuf bin Ahmad al-Kawneyn (colloq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somali Orthography
A number of writing systems have been used to transcribe the Somali language. Of these, the Somali Latin alphabet is the most widely used. It has been the official writing script in Somalia since the Supreme Revolutionary Council (Somalia), Supreme Revolutionary Council formally introduced it in October 1972, and was disseminated through a nationwide Somali Rural Literacy Campaign, rural literacy campaign. Prior to the twentieth century, the Arabic script was used for writing Somali. An extensive literary and administrative corpus exists in Arabic script. It was the main script historically used by the various Somali sultans to keep records. Writing systems developed locally in the twentieth century include the Osmanya alphabet, Osmanya, Borama alphabet, Borama and Kaddare alphabet, Kaddare scripts. Latin script The Somali Latin script, or Somali Latin alphabet, was developed by a number of leading scholars of Somali language, Somali, including Musa Haji Ismail Galal, B. W. And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaddare Alphabet
The Kaddare alphabet is a writing script created to transcribe Somali, a Cushitic language in the Afroasiatic language family. History The orthography was invented in 1952 by a Sufi Sheikh, named Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare. A phonetically robust writing system, the technical commissions that appraised the Kaddare script concurred that it was a very accurate orthography for transcribing Somali. Form The Kaddare script uses both upper and lower case letters, with the lower case represented in cursive. Many characters are transcribed without having to lift the pen. Several of Kaddare's letters are similar to those in the Osmanya script, while others bear a resemblance to Brahmi. As there are no dedicated characters for long vowels, a vowel is made long by simply writing it twice. See also *Somali orthography *Borama *Osmanya The Osmanya script ( so, Farta Cismaanya πππππ ππππππππ), also known as Far Soomaali (πππ πππ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Writing Systems
This is a list of writing systems (or scripts), classified according to some common distinguishing features. The usual name of the script is given first; the name of the language(s) in which the script is written follows (in brackets), particularly in the case where the language name differs from the script name. Other informative or qualifying annotations for the script may also be provided. Pictographic/ideographic writing systems Ideographic scripts (in which graphemes are ideograms representing concepts or ideas, rather than a specific word in a language), and pictographic scripts (in which the graphemes are iconic pictures) are not thought to be able to express all that can be communicated by language, as argued by the linguists John DeFrancis and J. Marshall Unger. Essentially, they postulate that no ''full'' writing system can be completely pictographic or ideographic; it must be able to refer directly to a language in order to have the full expressive capacity of a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cushitic Languages
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2012, the Cushitic languages with over one million speakers were Oromo, Somali, Beja, Afar, Hadiyya, Kambaata, Saho, and Sidama. Official status The Cushitic languages with the greatest number of total speakers are Oromo (37 million), Somali (22 million), Beja (3.2 million), Sidamo (3 million), and Afar (2 million). Oromo serves as one of the official working languages of Ethiopia and is also the working language of several of the states within the Ethiopian federal system including Oromia, Harari and Dire Dawa regional states and of the Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region. Somali is the first of two official languages of Somalia and three official languages of the self declared republic of Somaliland. It also serves as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Asiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic subregions of Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara/Sahel. With the exception of its Semitic branch, all branches of the Afroasiatic family are exclusively native to the African continent. Afroasiatic languages have over 500 million native speakers, which is the fourth-largest number of native speakers of any language family (after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and NigerβCongo). The phylum has six branches: Berber languages, Berber, Chadic languages, Chadic, Cushitic languages, Cushitic, Egyptian language, Egyptian, Semitic languages, Semitic, and Omotic languages, Omotic. The most widely spoken modern Afroasiatic language or dialect continuum by far is Arabic, a ''de facto'' group of Varieties of Arabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadi
A qΔαΈΔ« ( ar, ΩΨ§ΨΆΩ, QΔαΈΔ«; otherwise transliterated as qazi, cadi, kadi, or kazi) is the magistrate or judge of a '' sharΔ«ΚΏa'' court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works. History The term ''qΔαΈΔ«'' was in use from the time of Muhammad during the early history of Islam, and remained the term used for judges throughout Islamic history and the period of the caliphates. While the '' muftΔ«'' and '' fuqaha'' played the role in elucidation of the principles of Islamic jurisprudence (''UαΉ£Ε«l al-Fiqh'') and the Islamic law (''sharΔ«ΚΏa''), the ''qΔαΈΔ«'' remained the key person ensuring the establishment of justice on the basis of these very laws and rules. Thus, the ''qΔαΈΔ«'' was chosen from amongst those who had mastered the sciences of jurisprudence and law. The Abbasid caliphs created the office of "chief ''qΔαΈΔ«''" (''qΔαΈΔ« al-quαΈΔh''), who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |