|
GLRX
Glutaredoxin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GLRX'' gene. Interactions GLRX has been shown to interact with Wilson disease protein Wilson disease protein (WND), also known as ATP7B protein, is a copper-transporting P-type ATPase which is encoded by the ''ATP7B'' gene. The ATP7B protein is located in the trans-Golgi network of the liver and brain and balances the copper leve ... and ATP7A. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-5-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
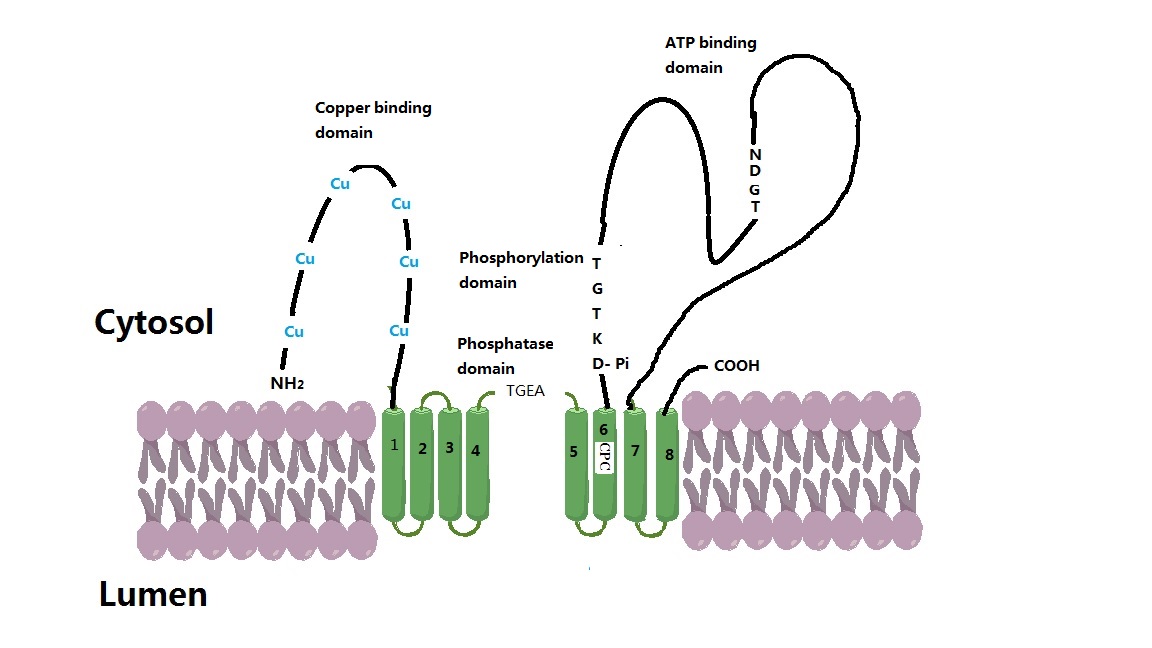
Wilson Disease Protein
Wilson disease protein (WND), also known as ATP7B protein, is a copper-transporting P-type ATPase which is encoded by the ''ATP7B'' gene. The ATP7B protein is located in the trans-Golgi network of the liver and brain and balances the copper level in the body by excreting excess copper into bile and plasma. Genetic disorder of the ATP7B gene may cause Wilson's disease, a disease in which copper accumulates in tissues, leading to neurological or psychiatric issues and liver diseases. Gene Wilson disease protein is associated with ''ATP7B'' gene, approximately 80 Kb, located on human chromosome 13 and consists of 21 exons. The mRNA transcribed by ''ATP7B'' gene has a size of 7.5 Kb, and which encodes a protein of 1465 amino acids. The gene is a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family and encodes a protein with several membrane-spanning domains, an ATPase consensus sequence, a hinge domain, a phosphorylation site, and at least two putative copper-binding sites. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |