|
GE-225
GE 210 advertisement from 1960 The GE-200 series was a family of small mainframe computers of the 1960s, built by General Electric (GE). GE marketing called the line ''Compatibles/200'' (GE-205/215/225/235). The GE-210 of 1960 is not compatible with the rest of the 200 series. 200 series models The main machine in the line was the GE-225 (1961). It used a 20-bit word, of which 13 bits could be used for an address. Along with the basic central processing unit (CPU) the system could also include a floating-point unit (the "Auxiliary Arithmetic Unit"), or a fixed-point decimal option with three six-bit decimal digits per word. It had 11 I/O channel controllers, and GE sold a variety of add-ons including disks, printers and other devices. The machines were built using discrete transistors, with a typical machine including about 10,000 transistors and 20,000 diodes. They used magnetic-core memory, and a standard 8 k-word system held 186,000 magnetic cores. They weighed ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartmouth Time Sharing System
The Dartmouth Time-Sharing System (DTSS) is a discontinued operating system first developed at Dartmouth College between 1963 and 1964. It was the first successful large-scale time-sharing system to be implemented, and was also the system for which the BASIC language was developed. DTSS was developed continually over the next decade, reimplemented on several generations of computers, and finally shut down in 1999. General Electric developed a similar system based on an interim version of DTSS, which they referred to as Mark II. Mark II and the further developed Mark III was widely used on their GE-600 series mainframe computers and formed the basis for their online services. These were the largest such services in the world for a time, eventually emerging as the consumer-oriented GEnie online service. Early history Professors John Kemeny and Thomas Kurtz at Dartmouth College purchased a Royal McBee LGP-30 computer around 1959, which was programmed by undergraduates in assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Spielberg
Arnold Meyer Spielberg (February 6, 1917 – August 25, 2020) was an American electrical engineer instrumental in contributions "to real-time data acquisition and recording that significantly contributed to the definition of modern feedback and control processes". For General Electric he designed, with his colleague Charles Propster, the GE-225 in 1959. He cited the first computer-controlled "point of sale" cash register as his greatest contribution. His children include filmmaker Steven Spielberg, and screenwriter Anne Spielberg. Early life and career Arnold Spielberg was born in Cincinnati on February 6, 1917. He was of Jewish descent. His mother, Rebecca (née Chechick), was born in Sudylkiv, Ukraine; his father, Samuel, was born in Kamianets-Podilskyi, Ukraine. They later immigrated to the United States, meeting and eventually marrying in Cincinnati. From the age of nine, he began building radios. He scrounged parts from garbage cans to assemble his first crystal re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
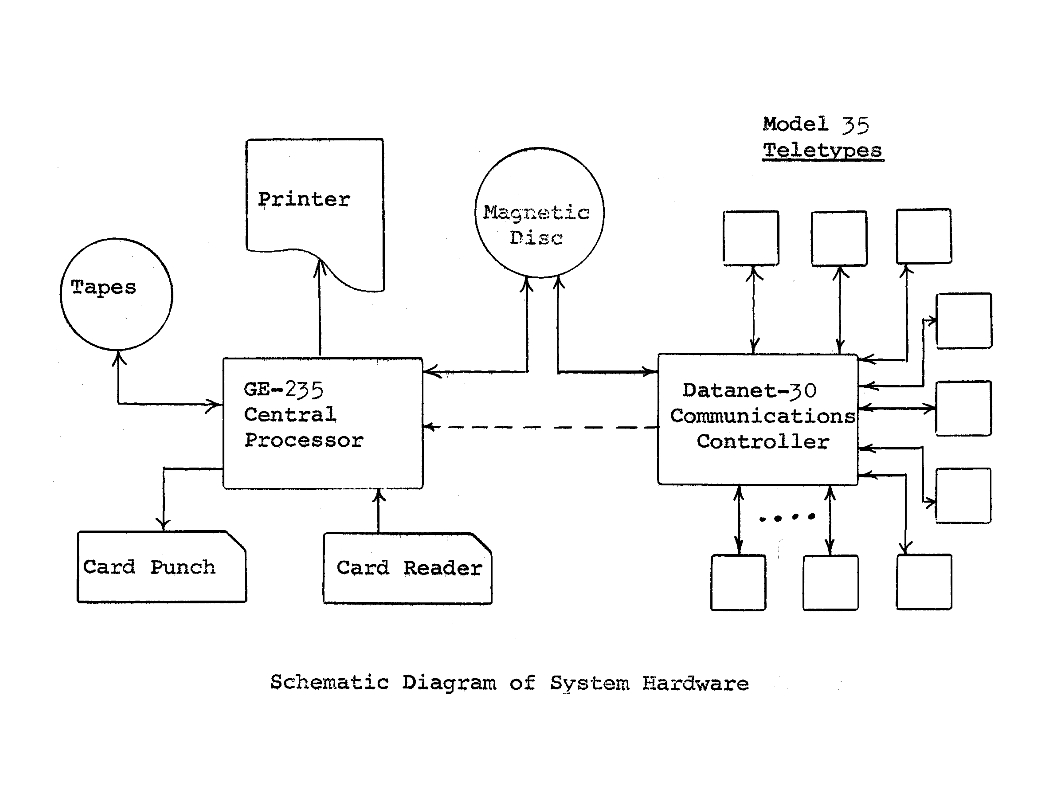
DATANET-30
The DATANET-30, or DN-30 for short, was a computer manufactured by General Electric designed in 1961-1963 to be used as a communications computer. It was later used as a front-end processor for data communications. It became the first front end communications computer. The names on the patent were Don Birmingham, Bob McKenzie, Bud Pine, and Bill Hill. The first free standing installations beginning in 1963 were Chrysler Corporation message switching systems replacing Teletype punched tape systems. In 1964, acting as a front end processor along with an interface to the GE-225 computer a professor at Dartmouth College developed the BASIC programming language. Multiple teletype units were attached to be the first time-sharing system. The DATANET-30 used magnetic-core memory with a cycle time of 6.94 μs. The word size was 18 bits and memory was available in sizes of 4K, 8K, or 16K words. The system could attach up to 128 asynchronous terminals, nominally at speeds of up to "3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Logic Unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on floating point numbers. It is a fundamental building block of many types of computing circuits, including the central processing unit (CPU) of computers, FPUs, and graphics processing units (GPUs). The inputs to an ALU are the data to be operated on, called operands, and a code indicating the operation to be performed; the ALU's output is the result of the performed operation. In many designs, the ALU also has status inputs or outputs, or both, which convey information about a previous operation or the current operation, respectively, between the ALU and external status registers. Signals An ALU has a variety of input and output net (electronics), nets, which are the electrical conductors used to convey Digital signal (electronics), digi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Multitasking
In computing, multitasking is the concurrent execution of multiple tasks (also known as processes) over a certain period of time. New tasks can interrupt already started ones before they finish, instead of waiting for them to end. As a result, a computer executes segments of multiple tasks in an interleaved manner, while the tasks share common processing resources such as central processing units (CPUs) and main memory. Multitasking automatically interrupts the running program, saving its state (partial results, memory contents and computer register contents) and loading the saved state of another program and transferring control to it. This " context switch" may be initiated at fixed time intervals (pre-emptive multitasking), or the running program may be coded to signal to the supervisory software when it can be interrupted (cooperative multitasking). Multitasking does not require parallel execution of multiple tasks at exactly the same time; instead, it allows more than o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batch Processing
Computerized batch processing is a method of running software programs called jobs in batches automatically. While users are required to submit the jobs, no other interaction by the user is required to process the batch. Batches may automatically be run at scheduled times as well as being run contingent on the availability of computer resources. History The term "batch processing" originates in the traditional classification of methods of production as job production (one-off production), batch production (production of a "batch" of multiple items at once, one stage at a time), and flow production (mass production, all stages in process at once). Early history Early computers were capable of running only one program at a time. Each user had sole control of the machine for a scheduled period of time. They would arrive at the computer with program and data, often on punched paper cards and magnetic or paper tape, and would load their program, run and debug it, and carry off their ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initially they were used in telegraphy, which developed in the late 1830s and 1840s as the first use of electrical engineering, though teleprinters were not used for telegraphy until 1887 at the earliest. The machines were adapted to provide a user interface to early mainframe computers and minicomputers, sending typed data to the computer and printing the response. Some models could also be used to create punched tape for data storage (either from typed input or from data received from a remote source) and to read back such tape for local printing or transmission. Teleprinters could use a variety of different communication media. These included a simple pair of wires; dedicated non-switched telephone circuits (leased lines); switched network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-sharing
In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users at the same time by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking.DEC Timesharing (1965), by Peter Clark, The DEC Professional, Volume 1, Number 1 Its emergence as the prominent model of computing in the 1970s represented a major technological shift in the history of computing. By allowing many users to interact concurrently with a single computer, time-sharing dramatically lowered the cost of providing computing capability, made it possible for individuals and organizations to use a computer without owning one, and promoted the interactive use of computers and the development of new interactive applications. History Batch processing The earliest computers were extremely expensive devices, and very slow in comparison to later models. Machines were typically dedicated to a particular set of tasks and operated by control panels, the operator manually entering small programs via switches in order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native Americans in Christian theology and the English way of life, the university primarily trained Congregationalist ministers during its early history before it gradually secularized, emerging at the turn of the 20th century from relative obscurity into national prominence. It is a member of the Ivy League. Following a liberal arts curriculum, Dartmouth provides undergraduate instruction in 40 academic departments and interdisciplinary programs, including 60 majors in the humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, and engineering, and enables students to design specialized concentrations or engage in dual degree programs. In addition to the undergraduate faculty of arts and sciences, Dartmouth has four professional and graduate schools: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entertainment Tonight
''Entertainment Tonight'' (or simply ''ET'') is an American Broadcast syndication, first-run syndicated news broadcasting news magazine, newsmagazine program that is distributed by CBS Media Ventures throughout the United States and owned by Paramount Streaming. ET also airs in Australia on Network 10. Format The format of the program is composed of stories of interest from throughout the entertainment industry, exclusive set visits, first looks at upcoming film and television projects, and one-on-one interviews with actors, musicians and other entertainment personalities and newsmakers. A one-hour weekend edition, ''ET Weekend'' (known as ''Entertainment This Week'' until September 1991), originally offered a recap of the week's entertainment news, with most or all episodes later transitioning to center (either primarily or exclusively) around some sort of special theme; though the weekend edition now utilizes either format depending on the episode, most commonly, the format of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |