|
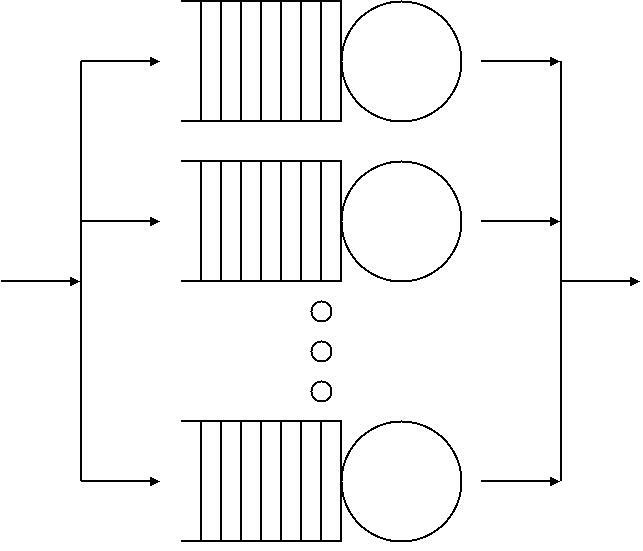
G-network
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, a G-network (generalized queueing network, often called a Gelenbe network) is an open network of G-queues first introduced by Erol Gelenbe as a model for queueing systems with specific control functions, such as traffic re-routing or traffic destruction, as well as a model for neural networks. A G-queue is a network of queues with several types of novel and useful customers: *''positive'' customers, which arrive from other queues or arrive externally as Poisson arrivals, and obey standard service and routing disciplines as in conventional network models, *''negative'' customers, which arrive from another queue, or which arrive externally as Poisson arrivals, and remove (or 'kill') customers in a non-empty queue, representing the need to remove traffic when the network is congested, including the removal of "batches" of customers *"triggers", which arrive from other queues or from outside the network, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product-form Solution
In probability theory, a product-form solution is a particularly efficient form of solution for determining some metric of a system with distinct sub-components, where the metric for the collection of components can be written as a product (mathematics), product of the metric across the different components. Using capital Pi notation a product-form solution has algebraic form :\text(x_1,x_2,x_3,\ldots,x_n) = B \prod_^n \text(x_i) where ''B'' is some constant. Solutions of this form are of interest as they are computationally inexpensive to evaluate for large values of ''n''. Such solutions in queueing networks are important for finding performance metrics in models of multiprogrammed and time-shared computer systems. Equilibrium distributions The first product-form solutions were found for equilibrium distributions of Markov chains. Trivially, models composed of two or more Independence (probability theory)#Independent random variables, independent sub-components exhibit a product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erol Gelenbe
Sami Erol Gelenbe (born 22 August 1945, Istanbul) is a Turkish and French computer scientist, electronic engineer and applied mathematician, renowned for pioneering work in computer system and network performance. His academic career spans several prestigious institutions and roles, including current positions as Professor at the Institute of Theoretical and Applied Informatics of the Polish Academy of Sciences since 2017, and visiting professorships at King's College London, the I3S Laboratory (French National Centre for Scientific Research, CNRS, Côte d'Azur University, University of Côte d'Azur) and the Abraham de Moivre Laboratory (CNRS, Imperial College London). A Fellow of several national academies, Gelenbe has chaired the Informatics Section of Academia Europaea since 2023. His extensive professorial tenures include roles at the University of Liège, Paris-Saclay University, University Paris-Saclay, Paris Descartes University, University Paris Descartes, New Jersey Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang, who created models to describe the system of incoming calls at the Copenhagen Telephone Exchange Company. These ideas were seminal to the field of teletraffic engineering and have since seen applications in telecommunications, traffic engineering, computing, project management, and particularly industrial engineering, where they are applied in the design of factories, shops, offices, and hospitals. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is '' Queue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackson's Theorem (queueing Theory)
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical probability theory, theory of probability, a Jackson network (sometimes Jacksonian network) is a class of queueing network where the equilibrium distribution is particularly simple to compute as the network has a product-form solution. It was the first significant development in the theory of queueing theory, networks of queues, and generalising and applying the ideas of the theorem to search for similar product-form solutions in other networks has been the subject of much research, including ideas used in the development of the Internet. The networks were first identified by James R. Jackson A version from January 1963 is available at http://www.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/296776.pdf and his paper was re-printed in the journal ''Management Science: A Journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences, Management Science’s'' ‘Ten Most Influential Titles of Management Sciences First Fifty Years.’ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Equation
In probability theory, a balance equation is an equation that describes the probability flux associated with a Markov chain In probability theory and statistics, a Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic process describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally ... in and out of states or set of states. Global balance The global balance equations (also known as full balance equations) are a set of equations that characterize the equilibrium distribution (or any stationary distribution) of a Markov chain, when such a distribution exists. For a continuous time Markov chain with state space \mathcal, transition rate from state i to j given by q_ and equilibrium distribution given by \pi, the global balance equations are given by ::\pi_i = \sum_ \pi_j q_, or equivalently :: \pi_i \sum_ q_ = \sum_ \pi_j q_. for all i \in S. Here \pi_i q_ represents the probability f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Come First Served
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of Queue area, waiting lines, or wikt:queue, queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang, who created models to describe the system of incoming calls at the Copenhagen Telephone Exchange Company. These ideas were seminal to the field of teletraffic engineering and have since seen applications in telecommunications, traffic engineering (transportation), traffic engineering, computing, project management, and particularly industrial engineering, where they are applied in the design of factories, shops, offices, and hospitals. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms of probability, axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure (mathematics), measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event (probability theory), event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of determinism, non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured Quantity, quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a network can perform complex tasks. There are two main types of neural networks. *In neuroscience, a ''biological neural network'' is a physical structure found in brains and complex nervous systems – a population of nerve cells connected by synapses. *In machine learning, an ''Neural network (machine learning), artificial neural network'' is a mathematical model used to approximate nonlinear functions. Artificial neural networks are used to solve artificial intelligence problems. In biology In the context of biology, a neural network is a population of biological neurons chemically connected to each other by synapses. A given neuron can be connected to hundreds of thousands of synapses. Each neuron sends and receives Electrochemistry, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Computation
Neural computation is the information processing performed by networks of neurons. Neural computation is affiliated with the philosophical tradition known as Computational theory of mind, also referred to as computationalism, which advances the thesis that neural computation explains cognition. The first persons to propose an account of neural activity as being computational was Warren Sturgis McCulloch, Warren McCullock and Walter Pitts in their seminal 1943 paper, ''A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity.'' There are three general branches of computationalism, including classicism, connectionism, and computational neuroscience. All three branches agree that cognition is computation, however, they disagree on what sorts of computations constitute cognition. The classicism tradition believes that computation in the brain is digital, analogous to digital computing. Both connectionism and computational neuroscience do not require that the computations that reali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Computer Journal
''The Computer Journal'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering computer science and information systems. Established in 1958, it is one of the oldest computer science research journals. It is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT. The authors of the best paper in each annual volume receive the Wilkes Award from BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT. Editors-in-chief The following people have been editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ...: * 1958–1969 Eric N. Mutch * 1969–1992 Peter Hammersley * 1993–2000 C. J. van Rijsbergen * 2000–2008 Fionn Murtagh * 2008–2012 Erol Gelenbe * 2012–2016 Fionn Murtagh * 2016–2020 Steve Furber * 2021–present Tom Crick References External links Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson Processes
In probability theory, statistics and related fields, a Poisson point process (also known as: Poisson random measure, Poisson random point field and Poisson point field) is a type of mathematical object that consists of points randomly located on a mathematical space with the essential feature that the points occur independently of one another. The process's name derives from the fact that the number of points in any given finite region follows a Poisson distribution. The process and the distribution are named after French mathematician Siméon Denis Poisson. The process itself was discovered independently and repeatedly in several settings, including experiments on radioactive decay, telephone call arrivals and actuarial science. This point process is used as a mathematical model for seemingly random processes in numerous disciplines including astronomy,G. J. Babu and E. D. Feigelson. Spatial point processes in astronomy. ''Journal of statistical planning and inference'', 50( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform that converts a Function (mathematics), function of a Real number, real Variable (mathematics), variable (usually t, in the ''time domain'') to a function of a Complex number, complex variable s (in the complex-valued frequency domain, also known as ''s''-domain, or ''s''-plane). The transform is useful for converting derivative, differentiation and integral, integration in the time domain into much easier multiplication and Division (mathematics), division in the Laplace domain (analogous to how logarithms are useful for simplifying multiplication and division into addition and subtraction). This gives the transform many applications in science and engineering, mostly as a tool for solving linear differential equations and dynamical systems by simplifying ordinary differential equations and integral equations into algebraic equation, algebraic polynomial equations, and by simplifyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |