|
GNOME Dictionary
GNOME Dictionary, also called gnome-dictionary, is a DICT client written in C by Emmanuele Bassi and others. It is part of the free software GNOME desktop suite. It allows users to look up words in various dictionary sources. gnome-dictionary was at first an independent DICT protocol client called gdict, created by Bradford Hovinen, Spiros Papadimitriou and Mike Hughes; it was included inside the gnome-utils meta-package during the 1.x release cycle. As a companion to the original application was also added an applet for gnome-panel. After the 2.0 release of GNOME, due to lack of direct maintainership, the code base of gdict passed the point of being maintainable. In October 2005, the current maintainer of gnome-dictionary Emmanuele Bassi decided to rewrite the application and applet from scratch, removing the old (and mostly deprecated) code. The new gnome-dictionary was added to GNOME during the 2.13 development cycle and became part of the 2.14 GNOME release. It supports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
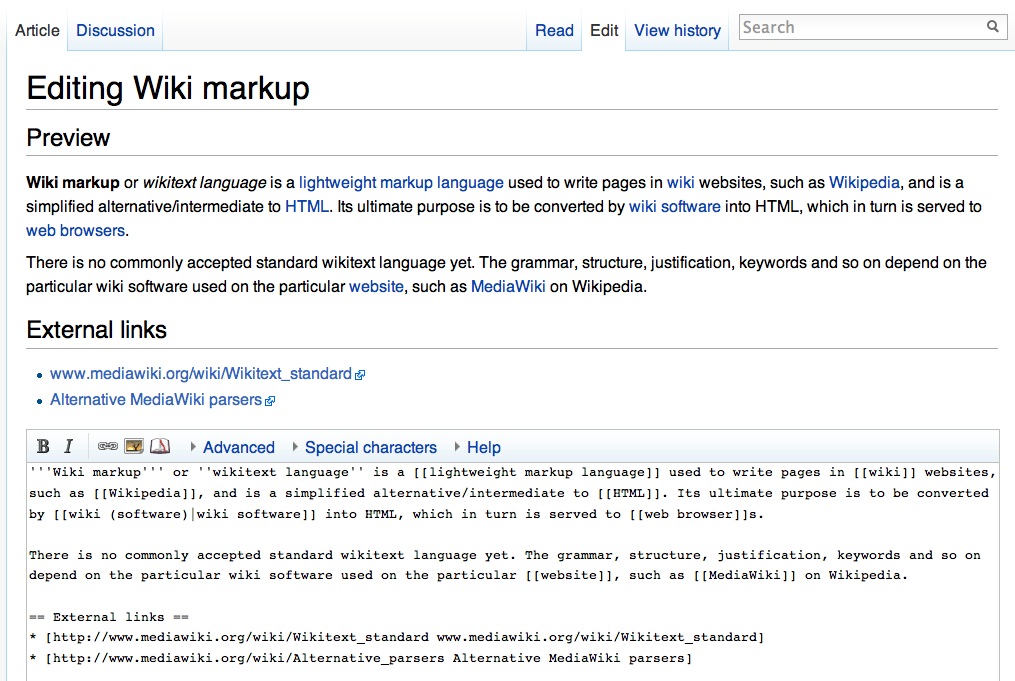
Wiki
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnome-panel
GNOME Panel is a highly configurable taskbar for GNOME. It formed a core part of the desktop in GNOME 1 and GNOME 2. It has been replaced in GNOME 3 by default with GNOME Shell, which only works with the Mutter (software), Mutter window manager. There are many ''applets'' for GNOME Panel available in one package called ''gnome-applets'' while some applets included with GNOME Panel as built-in, like a traditional start menu. GNOME Panel served as ''Fallback Mode'' until GNOME 3.8 when Mutter could not be executed, then it was replaced with a suite of officially supported GNOME Shell extensions named ''GNOME Classic''. Now it is part of GNOME Flashback, an official session for GNOME 3 which provides a user experience similar to GNOME 2. In GNOME 3, customizing GNOME Panel is done by pressing the key while right-clicking on the panel. Appearance By default, GNOME Flashback contains two panels (one on the top, and one to its opposite on the bottom) spanning the width of the scree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Software For Linux
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whistl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Dictionary Software
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything * Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism * Emancipate, to procure political rights, as for a disenfranchised group * Free will, control exercised by rational agents over their actions and decisions * Free of charge, also known as gratis. See Gratis vs libre. Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free format, a file format which can be used without restrictions * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment * Freeware, a broader class of software available at no cost Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME Applications
GNOME Core Applications is a software suite of approximately 30 application software that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have the look and feel of the GNOME desktop, and often utilize the Adwaita design language. Some applications have been written from scratch and others are ports. The employment of the newest graphical widgets offered by the latest version of GTK in order to implement the GNOME Human Interface Guidelines (HIG) ergonomically is the only feature which all GNOME Core Applications have in common. Some of the GNOME Core Applications are essential, while several are not, e.g. GNOME Weather. Most are graphical front-ends, e.g. GNOME Software, to underlying Linux system daemons, like e.g. journald, PackageKit, NetworkManager or PulseAudio. Configuration * Settings – main interface to configure various aspects of GNOME. Diverse panels represent graphical front-ends to configure the Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DICT Clients
DICT is a dictionary network protocol created by the DICT Development Group in 1997, described by RFC 2229. Its goal is to surpass the Webster protocol to allow clients to access a variety of dictionaries via a uniform interface. In section 3.2 of the DICT protocol RFC, queries and definitions are sent in clear-text, meaning that there is no encryption. Nevertheless, according to section 3.1 of the RFC, various forms of authentication (sans encryption) are supported, including Kerberos version 4. The protocol consists of a few commands a server must recognize so a client can access the available data and lookup word definitions. DICT servers and clients use TCP port 2628 by default. Queries are captured in the following URL scheme:dict://;@:/:::: Resources for free dictionaries from DICT protocol servers A repository of source files for the DICT Development group's dict protocol server (with a few sample dictionaries) is available online. Dictionaries of English * Bouvier's La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (computer Science)
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often for software development. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets. A library is also a collection of implementations of behavior, written in terms of a language, that has a well-defined interface by which the behavior is invoked. For instance, people who want to write a higher-level program can use a library to make system calls instead of implementing those system calls over and over again. In addition, the behavior is provided for reuse by multiple independent programs. A program invokes the library-provided behavior via a mechanism of the language. For example, in a simple imperative language such as C, the behavior in a library is invoked by using C's normal function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rewrite (programming)
A rewrite in computer programming is the act or result of re-implementing a large portion of existing functionality without re-use of its source code. When the rewrite is not using existing code at all, it is common to speak of a rewrite from scratch. Motivations A piece of software is typically rewritten when one or more of the following apply: *its source code is not available or is only available under an incompatible license *its code cannot be adapted to a new target platform *its existing code has become too difficult to handle and extend *the task of debugging it seems too complicated *the programmer finds it difficult to understand its source code *developers learn new techniques or wish to do a big feature overhaul which requires much change *developers learn that new codes written may extend content options that can fix or overwrite previous problems *the programming language of the source code has to be changed Risks Several software engineers, such as Joel Spolsky ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applet
In computing, an applet is any small application that performs one specific task that runs within the scope of a dedicated widget engine or a larger program, often as a plug-in. The term is frequently used to refer to a Java applet, a program written in the Java programming language that is designed to be placed on a web page. Applets are typical examples of transient and auxiliary applications that don't monopolize the user's attention. Applets are not full-featured application programs, and are intended to be easily accessible. History The word ''applet'' was first used in 1990 in ''PC Magazine''. However, the concept of an applet, or more broadly a small interpreted program downloaded and executed by the user, dates at least to RFC 5 (1969) by Jeff Rulifson, which described the Decode-Encode Language, which was designed to allow remote use of the oN-Line System over ARPANET, by downloading small programs to enhance the interaction. This has been specifically credited as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-like application is one that behaves like the corresponding Unix command or shell. Although there are general philosophies for Unix design, there is no technical standard defining the term, and opinions can differ about the degree to which a particular operating system or application is Unix-like. Some well-known examples of Unix-like operating systems include Linux and BSD. These systems are often used on servers, as well as on personal computers and other devices. Many popular applications, such as the Apache web server and the Bash shell, are also designed to be used on Unix-like systems. One of the key features of Unix-like systems is their ability to support multiple users and processes simultaneously. This allows users to run multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DICT
DICT is a dictionary network protocol created by the DICT Development Group in 1997, described by RFC 2229. Its goal is to surpass the Webster protocol to allow clients to access a variety of dictionaries via a uniform interface. In section 3.2 of the DICT protocol RFC, queries and definitions are sent in clear-text, meaning that there is no encryption. Nevertheless, according to section 3.1 of the RFC, various forms of authentication (sans encryption) are supported, including Kerberos version 4. The protocol consists of a few commands a server must recognize so a client can access the available data and lookup word definitions. DICT servers and clients use TCP port 2628 by default. Queries are captured in the following URL scheme:dict://;@:/:::: Resources for free dictionaries from DICT protocol servers A repository of source files for the DICT Development group's dict protocol server (with a few sample dictionaries) is available online. Dictionaries of English * Bouvier's L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME
A gnome is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, first introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and later adopted by more recent authors including those of modern fantasy literature. Its characteristics have been reinterpreted to suit the needs of various story tellers, but it is typically said to be a small humanoid that lives underground. Diminutive statues of gnomes introduced as lawn ornaments during the 19th century grew in popularity during the 20th century and came to be known as garden gnomes. History Origins The word comes from Renaissance Latin ''gnomus'', which first appears in ''A Book on Nymphs, Sylphs, Pygmies, and Salamanders, and on the Other Spirits'' by Paracelsus, published posthumously in Nysa in 1566 (and again in the Johannes Huser edition of 1589–1591 from an autograph by Paracelsus). The term may be an original invention of Paracelsus, possibly deriving the term from Latin ''gēnomos'' (itself represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |