|
G-cells
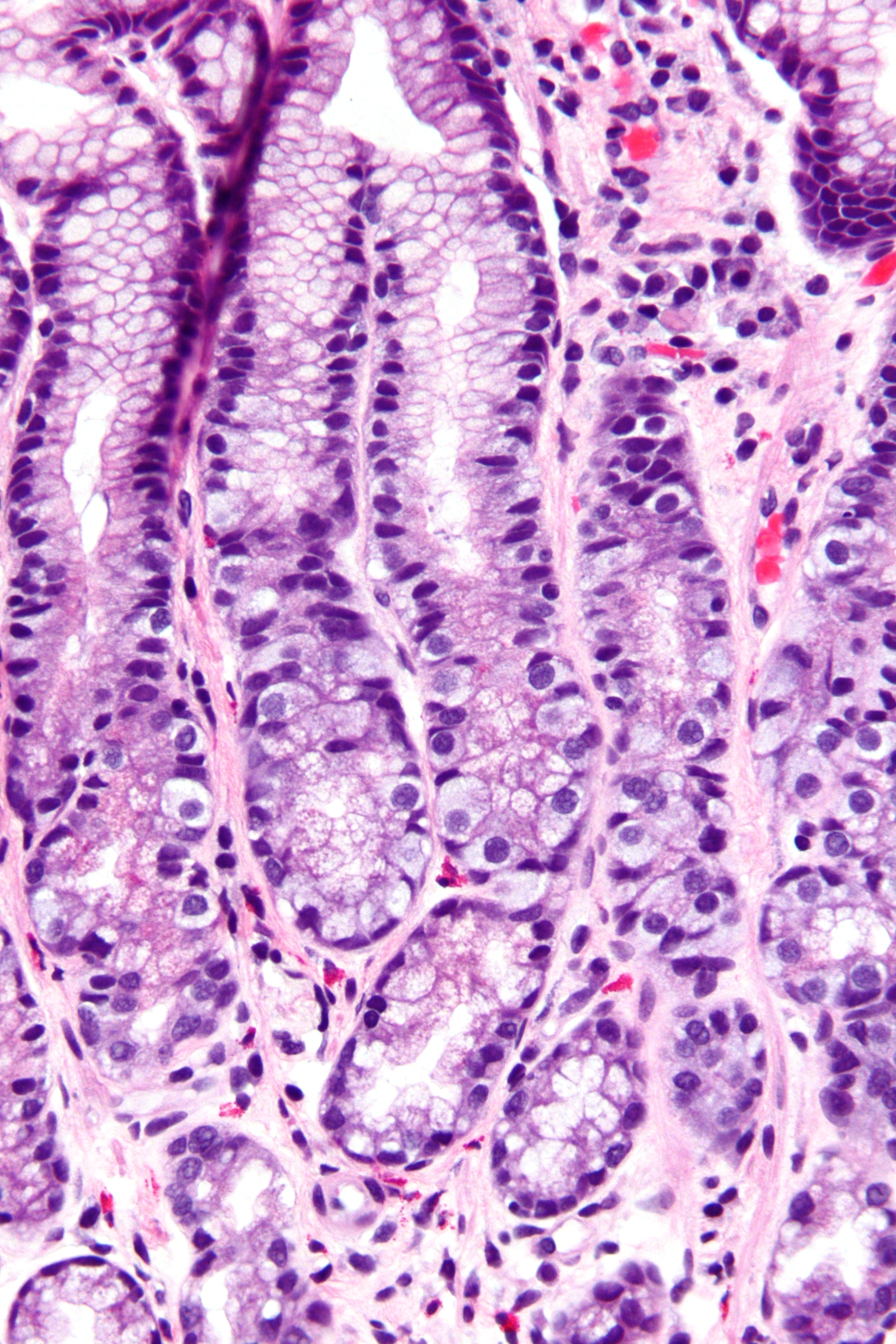
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum, and occasionally in the pancreas and duodenum. The vagus nerve innervates the G cells. Gastrin-releasing peptide is released by the post-ganglionic fibers of the vagus nerve onto G cells during parasympathetic stimulation. The peptide hormone bombesin also stimulates gastrin from G cells. Gastrin-releasing peptide, as well as the presence of amino acids in the stomach, stimulates the release of gastrin from the G cells. Gastrin stimulates enterochromaffin-like cells to secrete histamine. Gastrin also targets parietal cells by increasing the amount of histamine and the direct stimulation by gastrin, causing the parietal cells to increase HCl secretion in the stomach. G-cells frequently express PD-L1 during homeostasis which protects them f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PD-L1
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD274'' gene. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a 40kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the adaptive arm of immune systems during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. Normally the adaptive immune system reacts to antigens that are associated with immune system activation by exogenous or endogenous danger signals. In turn, clonal expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells and/or CD4+ helper cells is propagated. The binding of PD-L1 to the inhibitory checkpoint molecule PD-1 transmits an inhibitory signal based on interaction with phosphatases (SHP-1 or SHP-2) via Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Switch Motif (ITSM). This reduces the proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundic Glands
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands. There are two types of gland in the stomach, the oxyntic gland, and the pyloric gland. The major type of gastric gland is the oxyntic gland that is present in 80 per cent of the stomach, and is often referred to simply as the ''gastric gland''. The oxyntic gland is an exocrine gland and contains the parietal cells that produce hydrochloric acid, and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. The other type of gland in the stomach is the pyloric gland found in the pyloric region taking up the remaining 20 per cent of the stomach area. The pyloric gland secretes gastrin from its G cells. Pyloric glands are similar in structure to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyloric Glands
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands. There are two types of gland in the stomach, the oxyntic gland, and the pyloric gland. The major type of gastric gland is the oxyntic gland that is present in 80 per cent of the stomach, and is often referred to simply as the ''gastric gland''. The oxyntic gland is an exocrine gland and contains the parietal cells that produce hydrochloric acid, and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. The other type of gland in the stomach is the pyloric gland found in the pyloric region taking up the remaining 20 per cent of the stomach area. The pyloric gland secretes gastrin from its G cells. Pyloric glands are similar in structure to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several cran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Cell Types Derived From The Germ Layers
This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Cells derived from ectoderm Surface ectoderm Skin * Trichocyte * Keratinocyte Anterior pituitary * Gonadotrope * Corticotrope * Thyrotrope * Somatotrope * Lactotroph Tooth enamel * Ameloblast Neural crest Peripheral nervous system * Neuron * Glia ** Schwann cell ** Satellite glial cell Neuroendocrine system * Chromaffin cell * Glomus cell Skin * Melanocyte ** Nevus cell * Merkel cell Teeth * Odontoblast * Cementoblast Eyes * Corneal keratocyte Neural tube Central nervous system * Neuron * Glia ** Astrocyte ** Ependymocytes ** Muller glia (retina) ** Oligodendrocyte ** Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell ** Pituicyte (posterior pituitary) Pineal gland * Pinealocyte Cells derived from mesoderm Paraxial mesoderm Mesenchymal stem cell =Osteochondroprogenitor cell= * Bone ( Osteoblast → Osteocyte) * Cartilage (Chondroblast → Chondrocyte) =Myofibroblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Cell Hyperplasia - Very High Mag
G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''gee'' (pronounced ), plural ''gees''. History The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ' C' to distinguish voiced from voiceless . The recorded originator of 'G' is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, who added letter G to the teaching of the Roman alphabet during the 3rd century BC: he was the first Roman to open a fee-paying school, around 230 BCE. At this time, ' K' had fallen out of favor, and 'C', which had formerly represented both and before open vowels, had come to express in all environments. Ruga's positioning of 'G' shows that alphabetic order related to the letters' values as Greek numerals was a concern even in the 3rd century BC. According to some records, the original seventh letter, 'Z', had been purged from the Latin alphabet somewhat ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the stomach. They contain an extensive secretory network of canaliculi from which the HCl is secreted by active transport into the stomach. The enzyme hydrogen potassium ATPase (H+/K+ ATPase) is unique to the parietal cells and transports the H+ against a concentration gradient of about 3 million to 1, which is the steepest ion gradient formed in the human body. Parietal cells are primarily regulated via histamine, acetylcholine and gastrin signalling from both central and local modulators. Structure Canaliculus A canaliculus is an adaptation found on gastric parietal cells. It is a deep infolding, or little channel, which serves to increase the surface area, e.g. for secretion. The parietal cell membrane is dynamic; the numbers of canalic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discovered in 1910, it has been considered a local hormone (autocoid) because it lacks the classic endocrine glands to secrete it; however, in recent years, histamine has been recognized as a central neurotransmitter. Histamine is involved in the inflammatory response and has a central role as a mediator of itching. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by basophils and by mast cells found in nearby connective tissues. Histamine increases the permeability of the capillaries to white blood cells and some proteins, to allow them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues. It consists of an imidazole ring attached to an ethylamine chain; under physiological conditions, the amino group of the side-chain is protonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterochromaffin-like Cell
Enterochromaffin-like cells or ECL cells are a type of neuroendocrine cell found in the gastric glands of the gastric mucosa beneath the epithelium, in particular in the vicinity of parietal cells, that aid in the production of gastric acid via the release of histamine. They are also considered a type of enteroendocrine cell. Function ECL cells synthesize and secrete histamine. These cells are stimulated by the hormones gastrin (not depicted in the adjacent diagram) and pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating peptide. G cells are stimulated by vagal stimulation through the neurotransmitter gastrin-releasing peptide; this causes the G cells to secrete gastrin, which in turn stimulates ECL cells to release histamine. Note that this circuit is not activated by acetylcholine, which is of particular importance because the administration of atropine will not block the vagal stimulation of the G cells, as ACh is not the neurotransmitter for these cells. However, ECL cells are activate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |