|
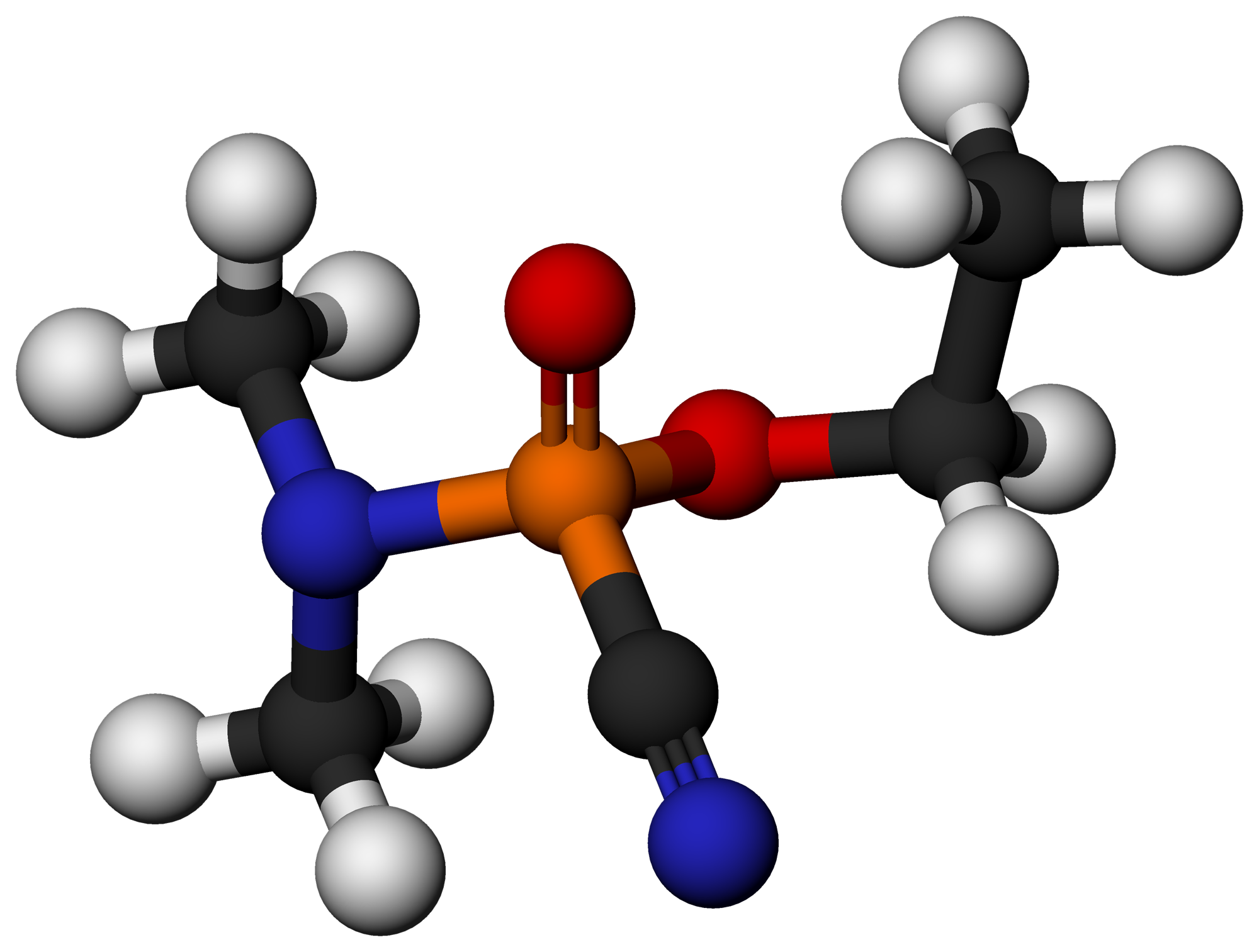
GV (nerve Agent)
GV (IUPAC name: 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl ''N'',''N''-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate) is an organophosphate nerve agent. GV is a part of a new series of nerve agents with properties similar to both the "G-series" and "V-series". It is a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with properties similar to other nerve agents, being a highly poisonous vapour. Treatment for poisoning with GV involves drugs such as atropine, benactyzine, obidoxime, and HI-6. See also * Fluorotabun *Methylfluorophosphonylcholine Methylfluorophosphonylcholine (MFPCh) is an extremely toxic chemical compound related to the G-series nerve agents. It is an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which is around 100 times more potent than sarin at inhibiting acetylchol ... * VG (nerve agent) References External links * * Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Dimethylamino compounds Phosphorofluoridates G-series nerve agents {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product physica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nerve agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to such agents wear a full body suit in addition to a respirato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
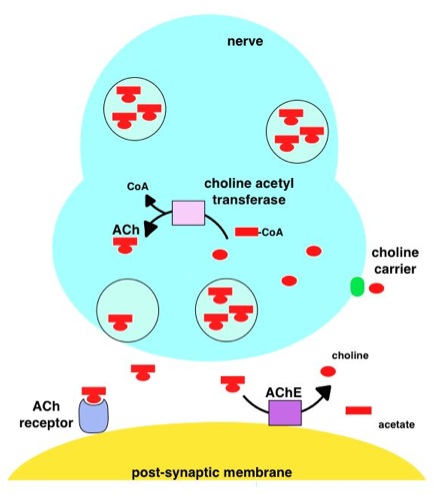
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ... that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings. Common side effects include a dry mouth, large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with angle closure glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, that has not been well studied. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system. Atropine occurs n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benactyzine
Benactyzine is an anticholinergic drug that was used as an antidepressant in the treatment of depression and associated anxiety before it was pulled from the U.S. market by the FDA due to its ineffectiveness. Its use for these indications was limited by side effects such as dry mouth and nausea, and at high doses it can cause more severe symptoms such as deliriant and hallucinogenic effects. "Large doses of benactyzine in normal subjects may produce a state resembling the action of mescaline or LSD." Brand names have included: Suavitil, Phebex, Phobex, Cedad, Cevanol, Deprol, Lucidil, Morcain, Nutinal, Parasan. While there was some tentative evidence of effectiveness when combined with meprobamate Meprobamate—marketed as Miltown by Wallace Laboratories and Equanil by Wyeth, among others—is a carbamate derivative used as an anxiolytic drug. It was the best-selling minor tranquilizer for a time, but has largely been replaced by the be ..., with the medication no longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obidoxime
Obidoxime is a member of the oxime family used to treat nerve gas poisoning. Oximes are drugs known for their ability to reverse the binding of organophosphorus compounds to the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). AChE is an enzyme that removes acetylcholine from the synapse after it creates the required stimulation on the next nerve cell. If it gets inhibited, acetylcholine is not removed after the stimulation and multiple stimulations are made, resulting in muscle contractions and paralysis. Organophosphates (such as nerve gases) are well-known inhibitors of AChE. They bind to a specific place on the enzyme and prevent it from functioning normally by changing the OH group on the serine residue and by protonating (quaternary nitrogen, R4N+) the nearby nitrogen atom located in the histidine residue. Function Oximes such as obidoxime, pralidoxime and asoxime (HI-6) are used to restore enzyme functionality. They have greater affinity for the organic phosphate residue tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HI-6
Asoxime chloride, or more commonly HI-6, is a Hagedorn oxime used in the treatment of organophosphate poisoning Organophosphate poisoning is poisoning due to organophosphates (OPs). Organophosphates are used as insecticides, medications, and nerve agents. Symptoms include increased saliva and tear production, diarrhea, vomiting, small pupils, sweating, mus .... References Cholinesterase reactivators Aldoximes Carboxamides Pyridinium compounds Chlorides {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorotabun
Fluorotabun is a highly toxic organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series. It's the fluorinated analog of tabun, i.e. the cyanide group is replaced by a fluorine atom. GAF is considered an ineffective GA-like agent. It is less effective than GAA. See also *Tabun (nerve agent) *GV (nerve agent) GV (IUPAC name: 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl ''N'',''N''-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate) is an organophosphate nerve agent. GV is a part of a new series of nerve agents with properties similar to both the "G-series" and "V-series". It is a potent ace ... References G-series nerve agents Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Organophosphates Ethyl esters Dimethylamino compounds {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylfluorophosphonylcholine
Methylfluorophosphonylcholine (MFPCh) is an extremely toxic chemical compound related to the G-series nerve agents. It is an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which is around 100 times more potent than sarin at inhibiting acetylcholinesterase ''in vitro'', and around 10 times more potent ''in vivo'', depending on route of administration and animal species tested. MFPCh is resistant to oxime reactivators, meaning the acetylcholinesterase inhibited by MFPCh can't be reactivated by oxime reactivators. MFPCh also acts directly on the acetylcholine receptors. However, despite its high toxicity, methylfluorophosphonylcholine is a relatively unstable compound and degrades rapidly in storage, so it was not deemed suitable to be weaponised for military use.Black RM, Harrison JM. The chemistry of organophosphorus chemical warfare agents. Chapter 10 of The chemistry of organophosphorus compounds. Volume 4, Ter- and quinque-valent phosphorus acids and their derivatives. (1996) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VG (nerve Agent)
VG (IUPAC name: ''O'',''O''-diethyl ''S''- -(diethylamino)ethylphosphorothioate) (also called Amiton or Tetram) is a "V-series" nerve agent chemically similar to the better-known VX nerve agent. Tetram is the common Russian name for the substance. Amiton was the trade name for the substance when it was marketed as an insecticide by ICI in the mid-1950s. Chemical With a toxicity of about 1/10 that of VX, i.e. similar to that of sarin, it is now considered too dangerous for use in agriculture but unlike other nerve agents it is classified under Schedule 2 of the Chemical Weapons Convention rather than the more restrictive Schedule 1. It is thought that North Korea may have military stockpiles of this chemical . During the early 1950s at least three chemical companies working on organo-phosphorus insecticides independently discovered the severe toxicity of these chemicals. In 1952, Dr. Ranajit Ghosh, a chemist working for ICI at their Plant Protection Laboratories at Jealot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |