|
GSK-189,254
GSK-189,254 is a potent and selective H3 histamine receptor inverse agonist developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It has subnanomolar affinity for the H3 receptor ( Ki = 0.2nM) and selectivity of over 10,000x for H3 over other histamine receptor subtypes. Animal studies have shown it to possess not only stimulant and nootropic effects, but also analgesic action suggesting a role for H3 receptors in pain processing in the spinal cord. GSK-189,254 and several other related drugs are currently being investigated as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, as well as possible use in the treatment of conditions such as narcolepsy, or neuropathic pain Neuropathic pain is pain caused by damage or disease affecting the somatosensory system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuous ... which do not respond well to conventional analgesic drugs. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine H3 Receptor
Histamine H3 receptors are expressed in the central nervous system and to a lesser extent the peripheral nervous system, where they act as autoreceptors in presynaptic histaminergic neurons and control histamine turnover by feedback inhibition of histamine synthesis and release. The H3 receptor has also been shown to presynaptically inhibit the release of a number of other neurotransmitters (i.e. it acts as an inhibitory heteroreceptor) including, but probably not limited to dopamine, Gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABA, acetylcholine, noradrenaline, histamine and serotonin. The gene sequence for H3 receptors expresses only about 22% and 20% homology with both H1 and H2 receptors respectively. There is much interest in the histamine H3 receptor as a potential therapeutic target because of its involvement in the neuronal mechanism behind many cognitive disorders and especially its location in the central nervous system.Rapanelli, Maximiliano. “The Magnificent Two: Histamine and the H3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by damage or disease affecting the somatosensory system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuous and/or episodic (paroxysmal) components. The latter resemble stabbings or electric shocks. Common qualities include burning or coldness, "pins and needles" sensations, numbness and itching. Up to 7%-8% of the European population is affected, and in 5% of persons it may be severe. Neuropathic pain may result from disorders of the peripheral nervous system or the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Thus, neuropathic pain may be divided into peripheral neuropathic pain, central neuropathic pain, or mixed (peripheral and central) neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain may occur in isolation or in combination with other forms of pain. Medical treatments focus on identifying the underlying cause and relieving pain. In cases of neuropathy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootropics
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3 Receptor Antagonists
H3, H03 or H-3 may refer to: Entertainment * ''Happy Hustle High'', a manga series by Rie Takada, originally titled "H3 School!" * H3 (film), ''H3'' (film), a 2001 film about the 1981 Irish hunger strike * h3h3Productions, styled "[h3]", a satirical YouTube channel Science * Triatomic hydrogen (H3), an unstable molecule * Trihydrogen cation (H3+), one of the most abundant ions in the universe * Tritium (Hydrogen-3, or H-3), an isotope of hydrogen * ATC code H03 ''Thyroid therapy'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * British NVC community H3, a heath community of the British National Vegetation Classification system * Histamine H3 receptor, Histamine H3 receptor, a human gene * Histone H3, a component of DNA higher structure in eukaryotic cells * *h3, , one of the three laryngeals in the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language * Hekla 3 eruption, a huge volcanic eruption around 1000 BC Computing * , the level-3 HTML element#heading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSK Plc Brands , a rendering pipeline
{{disambiguation ...
GSK may refer to: * Galatasaray S.K., a Turkish sports club based in Istanbul * Glycogen synthase kinase * Golden State Killer, a California serial rapist and murderer * GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline, a multinational pharmaceutical corporation * GTK Scene Graph Kit GTK Scene Graph Kit (GSK) is the rendering and scene graph API for GTK introduced with version 3.90. GSK lies between the graphical control elements (widgets) and the rendering. Like GDK, GSK is part of GTK and licensed under the GNU Lesser Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a long-term neurological disorder that involves a decreased ability to regulate sleep–wake cycles. Symptoms often include periods of excessive daytime sleepiness and brief involuntary sleep episodes. About 70% of those affected also experience episodes of sudden loss of muscle strength, known as cataplexy. Narcolepsy paired with cataplexy is evidenced to be an autoimmune disorder. These experiences of cataplexy can be brought on by strong emotions. Less commonly, there may be vivid hallucinations or an inability to move (sleep paralysis) while falling asleep or waking up. People with narcolepsy tend to sleep about the same number of hours per day as people without, but the quality of sleep tends to be lessened. Narcolepsy is a clinical syndrome of hypothalamic disorder, however, the exact cause of narcolepsy is unknown, with potentially several causes. In up to 10% of cases, there is a family history of the disorder. Often, those affected have low levels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
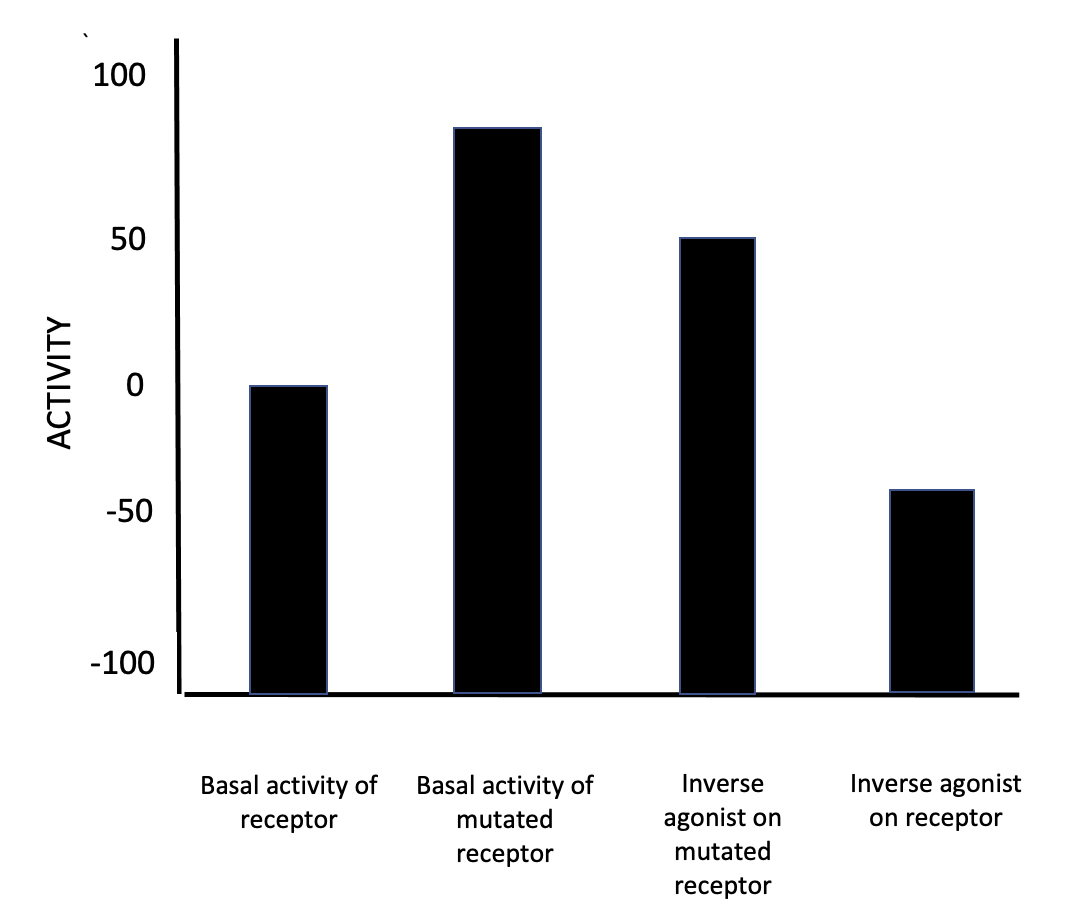
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affects a person's ability to function and carry out everyday activities. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Consciousness is not affected. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning, and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging. Several diseases and injuries to the brain, such as a stroke, can give rise to dementia. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |