|
GAZ-3309
GAZ-3307 and GAZ-3309 (nickname GAZon) are fourth-generation Russian trucks produced by the medium-duty Gorky Automobile Plant. The flatbed truck carburetor GAZ-3307 was announced in late 1989, and the turbodiesel truck GAZ-3309 was announced at the end of 1994. GAZ-3307 will replace the third-generation truck family GAZ-52/53, which were discontinued in early 1993. These trucks have 4.5 tons carrying capacity and are designed for use on all types of paved roads. The fourth-generation GAZ truck family includes 5-ton diesel truck GAZ-4301 (1984-1995) and 3-ton diesel truck GAZ-3306 (1993-1995). Since 1999, Gorky has offered a 2-3 ton all terrain truck GAZ Sadko (4×4) with a single rear axle and busbar system for centralized control of air pressure in the tires. Since 2005, the company has offered 4-ton all-terrain truck GAZ-33086 "Zemlyak" with a busbar gable rear axle. History and development of the fourth generation of GAZ trucks (4×2) In the early 1980s, when designing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAZ-3309
GAZ-3307 and GAZ-3309 (nickname GAZon) are fourth-generation Russian trucks produced by the medium-duty Gorky Automobile Plant. The flatbed truck carburetor GAZ-3307 was announced in late 1989, and the turbodiesel truck GAZ-3309 was announced at the end of 1994. GAZ-3307 will replace the third-generation truck family GAZ-52/53, which were discontinued in early 1993. These trucks have 4.5 tons carrying capacity and are designed for use on all types of paved roads. The fourth-generation GAZ truck family includes 5-ton diesel truck GAZ-4301 (1984-1995) and 3-ton diesel truck GAZ-3306 (1993-1995). Since 1999, Gorky has offered a 2-3 ton all terrain truck GAZ Sadko (4×4) with a single rear axle and busbar system for centralized control of air pressure in the tires. Since 2005, the company has offered 4-ton all-terrain truck GAZ-33086 "Zemlyak" with a busbar gable rear axle. History and development of the fourth generation of GAZ trucks (4×2) In the early 1980s, when designing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAZ Sadko
The GAZ-3308 "Sadko" (russian: Садко) is a Russian-built, 2.5-ton, 4-wheel-drive cargo truck. The Sadko is produced by the Gorky Automobile Plant (GAZ). It is named after Sadko, a protagonist in many ''bylinas'' of the Novgorod cycle. Sadko has been replaced in production by the Sadko Next (Ru:САДКО NEXT). History The current GAZ-3308 series of vehicles served as a replacement for the GAZ-66, which was produced for approximately 35 years (from 1964 until 1999). The first prototype was developed by the Gorky Automobile Plant in 1995 under the designation GAZ-33097. Series production began in December, 1997, receiving the designation GAZ-3308 and the name "Sadko." In the Russian Army it replaced the GAZ-66-40 cab-over-engine truck. For this purpose certain modifications were implemented including the cab from the GAZ-3309 with fenders featuring enlarged wheel arches as well as drive axles and transmission analogous to those used on the GAZ-66-40. Since 2003, most GAZ-33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gorky (, ; 1932–1990), is the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast and the Volga Federal District. The city is located at the confluence of the Oka and the Volga rivers in Central Russia, with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.7 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Nizhny Novgorod is the sixth-largest city in Russia, the second-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. It is an important economic, transportation, scientific, educational and cultural center in Russia and the vast Volga-Vyatka economic region, and is the main center of river tourism in Russia. In the historic part of the city there are many universities, theaters, museums and churches. The city w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadko Next
Sadko (russian: Садко) is the principal character in a Russian medieval epic ''bylina''. He was an adventurer, merchant, and ''gusli'' musician from Novgorod. Textual notes "Sadko" is a version of the tale translated by Arthur Ransome in ''Old Peter's Russian tales'' (1916). Kate Blakey's translation of a variant, "Sadko, the Rich Merchant Guest", appeared in the ''Slavonic Review'' (1924). A bylina version collected by P. N. Rybnikov has been translated by James Bailey. Synopsis Sadko of Novgorod played the ''gusli'' on the shores of a lake and river. The Tsar of the Sea enjoyed his music, and offered to help him. Sadko was instructed to make a bet with the local merchants about catching a gold-finned fish in the lake; when he caught it (as provided by the Sea Tsar), the merchants had to pay the wager, making Sadko a rich merchant. Sadko traded on the seas with his new wealth, but did not pay proper respects to the Tsar as per their agreement. The Tsar stopped Sadk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk Region (voblast) and Minsk District (raion). As of January 2021, its population was 2 million, making Minsk the 11th most populous city in Europe. Minsk is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). First documented in 1067, Minsk became the capital of the Principality of Minsk before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It received town privileges in 1499. From 1569, it was the capital of the Minsk Voivodeship, an administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of a region annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Partition of Poland. From 1919 to 1991, aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutz AG
Deutz AG is a German internal combustion engine manufacturer, based in Porz, Cologne, Germany. History The company was founded by Nicolaus Otto, the inventor of the four-stroke internal combustion engine, and his partner Eugen Langen on 31 March 1864, as N. A. Otto & Cie, later renamed to Gasmotoren-Fabrik Deutz after moving operations in 1869 from Cologne to Deutz, located on the opposite side of the Rhine, also called "the wrong side" in Cologne. In the early years, Otto and Langen were interested only in producing stationary engines, not automobiles. Georgano, G.N. ''Cars: Early and Vintage, 1886-1930''. (London: Grange-Universal, 1985) The technical director, Gottlieb Daimler, was eager to produce automobiles. In the middle of the 1870s, it was suggested that he transfer to the company's St. Petersburg factory to reduce his influence. He resigned, taking Wilhelm Maybach with him. Deutz also produced agricultural machines such as combine harvesters and tractors, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
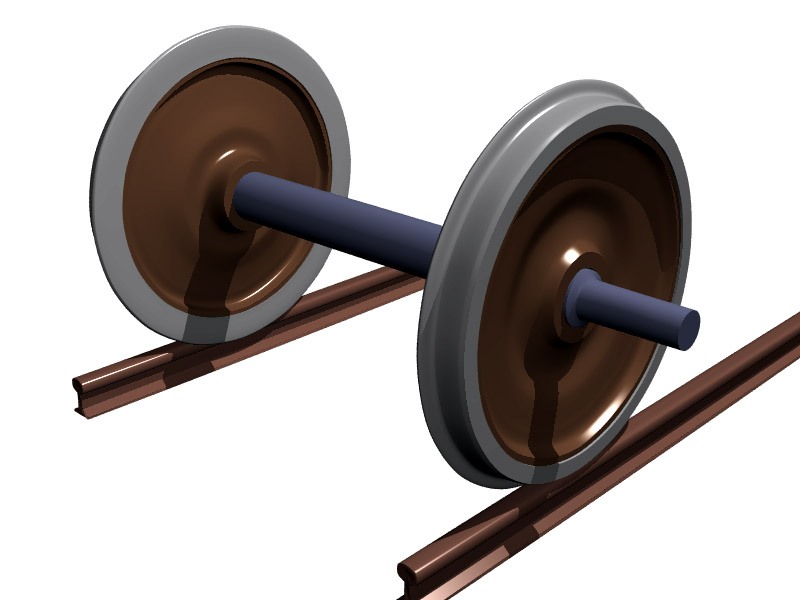
Axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type axle is referred to as a ''spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft which rotates with the wheel, being either bolted or splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft''. However, in looser usage, an entire assembly including the surrounding axle housing (typically a casting) is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4×4
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges. A four-wheel drive vehicle with torque supplied to both axles is described as "all-wheel drive" (AWD). However, "four-wheel drive" typically refers to a set of specific components and functions, and intended off-road application, which generally complies with modern use of the terminology. Definitions Four-wheel-drive systems were developed in many different markets and used in many different vehicle platforms. There is no universally accepted set of terminology that describes the various architectures and functions. The terms used by various manufacturers often reflect marketing rather than engineering considerations or significant technical diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road Surface
A road surface (British English), or pavement (American English), is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road or walkway. In the past, gravel road surfaces, hoggin, cobblestone and granite setts were extensively used, but these have mostly been replaced by asphalt or concrete laid on a compacted base course. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the 20th century and are of two types: metalled (hard-surfaced) and unmetalled roads. Metalled roadways are made to sustain vehicular load and so are usually made on frequently used roads. Unmetalled roads, also known as gravel roads, are rough and can sustain less weight. Road surfaces are frequently marked to guide traffic. Today, permeable paving methods are beginning to be used for low-impact roadways and walkways. Pavements are crucial to countries such as United States and Canada, which heavily depend on road transpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbo-diesel
The term turbo-diesel, also written as turbodiesel and turbo diesel, refers to any diesel engine equipped with a turbocharger. As with other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can significantly increase its efficiency and power output, especially when used in combination with an intercooler. Turbocharging of diesel engines began in the 1920s with large marine and stationary engines. Trucks became available with turbo-diesel engines in the mid-1950s, followed by passenger cars in the late 1970s. Since the 1990s, the compression ratio of turbo-diesel engines has been dropping. Principle Diesel engines are typically well suited to turbocharging due to two factors: * A "lean" air–fuel ratio, caused when the turbocharger supplies excess air into the engine, is not a problem for diesel engines, because the torque control is dependent on the mass of fuel that is injected into the combustion chamber (i.e. air-fuel ratio), rather than the quantity of the air-fuel mixture. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
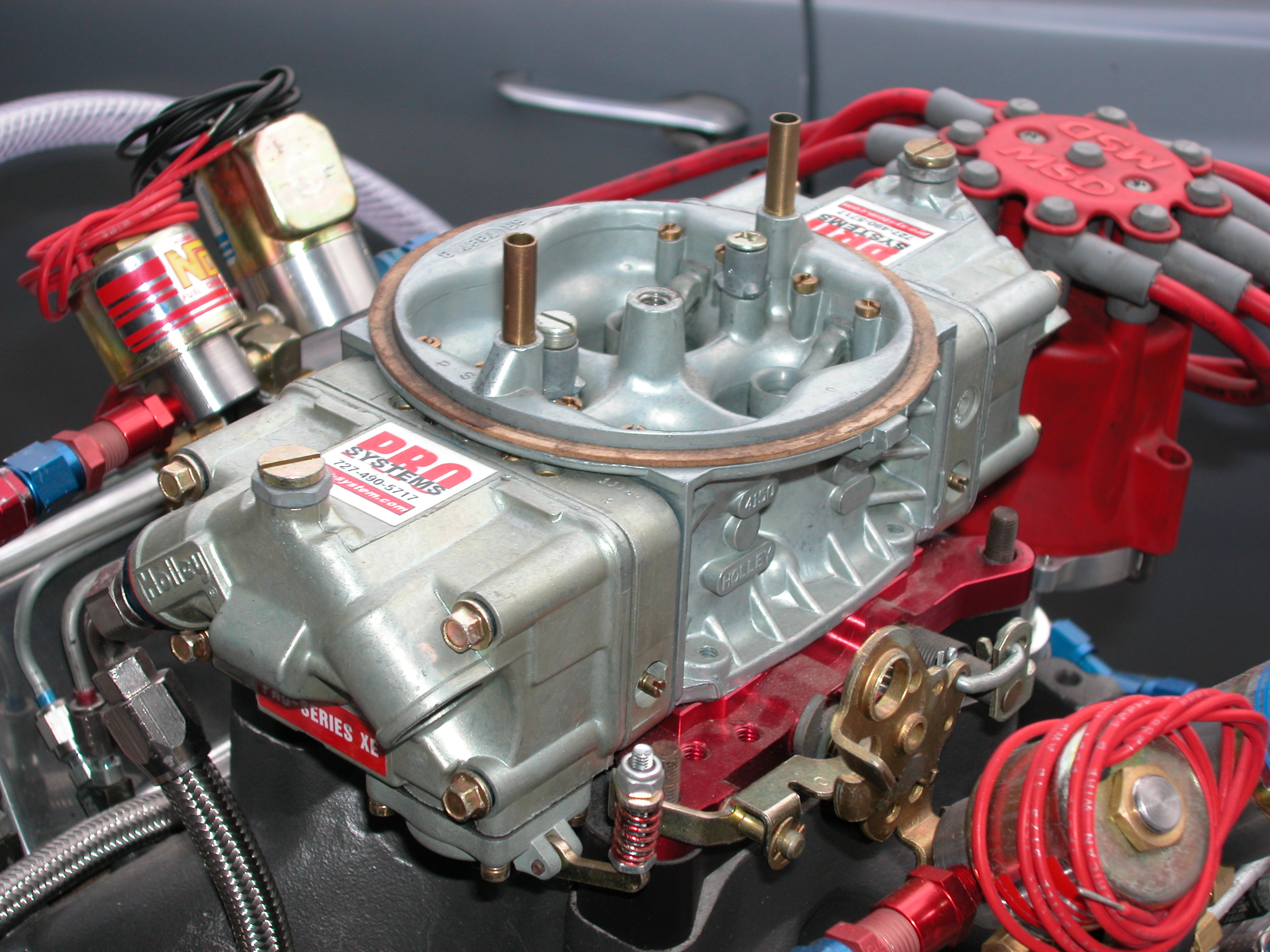
Carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |