|
G.9960
G.hn is a specification for home networking with data rates up to 2 Gbit/s and operation over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber. A single G.hn semiconductor device is able to network over any of the supported home wire types. Some benefits of a multi-wire standard are lower equipment development costs and lower deployment costs for service providers (by allowing customer self-install). History G.hn was developed under the International Telecommunication Union's Telecommunication Standardization sector (the ITU-T) and promoted by the HomeGrid Forum and several other organizations. ITU-T Recommendation (the ITU's term for standard) G.9960, which received approval on October 9, 2009,New ITU standard opens doors for unifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Error Correction
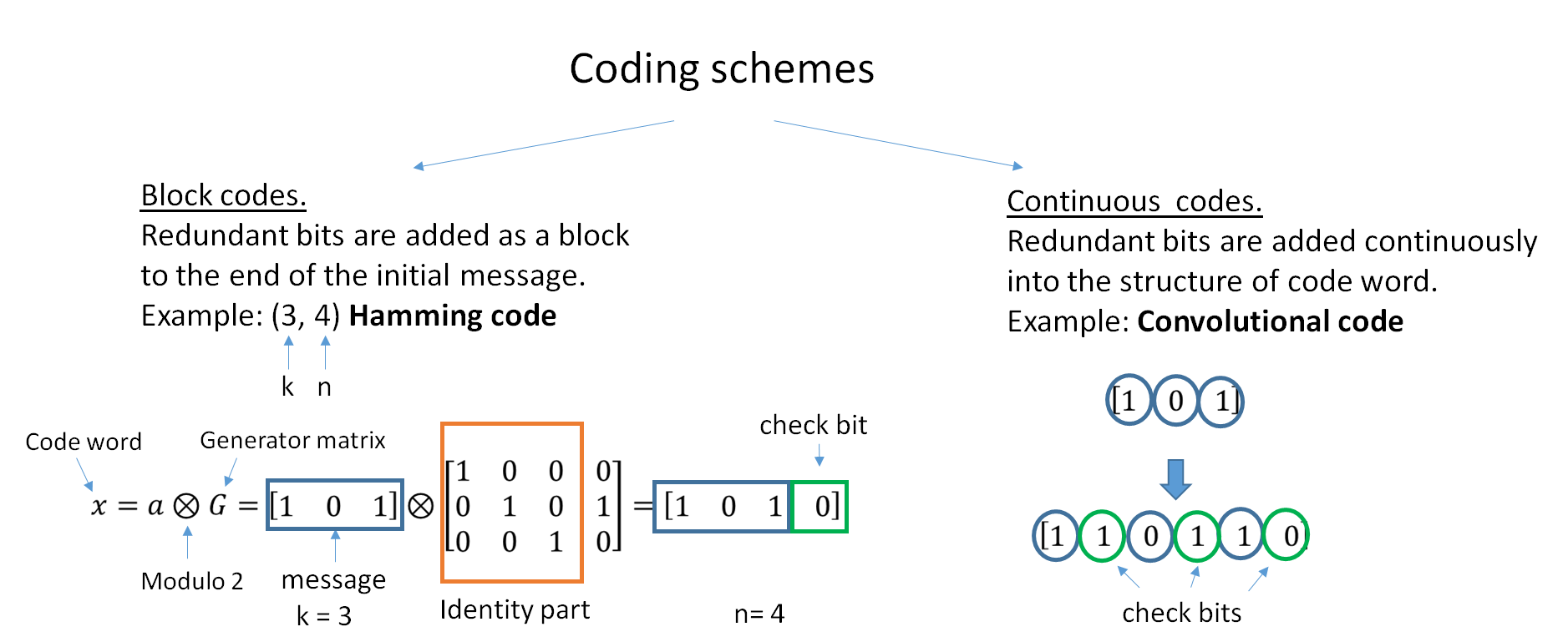
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-density Parity-check Code
In information theory, a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code is a linear error correcting code, a method of transmitting a message over a noisy transmission channel. An LDPC code is constructed using a sparse Tanner graph (subclass of the bipartite graph). LDPC codes are capacity-approaching codes, which means that practical constructions exist that allow the noise threshold to be set very close to the theoretical maximum (the Shannon limit) for a symmetric memoryless channel. The noise threshold defines an upper bound for the channel noise, up to which the probability of lost information can be made as small as desired. Using iterative belief propagation techniques, LDPC codes can be decoded in time linear to their block length. LDPC codes are finding increasing use in applications requiring reliable and highly efficient information transfer over bandwidth-constrained or return-channel-constrained links in the presence of corrupting noise. Implementation of LDPC codes ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer; The layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to broadcast on, the line code to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified by the physical layer. Role The physical layer defines the means of transmitting a stream of raw bits over a physical data link connecting network nodes. The bitstream may be grouped into code words or symbols and converted to a physical signal that is transmitted over a transmission medium. The physical layer consists of the electronic circuit transmission technologies of a network. It is a fundamental layer underlying the higher level functions in a network, and can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Networking
A home network or home area network (HAN) is a type of computer network that facilitates communication among devices within the close vicinity of a home. Devices capable of participating in this network, for example, smart devices such as network printers and handheld mobile computers, often gain enhanced emergent capabilities through their ability to interact. These additional capabilities can be used to increase the quality of life inside the home in a variety of ways, such as automation of repetitive tasks, increased personal productivity, enhanced home security, and easier access to entertainment. Origins Establishing this kind of network is often necessary for sharing residential Internet access to all networked devices. Based on techniques to mitigate IPv4 address exhaustion, most Internet service providers provide only a single wide area network-facing IP address for each residential customer. Therefore, such networks require network address translation in the network r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Rate
In telecommunication and information theory, the code rate (or information rateHuffman, W. Cary, and Pless, Vera, ''Fundamentals of Error-Correcting Codes'', Cambridge, 2003.) of a forward error correction code is the proportion of the data-stream that is useful (non- redundant). That is, if the code rate is k/n for every bits of useful information, the coder generates a total of bits of data, of which n-k are redundant. If is the gross bit rate or data signalling rate (inclusive of redundant error coding), the net bit rate (the useful bit rate exclusive of error correction codes) is \leq R \cdot k/n. For example: The code rate of a convolutional code will typically be , , , , , etc., corresponding to one redundant bit inserted after every single, second, third, etc., bit. The code rate of the octet oriented Reed Solomon block code denoted RS(204,188) is 188/204, meaning that redundant octets (or bytes) are added to each block of 188 octets of useful information. A f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token Passing
On a local area network, token passing is a channel access method where a packet called a ''token'' is passed between nodes to authorize that node to communicate. In contrast to polling access methods, there is no pre-defined "master" node. The most well-known examples are IBM Token Ring and ARCNET, but there were a range of others, including FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface), which was popular in the early to mid 1990s. Token passing schemes degrade deterministically under load, which is a key reason why they were popular for industrial control LANs such as MAP, (Manufacturing Automation Protocol). The advantage over contention based channel access (such as the CSMA/CD of early Ethernet), is that collisions are eliminated, and that the channel bandwidth can be fully utilized without idle time when demand is heavy. The disadvantage is that even when demand is light, a station wishing to transmit must wait for the token, increasing latency. Some types of token passing sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great force, the scientific use of the term implies nothing about the magnitude of the force. Some examples of physical interactions that scientists would consider collisions are the following: * When an insect lands on a plant's leaf, its legs are said to collide with the leaf. * When a cat strides across a lawn, each contact that its paws make with the ground is considered a collision, as well as each brush of its fur against a blade of grass. * When a boxer throws a punch, their fist is said to collide with the opponents body. * When an astronomical object merges with a black hole, they are considered to collide. Some colloquial uses of the word collision are the following: * A traffic collision involves at least one automobile. * A mid-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSMA/CARP
