|
GR 8 (galaxy)
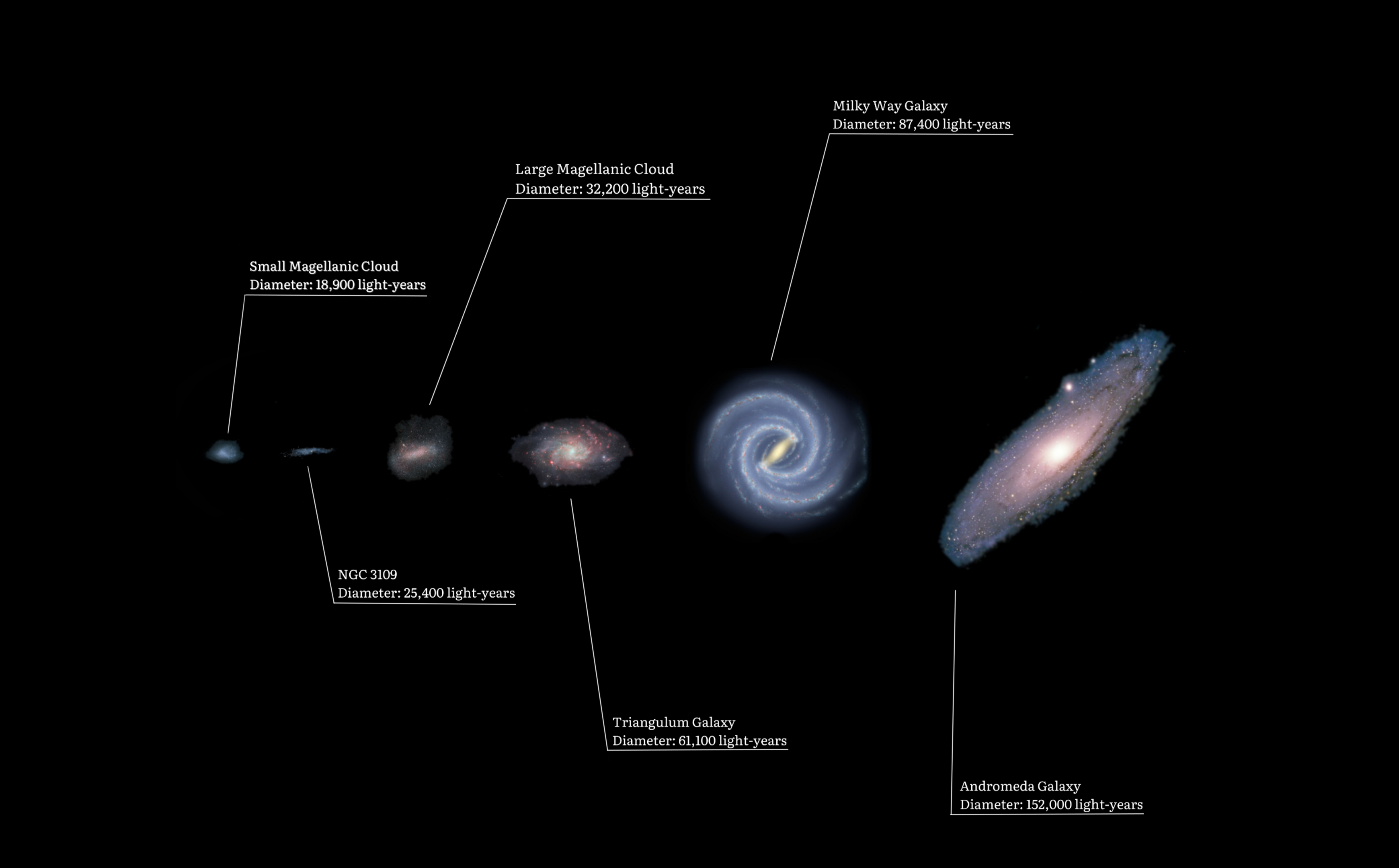
GR 8 (also known as UGC 8091) is a gas-rich dwarf irregular galaxy. In 1995, Tolstoy et al. estimated its distance (with the Hipparcos correction of 1997 applied) to be approximately from Earth. It is around 2.8 Mly from UGC 9128. It is still an open question whether it is a member of the Local Group or possibly the Virgo Cluster. GR 8 was discovered at the Lick Observatory The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The observatory is managed by th ... using the 20-inch astrograph in either 1946, 1947, or 1951. References External links Irregular Galaxy GR 8: Footprint Galaxy{{Virgo Dwarf irregular galaxies Virgo (constellation) 08091 44491 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Irregular Galaxies
An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a Spiral galaxy, spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a bulge (astronomy), nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure. Collectively they are thought to make up about a quarter of all galaxies. Some irregular galaxies were once spiral or elliptical galaxies but were deformed by an uneven external gravitational force. Irregular galaxies may contain abundant amounts of gas and dust. This is not necessarily true for dwarf irregulars. Irregular galaxies are commonly small, about one tenth the mass of the Milky Way galaxy. Due to their small sizes, they are prone to environmental effects like crashing with large galaxies and intergalactic clouds. Types There are three major types of irregular galaxies: * An Irr-I galaxy (Irr I) is an irregular galaxy that f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrograph
An astrograph (or astrographic camera) is a telescope designed for the sole purpose of astrophotography. Astrographs are mostly used in wide-field astronomical surveys of the sky and for detection of objects such as asteroids, meteors, and comets. Improvements in photography in the middle 19th century led to designs dedicated to astrophotography, and they were also popular in the 20th century. As in other photography, chemicals were used that respond to light, recorded on a glass photographic plate or sometimes on photographic film. Many observatories of this period used an astrograph, beside instruments like the transit telescope, great refractors, and chronometers, or instruments for observing the Sun. Astrographs were often used to make surveys of the night sky, and one of the famous projects was Carte du Ciel. Discoveries using an astrograph include then-planet Pluto. Rather than looking through the telescope, it was discovered by using a blink comparator with im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lick Observatory
The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The observatory is managed by the University of California Observatories, with headquarters on the University of California, Santa Cruz campus, where its scientific staff moved in the mid-1960s. It is named after James Lick. The first new moon of Jupiter to be identified since the time of Galileo was discovered at this observatory; Amalthea, the planet's fifth moon, was discovered at this observatory in 1892. Early history Lick Observatory is the world's first permanently occupied mountain-top observatory. The observatory, in a Classical Revival style structure, was constructed between 1876 and 1887, from a bequest from James Lick of $700,000, . Lick, originally a carpenter and piano maker, had arrived from Peru in San Francisco, California, in late 1847; after ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a large cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Virgo Supercluster, of which the Local Group (containing our Milky Way galaxy) is a member. The Local Group actually experiences the mass of the Virgo Supercluster as the Virgocentric flow. It is estimated that the Virgo Cluster's mass is 1.2 out to 8 degrees of the cluster's center or a radius of about 2.2 Mpc. Many of the brighter galaxies in this cluster, including the giant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, were discovered in the late 1770s and early 1780s and subsequently included in Charles Messier's catalogue of non-cometary fuzzy objects. Described by Messier as nebulae without stars, their true nature was not recognized until the 1920s. The cluster subtends a maximum arc of approximately 8 degrees centered in the constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, NGC 185, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UGC 9128
UGC 9128 is a dwarf irregular galaxy around 6.8–7.8 Mly (2.1–2.4 Mpc MPC, Mpc or mpc may refer to: Astronomy * Megaparsec (Mpc), unit of length used in astronomy * Minor Planet Center, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory ** ''Minor Planet Circulars'' (MPC, M.P.C. or MPCs), astronomical publication from the Minor ...) away; it is thought to be in the Local Group, although its membership is not certain. The galaxy has a mass of about , around 100 million stars, and a diameter of around 3300 ly. It is therefore quite faint, and so was only discovered in the 20th century. UGC 9128 is around 2.7 Mly from GR 8, which is its nearest neighbour. UGC 9128 is a starburst galaxy, with the peak of star formation being 20–100 million years ago. It is thought to have both a halo and disc. References Dwarf irregular galaxies Boötes 09128 50961 {{galaxy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |