|
Fテ。fnir
In Nordic and wider Germanic mythology, Fテ。fnir (Old Norse pronunciation: 坰ノ騨迅nノ决 is a mighty dwarf who is the son of Hreidmar, and brother of Regin and テ鍍r. Once cursed by Andvari's ring and gold, Fafnir slays his father out of greed and becomes a dragon. Fafnir's brother Regin assisted Sigurd in obtaining Gram, the sword he used to kill Fテ。fnir. Narrative There have been many renditions of Fテ。fnir's tale throughout history, but they all follow a standard structure. Loki kills the brother of Regin and Fテ。fnir, テ鍍r, while he is in the shape of an otter. As payment, Loki, Odin, and Hナ渡ir had to fill the otter's skin with gold. Loki collects the gold from the pike Andvari and returns the ransom to Hreidmar, Otr's father. When Hreidmar refuses to share the gold, Fテ。fnir murders him out of greed. Fテ。fnir then takes his treasure into the wilderness and turns into a dragon to guard it. And by use of the sword, Gram, Sigurd defeats Fテ。fnir in his serpentine form. Regin, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
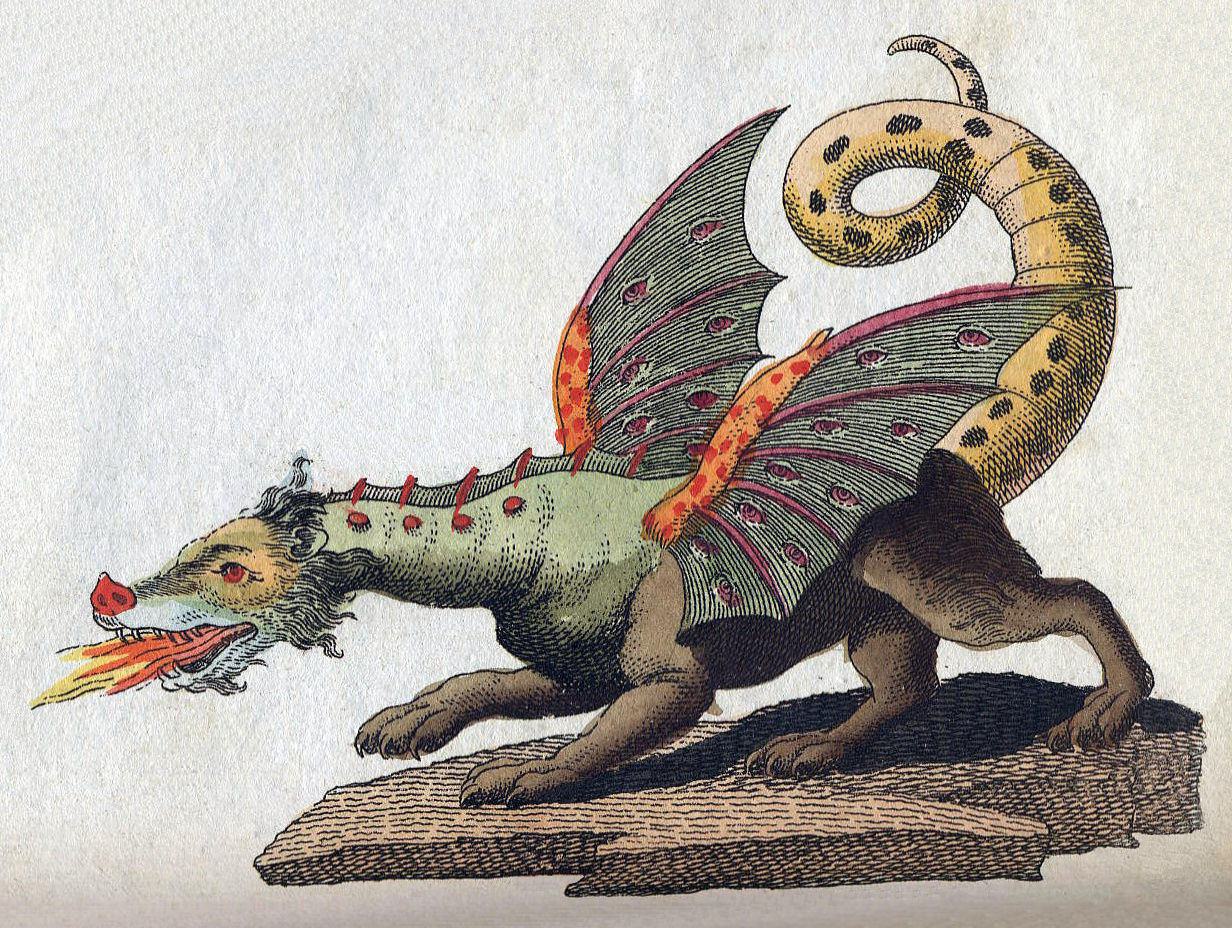
Germanic Dragon
Dragons are present in Germanic mythology and folklore, where they are often portrayed as large venomous serpents. Especially in later tales, however, they share many common features with other dragons in European mythology. Origin, appearance and terminology In early depictions, as with dragons in other cultures, the distinction between Germanic dragons and regular snakes is blurred, with both being referred to as Old Norse or Old English from Proto-Germanic *wurmiz. ''Wyrm'' has since been borrowed back into Modern English to mean "dragon", while the descendent term ''worm'' remains used in Modern English to refer to dragons, especially those lacking wings. In Fテ。fnismテ。l, the dragon Fテ。fnir is described as flightless and snake-like, and is referred to as an . In the later Vテカlsunga saga, however, he has shoulders, suggesting legs, wings or both, and is referred to as both a and an . Similarly, the dragon in Beowulf is referred to as both a and a , although in some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regin
In Norse mythology, Reginn (Old Norse: 癩ア癪≪埔癪≪埓/癩ア癪≪埒癪≪堊 ; often anglicized as Regin or Regan) is a son of Hreiテーmarr and the foster father of Sigurd. His brothers are Fafnir and テ鍍r. Regin in the sagas When Loki mistakenly kills テ鍍r, Hreiテーmarr demands to be repaid with the amount of gold it takes to fill テ鍍r's skin and cover the outside. Loki takes this gold from the dwarf Andvari, who curses it and especially the ring Andvaranaut. Fafnir kills his father for this gold, but eventually becomes a greedy dragon. Reginn gets none of the gold, but he becomes smith to the king and foster father to Sigurd, teaching him many languages as well as sports, chess, and runes. Reginn had all wisdom and deftness of hand. Of his two brothers, he has the ability to work iron as well as silver and gold and he makes many beautiful and useful things. While Sigurd is living with Reginn, Reginn challenges Sigurd's respect in the kingdom. He tells Sigurd to ask for a horse. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Dragon
The European dragon is a legendary creature in folklore and mythology among the overlapping cultures of Europe. The Roman poet Virgil in his poem ''Culex'' lines 163-201, describing a shepherd having a fight with a big constricting snake, calls it "serpens" and also "draco", showing that in his time the two words probably could mean the same thing. In and after the early Middle Ages, the European dragon is typically depicted as a large, fire-breathing, scaly, horned, lizard-like creature; the creature also has leathery, bat-like wings, four legs, and a long, muscular prehensile tail. Some depictions show dragons with one or more of: feathered wings, crests, ear frills, fiery manes, ivory spikes running down its spine, and various exotic decorations. In folktales, dragon's blood often contains unique powers, keeping them alive for longer or giving them poisonous or acidic properties. The typical dragon in Christian culture protects a cavern or castle filled with gold and trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram (mythology)
In Norse mythology, Gram (Old Norse ''Gramr'', meaning "Wrath"), also known as Balmung or Nothung, is the sword that Sigurd used to kill the dragon Fafnir. It is primarily used by the Vテカlsungs in the ''Volsunga Saga''. However, it is also seen in other legends, such as the ''Thidrekssaga'' in which it is wielded by Hildebrand. Depending on the story and source material, Gram may have other names. In ''The Nibelungenlied'' it is named Balmung. In Richard Wagner's work, ''Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (''The Ring of the Nibelung''), it is referred to as Nothung. Description Nowhere in the ''Volsunga Saga'' is a clear description of Gram given, but there is enough scattered throughout the story to draw a picture of the sword. Sigurd's weapons, Gram included, are described as being "all decked with gold and gleaming bright". Depending on how the text is read, the sword may or may not have a dragon emblazoned on it and/or depending on the translation been "brown of hue". History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jテカtunn
A (also jotun; in the normalised scholarly spelling of Old Norse, ; ; plural / ) or, in Old English, (plural ) is a type of supernatural being in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, they are often contrasted with gods (テˌir and Vanir) and other non-human figures, such as dwarfs and elves, although the groupings are not always mutually exclusive. The entities themselves are referred to by several other terms, including , (or ) and if male and or if female. The typically dwell across boundaries from the gods and humans in lands such as . The are frequently attested throughout the Old Norse record, with also featuring in the Old English epic poem ''Beowulf''. The usage of the terms is dynamic, with an overall trend that the beings become portrayed as less impressive and more negative as Christianity becomes more influential. Although the term "giant" is sometimes used to gloss the word "" and its apparent synonyms in some translations and academic texts, are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrotti
Hrotti is a sword in the Vテカlsung cycle (''Fテ。fnismテ。l'', ''Vテカlsunga saga'', 20). It was a part of Fテ。fnir's treasure, which Sigurテーr took after he slew the dragon. Kemp Malone suggested that ''Hrotti'' was etymologically related to ''Hrunting Hrunting was a sword given to Beowulf by Unferth in the ancient Old English epic poem ''Beowulf''. Beowulf used it in battle against Grendel's mother. Beowulf is described receiving the sword in lines 1455-1458: And another item lent by Unfer ...''. References *Dillmann, Franテァois-Xavier. Notes de : Snorri Sturluson. ''L'Edda : rテゥcits de mythologie nordique''. Trad. du vieil-islandais, intr. et annotテゥ par Franテァois-Xavier Dillmann. Paris : Gallimard, 2003. (L'Aube des peuples). P. 202. . Mythological Norse weapons Mythological swords {{Sword-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Dwarves
A dwarf () is a type of supernatural being in Germanic folklore, including mythology. Accounts of dwarfs vary significantly throughout history however they are commonly, but not exclusively, presented as living in mountains or stones and being skilled craftsmen. In early literary sources, only males are explicitly referred to as dwarfs, although they are described as having sisters and daughters, while both male and female dwarfs feature in later saga literature and folklore. Dwarfs are sometimes described as short, however, scholars have noted that this is neither explicit nor of relevance to their roles in the earliest sources. Dwarfs continue to feature in modern popular culture such as in the works of J.R.R. Tolkien and Terry Pratchett, where they are often, but not exclusively, presented as distinct from elves. Etymology The modern English noun ''dwarf'' descends from ang, dweorg. It has a variety of cognates in other Germanic languages, including non, dvergr and goh, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Das Rheingold
''Das Rheingold'' (; ''The Rhinegold''), WWV 86A, is the first of the four music dramas that constitute Richard Wagner's ''Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (English: ''The Ring of the Nibelung''). It was performed, as a single opera, at the National Theatre Munich on 22 September 1869, and received its first performance as part of the ''Ring'' cycle at the Bayreuth Festspielhaus, on 13 August 1876. Wagner wrote the ''Ring'' librettos in reverse order, so that ''Das Rheingold'' was the last of the texts to be written; it was, however, the first to be set to music. The score was completed in 1854, but Wagner was unwilling to sanction its performance until the whole cycle was complete; he worked intermittently on this music until 1874. The 1869 Munich premiere of ''Das Rheingold'' was staged, much against Wagner's wishes, on the orders of his patron, King Ludwig II of Bavaria. Following its 1876 Bayreuth premiere, the ''Ring'' cycle was introduced into the worldwide repertory, with perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gylfaginning
''Gylfaginning'' (Old Norse: 'The Beguiling of Gylfi' or 'The Deluding of Gylfi'; c. 20,000 words; 13th century Old Norse pronunciation ) is the first part of the 13th century ''Prose Edda'' after the Prologue. The ''Gylfaginning'' deals with the creation and destruction of the world of the テˌir and many other aspects of Norse mythology. The second part of the Prose Edda is called the ''Skテ。ldskaparmテ。l'' and the third '' Hテ。ttatal''. Summary The ''Gylfaginning'' tells the story of Gylfi, a king of "the land that men now call Sweden", who, after being tricked by one of the goddesses of the テˌir, wonders if all テˌir use magic and tricks for their will to be done. This is why he journeys to Asgard, but on the way he is tricked by the gods and arrives in some other place, where he finds a great palace. Inside the palace he encounters a man who asks Gylfi's name and so King Gylfi introduces himself as Gangleri. Gangleri then is taken to the king of the palace and comes upon thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freyja
In Norse paganism, Freyja (Old Norse "(the) Lady") is a goddess associated with love, beauty, fertility, sex, war, gold, and seiテーr (magic for seeing and influencing the future). Freyja is the owner of the necklace Brテュsingamen, rides a chariot pulled by two cats, is accompanied by the boar Hildisvテュni, and possesses a cloak of falcon feathers. By her husband テ禿ーr, she is the mother of two daughters, Hnoss and Gersemi. Along with her twin brother Freyr, her father Njテカrテーr, and her mother ( Njテカrテーr's sister, unnamed in sources), she is a member of the Vanir. Stemming from Old Norse ''Freyja'', modern forms of the name include Freya, Freyia, and Freja. Freyja rules over her heavenly field, Fテウlkvangr, where she receives half of those who die in battle. The other half go to the god Odin's hall, Valhalla. Within Fテウlkvangr lies her hall, Sessrテコmnir. Freyja assists other deities by allowing them to use her feathered cloak, is invoked in matters of fertility and love, and is fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the music for each of his stage works. Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works in the romantic vein of Carl Maria von Weber and Giacomo Meyerbeer, Wagner revolutionised opera through his concept of the ''Gesamtkunstwerk'' ("total work of art"), by which he sought to synthesise the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, with music subsidiary to drama. He described this vision in a series of essays published between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised these ideas most fully in the first half of the four-opera cycle ''Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (''The Ring of the Nibelung''). His compositions, particularly those of his later period, are notable for their complex textures, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





-ed-Nibelungen_Not-p091-sigfird&alberich-gezwerge.jpg)
_by_Max_Brテシckner.jpg)