In computer networking, carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance and resolution using priorities (CSMA/CARP) is a channel access method. CSMA/CARP is similar in nature to the carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) channel access method used in Ethernet networks, but CSMA/CARP provides no detection of network collisions. Instead of detecting network collisions, CSMA/CARP attempts to avoid collisions by using a system of transmission priorities. When a station wants to transmit on a CSMA/CARP network it first listens for network traffic and if the medium is clear instead of immediately transmitting as a station would in CSMA/CD it waits a predefined amount of time. This waiting period is called the interframe spacing (IFS) and it varies by the type of data being transmitted. High priority data will transmit almost immediately whereas lower priority data such as polling will have a longer IFS. This system allows CSMA/CARP to avoid many col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Encryption Standard
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael (), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. AES is a variant of the Rijndael block cipher developed by two Belgian cryptographers, Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, who submitted a proposal to NIST during the AES selection process. Rijndael is a family of ciphers with different key and block sizes. For AES, NIST selected three members of the Rijndael family, each with a block size of 128 bits, but three different key lengths: 128, 192 and 256 bits. AES has been adopted by the U.S. government. It supersedes the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which was published in 1977. The algorithm described by AES is a symmetric-key algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting the data. In the United States, AES was announced by the NIST as U.S. FIPS PUB 197 (FIPS 197) on Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Repeat Request
Automatic repeat request (ARQ), also known as automatic repeat query, is an error-control method for data transmission that uses acknowledgements (messages sent by the receiver indicating that it has correctly received a packet) and timeouts (specified periods of time allowed to elapse before an acknowledgment is to be received) to achieve reliable data transmission over an unreliable communication channel. If the sender does not receive an acknowledgment before the timeout, it re-transmits the packet until it receives an acknowledgment or exceeds a predefined number of retransmissions. Variations of ARQ protocols include Stop-and-wait ARQ, Go-Back-N ARQ, and Selective Repeat ARQ. All three protocols usually use some form of sliding window protocol to help the sender determine which (if any) packets need to be retransmitted. These protocols reside in the data link or transport layers (layers 2 and 4) of the OSI model. Examples The Transmission Control Protocol uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Division Multiple Access
Time-division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This allows multiple stations to share the same transmission medium (e.g. radio frequency channel) while using only a part of its channel capacity. Dynamic TDMA is a TDMA variant that dynamically reserves a variable number of time slots in each frame to variable bit-rate data streams, based on the traffic demand of each data stream. TDMA is used in the digital 2G cellular systems such as Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), IS-136, Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) and iDEN, and in the Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) standard for portable phones. TDMA was first used in satellite communication systems by Western Union in its Westar 3 communications satelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCMP (cryptography)
Counter Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (Counter Mode CBC-MAC Protocol) or CCM mode Protocol (CCMP) is an encryption protocol designed for Wireless LAN products that implements the standards of the IEEE 802.11i amendment to the original IEEE 802.11 standard. CCMP is an enhanced data cryptographic encapsulation mechanism designed for data confidentiality and based upon the Counter Mode with CBC-MAC ( CCM mode) of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) standard. It was created to address the vulnerabilities presented by Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), a dated, insecure protocol. Technical details CCMP uses CCM that combines CTR mode for data confidentiality and cipher block chaining message authentication code (CBC-MAC) for authentication and integrity. CCM protects the integrity of both the MPDU data field and selected portions of the IEEE 802.11 MPDU header. CCMP is based on AES processing and uses a 128-bit key and a 128-bit block size. CCMP us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Round_Function.png)