|
GOES-15
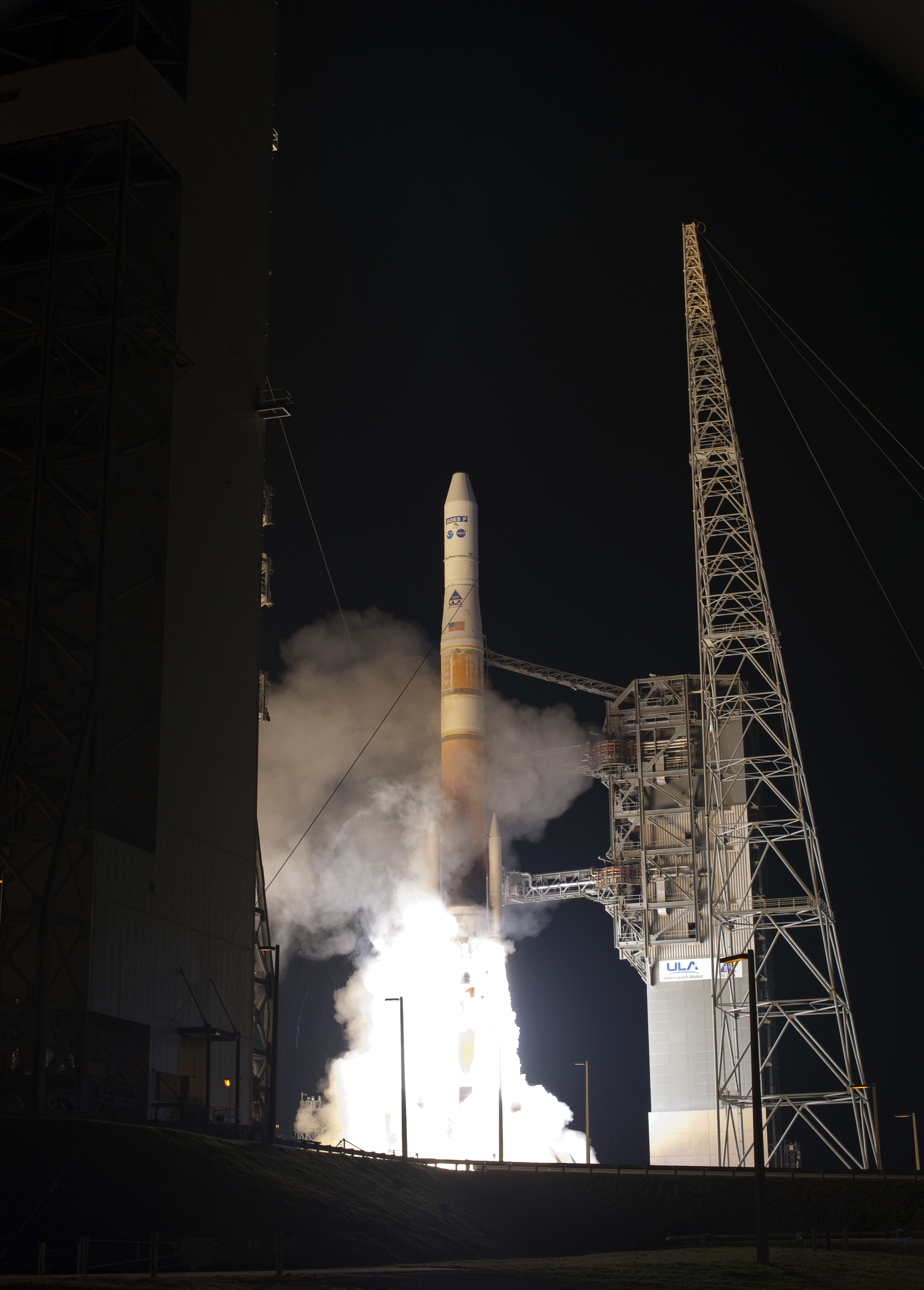
GOES-15, previously known as GOES-P, is an American weather satellite, which forms part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The spacecraft was constructed by Boeing, and is the last of three GOES satellites to be based on the BSS-601 bus. It was launched in 2010, while the other BSS-601 GOES satellites -- GOES-13 and GOES-14—were launched in May 2006 and June 2009 respectively. It was the sixteenth GOES satellite to be launched. Launch GOES-15 was launched atop a Delta IV-M+(4,2) rocket flying from Space Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 23:57 UTC on 4 March 2010, forty minutes into a sixty-minute launch window. Upon reaching geostationary orbit on 16 March, it was redesignated GOES-15. On 6 December 2011, it was activated as the GOES-West satellite, replacing GOES-11. Design At launch, the mass of the satellite was . It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GOES-P Launched By Delta IV Rocket
GOES-15, previously known as GOES-P, is an American weather satellite, which forms part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The spacecraft was constructed by Boeing, and is the last of three GOES satellites to be based on the BSS-601 bus. It was launched in 2010, while the other BSS-601 GOES satellites -- GOES-13 and GOES-14—were launched in May 2006 and June 2009 respectively. It was the sixteenth GOES satellite to be launched. Launch GOES-15 was launched atop a Delta IV-M+(4,2) rocket flying from Space Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 23:57 UTC on 4 March 2010, forty minutes into a sixty-minute launch window. Upon reaching geostationary orbit on 16 March, it was redesignated GOES-15. On 6 December 2011, it was activated as the GOES-West satellite, replacing GOES-11. Design At launch, the mass of the satellite was . It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GOES-15
GOES-15, previously known as GOES-P, is an American weather satellite, which forms part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The spacecraft was constructed by Boeing, and is the last of three GOES satellites to be based on the BSS-601 bus. It was launched in 2010, while the other BSS-601 GOES satellites -- GOES-13 and GOES-14—were launched in May 2006 and June 2009 respectively. It was the sixteenth GOES satellite to be launched. Launch GOES-15 was launched atop a Delta IV-M+(4,2) rocket flying from Space Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 23:57 UTC on 4 March 2010, forty minutes into a sixty-minute launch window. Upon reaching geostationary orbit on 16 March, it was redesignated GOES-15. On 6 December 2011, it was activated as the GOES-West satellite, replacing GOES-11. Design At launch, the mass of the satellite was . It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GOES-17
GOES-17 (designated pre-launch as GOES-S) is an environmental satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The satellite is second in the four-satellite GOES-R series (GOES-16, -17, - T, and - U). GOES-17 supports the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system, providing multi-spectral imaging for weather forecasts and meteorological and environmental research. The satellite was built by Lockheed Martin, based on the A2100A platform, and expected to have a useful life of 15 years (10 years operational after five years of standby as an on-orbit replacement). GOES-17 is intended to deliver high-resolution visible and infrared imagery and lightning observations of more than half the globe. The satellite was launched on 1 March 2018 and reached geostationary orbit on 12 March 2018. In May 2018, during the satellite's testing phase after launch, a problem was discovered with its primary instrument, the Advanced Baseline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service division, supports weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorology research. Spacecraft and ground-based elements of the system work together to provide a continuous stream of environmental data. The National Weather Service (NWS) and the Meteorological Service of Canada use the GOES system for their North American weather monitoring and forecasting operations, and scientific researchers use the data to better understand land, atmosphere, ocean, and climate dynamics. The GOES system uses geosynchronous equatorial satellites that, since the launch of SMS-1 in 1974, have been a basic element of U.S. weather monitoring and forecasting. The procurement, design, and manufacture of GOES satellites is overseen by NASA. NOAA is the official provider of both GOES ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on weather are monitored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GOES 11
GOES-11, known as GOES-L before becoming operational, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched in 2000, and operated at the GOES-WEST position, providing coverage of the west coast of the United States, until December 6, 2011. Launch GOES-L was launched aboard an International Launch Services Atlas IIA rocket, flying from Space Launch Complex 36A at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 07:07 UTC on 3 May. The launch was originally scheduled for 15 March 1999, however it was delayed to allow the Eutelsat W3 satellite to be launched first. Following this, it was rescheduled for 15 May. On 30 April, the Centaur upper stage of a Titan IV(401)B failed during the launch of USA-143. Since a version of the Centaur was also used on the Atlas II, the launch of GOES-L was delayed a week to ensure that the same problem woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on weather are monitored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GOES 14
GOES-14, known as GOES-O prior to reaching its operational orbit, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system. The spacecraft was built by Boeing and is based on the BSS-601 bus. It is the second of three GOES satellites to use the BSS-601 bus, after GOES-13, which was launched in May 2006. It was launched by United Launch Alliance aboard a Delta IV-M+(4,2) rocket at 22:51 UTC on 27 June 2009, from Space Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Upon reaching geostationary orbit, on 7 July, it was redesignated GOES-14. It underwent a 6-month series of post-launch tests before completing its "check-out" phase and then was placed into "orbital storage mode" or stand-by. Its first full disk image was sent on 27 July 2009 GOES-14 was brought out of storage and began one-minute rapid scans of Tropical Storm Isaac on 24 August 2012. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSS-601
The Boeing 601 (sometimes referred to as the BSS-601, and previously as the HS-601) is a communications satellite bus designed in 1985 and introduced in 1987 by Hughes Space and Communications Company. The series was extremely popular in the 1990s, with more than 84 purchased by customers globally. The more advanced 601HP derivative (for "high power") was introduced in 1995. Hughes, and the 601 platforms, were acquired by Boeing in 2000. The last commercial 601 satellite was ordered in 2001 and launched in 2004. The NASA Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) Program Office in December 2007 selected the BSS-601HP for its third generation TDRS spacecraft, adding the two 15-foot (4.5m) diameter steerable antennas. The TDRS-M satellite, launched on August 18, 2017, became the last 601 satellite to reach orbit. Background The Boeing-601 model was Hughes’ first major design and development for a communications satellite with three-axis, or body stabilization. All previous Hug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
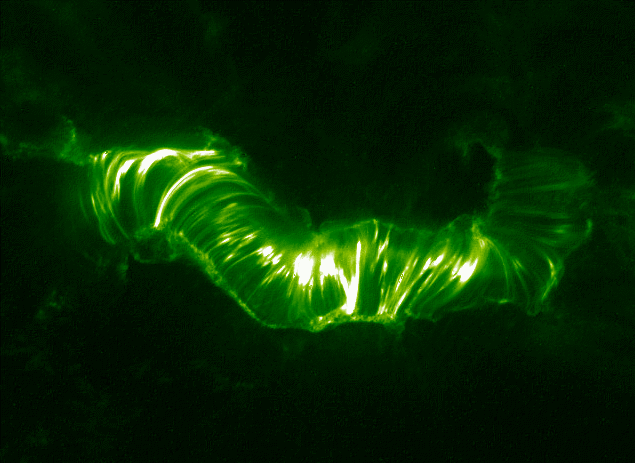
Solar Flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ''stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASAspaceflight
''NASASpaceflight.com'' is a private news website and forum which launched in 2005, covering crewed and uncrewed spaceflight and aerospace engineering news. Its original reporting has been referenced by various news outlets on spaceflight-specific news, such as MSNBC, USA Today and ''The New York Times'' among others. NASASpaceflight also produces videos and live streams of rocket launches online, with a special focus on developments at SpaceX's Starbase facility, for which they were recognized with an award by SpaceNews. NSF is owned and operated by managing editor Chris Bergin and content is produced by a team of spaceflight reporters, journalists, contributors, editors, photographers, and videographers across the United States and other countries. NASASpaceflight and NASASpaceflight.com are not affliated with NASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii (also the last ones admitted to the Union), and all other offshore insular areas, such as American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The colloquial term "Lower48" is used also, especially in relation to just Alaska (Hawaii is farther south). The related but distinct term continental United States includes Alaska (which is also on the continent of North America but separated from the 48 states by British Columbia and Yukon of Canada), but excludes the Hawaiian Islands and all U.S. territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific. The greatest distance (on a great-circle route) entirely within the contiguous U.S. is 2,802 miles (4,509 km), between Florida and the State of Washington; th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)