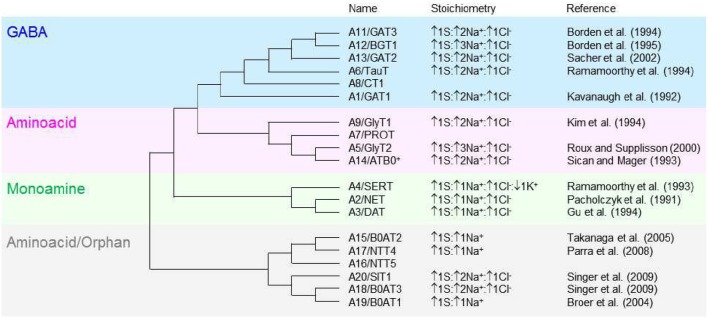
|
GABA Transporter Type 2
GABA transporter 2 (GAT2; SLC6A13) also known as sodium- and chloride-dependent GABA transporter 2 is one of four GABA transporters, GAT1 ( SLC6A1), GAT2 (SLC6A13), GAT3 ( SLC6A11) and BGT1 ( SLC6A12). Note that GAT2 is different from BGT1 despite the fact that the latter transporter is sometimes referred at as (mouse) GAT-2. All these transporters are highly hydrophobic proteins with 12 transmembrane segments, extracellular glycosylation sites, and intracellular consensus sites for phosphorylation, and there is over 50% amino acid homology between each of them. Each binds GABA with varying affinities with BGT1 having the lowest affinity and GAT3 the highest. GAT2 (SLC6A13) is predominantly expressed in hepatocytes in the liver, but is also found in proximal tubules in the kidney as well as in the leptomeninges and in some blood vessels in the brain. Biological function Brain Deletion of the GAT2 gene in mice does not appear to have any dramatic effects on brain function in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABA Transporter
GABA transporters ( Gamma-Aminobutyric acid transporters) belong to the family of neurotransmitters known as sodium symporters, also known as solute carrier 6 ( SLC6). These are large family of neurotransmitter which are Na+ concentration dependent. They are found in various regions of the brain in different cell types, such as neurons and astrocytes. These transporters are primarily responsible for the regulation of extracellular GABA concentration during basal and synaptic activity. They are responsible for creating a GABA gradient which is determined by the membrane potential, and the concentration of Na+ and Cl−. They are also present on the plasma membrane of neurons and glia which help define their function of regulation of GABA concentration as they act as the receptors that facilitate recycling of GABA in the extracellular space. GABA transporters are a common target for anticonvulsant drugs against seizure disorders such as epilepsy. Types The GABA transporter group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter Transporters
Neurotransmitter transporters are a class of membrane transport proteins that span the cellular membranes of neurons. Their primary function is to carry neurotransmitters across these membranes and to direct their further transport to specific intracellular locations. There are more than twenty types of neurotransmitter transporters. Vesicular transporters move neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles, regulating the concentrations of substances within them. Vesicular transporters rely on a proton gradient created by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in order to carry out their work: v-ATPase hydrolyzes ATP, causing protons to be pumped into the synaptic vesicles and creating a proton gradient. Then the efflux of protons from the vesicle provides the energy to bring the neurotransmitter into the vesicle. Neurotransmitter transporters frequently use electrochemical gradients that exist across cell membranes to carry out their work. For example, some transporters use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Proteins
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically modern huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Tubule
The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. It can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal straight tubule (PST). Structure The most distinctive characteristic of the proximal tubule is its luminal brush border. Brush border cell The luminal surface of the epithelial cells of this segment of the nephron is covered with densely packed microvilli forming a border readily visible under the light microscope giving the brush border cell its name. The microvilli greatly increase the luminal surface area of the cells, presumably facilitating their reabsorptive function as well as putative flow sensing within the lumen. The cytoplasm of the cells is densely packed with mitochondria, which are largely found in the basal region within the infoldings of the basal plasma membrane. The high quantity of mitochondria gives the cells an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of such a condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC6A1
GABA transporter 1 (GAT1) also known as sodium- and chloride-dependent GABA transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC6A1'' gene and belongs to the solute carrier 6 (SLC6) family of transporters. It mediates gamma-aminobutyric acid's translocation from the extracellular to intracellular spaces within brain tissue and the central nervous system as a whole. Structure GAT1 is a 599 amino acid protein that consists of 12 transmembrane domains with an intracellular N-terminus and C-terminus. Function GAT1 is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter, which removes GABA from the synaptic cleft by shuttling it to presynaptic neurons (where GABA can be recycled) and astrocytes (where GABA can be broken down). GABA Transporter 1 uses energy from the dissipation of a Na+ gradient, aided by the presence of a Cl− gradient, to translocate GABA across CNS neuronal membranes. The stoichiometry for GABA Transporter 1 is 2 Na+: 1 Cl−: 1 GABA. The presence of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurine
Taurine (), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight. It is named after Latin (cognate to Ancient Greek ταῦρος, ''taûros'') meaning bull or ox, as it was first isolated from ox bile in 1827 by German scientists Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin. It was discovered in human bile in 1846 by Edmund Ronalds. It has many biological roles, such as conjugation of bile acids, antioxidation, osmoregulation, membrane stabilization, and modulation of calcium signaling. It is essential for cardiovascular function, and development and function of skeletal muscle, the retina, and the central nervous system. It is an unusual example of a naturally occurring sulfonic acid. Chemical and biochemical features Taurine exists as a zwitterion , as verified by X-ray crystallography. The sulfonic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomeninges
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges is to protect the central nervous system. Structure Dura mater The dura mater ( la, tough mother) (also rarely called ''meninx fibrosa'' or ''pachymeninx'') is a thick, durable membrane, closest to the skull and vertebrae. The dura mater, the outermost part, is a loosely arranged, fibroelastic layer of cells, characterized by multiple interdigitating cell processes, no extracellular collagen, and significant extracellular spaces. The middle region is a mostly fibrous portion. It consists of two layers: the endosteal layer, which lies closest to the skull, and the inner meningeal layer, which lies closer to the brain. It contains large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |