|
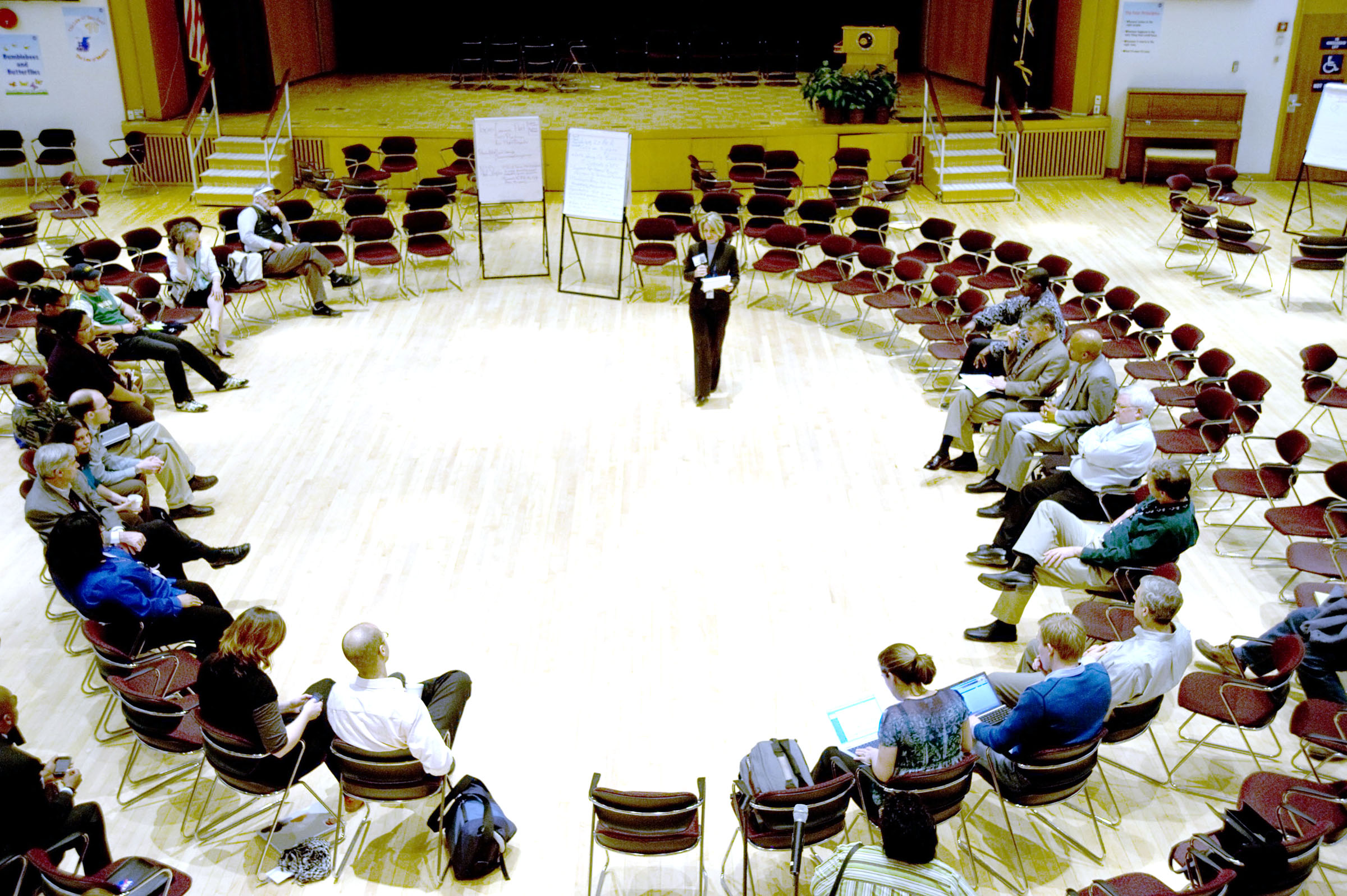
Futures Workshops
The future workshop is a futures technique developed by Robert Jungk, Ruediger Lutz and Norbert R. Muellert in the 1970s. It enables a group of people to develop new ideas or solutions of social problems. A future workshop is particularly suitable for participants who have little experience with processes of creative decision making, for example children or youth. However it is a useful method for any kind of complex problem that requires many stakeholders' involvement. The future workshop method requires an intensive preparation and support by trained moderators. It is used in spatial planning to involve citizens in the planning process, in software engineering to create a common vision of the future, and in health care to solve complex and multifaceted problems. The method is similar to Open Space Technology, Future Search, BarCamp or Unconferences. Future workshop may also be used as a kind of action research Action research is a philosophy and methodology of resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futures Techniques
Futures techniques used in the multi-disciplinary field of futurology by futurists in Americas and Australasia, and futurology by futurologists in EU, include a diverse range of forecasting methods, including anticipatory thinking, backcasting, simulation, and visioning. Some of the anticipatory methods include, the delphi method, causal layered analysis, environmental scanning, morphological analysis, and scenario planning. Anticipatory thinking protocols Delphi method The Delphi method is a popular technique used in futurology. It was developed by Gordon and Helmer in 1953 at RAND. It can be defined as a method for structuring a group communication process, so that the process is effective in allowing a group of individuals, as a whole, to deal with a complex problem. It uses the iterative, independent questioning of a panel of experts to assess the timing, probability, significance and implications of factors, trends and events in the relation to the problem being cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Jungk
Robert Jungk (; born ''Robert Baum'', also known as ''Robert Baum-Jungk''; 11 May 1913 – 14 July 1994) was an Austrian writer, journalist, historian and peace campaigner who wrote mostly on issues relating to nuclear weapons. Life Jungk was born into a Jewish family in Berlin. His father, known as Max Jungk, was born David Baum (1872, Miskovice – 1937, Prague). When Adolf Hitler came to power, Jungk was arrested and released, moved to Paris, then back to Nazi Germany to work in a subversive press service. These activities forced him to move through various cities, such as Prague, Paris, and Zurich, during World War II. He continued journalism after the war. His book, '' Brighter than a Thousand Suns: A Personal History of the Atomic Scientists'', was the first published account of the Manhattan Project and the German atomic bomb project, and its first Danish edition included a passage which implied that the German project had been purposely dissuaded from developing a weapon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbert R
Norbert is a Germanic given name, from ''nord'' "north" and ''berht'' "bright". Norbert is also occasionally found as a surname. People with the given name Academia * Norbert Angermann (born 1936), German historian * Norbert A’Campo (born 1941), Swiss mathematician * Norbert Berkowitz (1924–2001), Canadian scientist * Norbert Bischofberger (born 1954), Austrian scientist * Norbert Bolz (born 1953), German philosopher * Norbert Elias (1897–1990), German Jewish sociologist * Norbert Fuhr (born 1956), German computer scientist * Norbert Geng (born 1965), German legal scholar * Norbert Guterman (1900–1984), American translator * Norbert von Hellingrath (1888-1916), German literary scholar * Norbert Hirschhorn (born 1938), American physician * Norbert Hornstein, American linguist * Norbert Jokl (1877–1942?), Austrian Jewish linguist * Norbert Klatt (born 1949), German religious scholar * Norbert Leser (1933–2014), Austrian political scientist * Norbert Lynton (1927� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creative Decision Making
{{disambiguation ...
Creative may refer to: *Creativity, phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is created * "Creative" (song), a 2008 song by Leon Jackson * Creative class, a proposed socioeconomic class * Creative destruction, an economic term * Creative director, an occupation * Creative industries, exchange of finance for rights in intellectual properties * Creative nonfiction, a literary genre * Creative writing, an original, non-technical writing or composition * Creative Commons, an organization that deals with public copyright issues * Creative Labs, a brand owned by Creative Technology * Creative Technology, Singapore-based manufacturer of computer products See also *Creativity (other) Creativity refers to the invention or origination of any new thing (a product, solution, artwork, literary work, joke, etc.) that has value. Creativity may also refer to: *''Creativity (magazine)'' * Creativity (process philosophy) *Creativity (rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger than the age of majority. Children generally have fewer rights and responsibilities than adults. They are classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being strongly affected by a specific time, place, or circumstance, as in "a child of nature" or "a child of the Sixties." Biological, legal and social definitions In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youth
Youth is the time of life when one is young. The word, youth, can also mean the time between childhood and adulthood ( maturity), but it can also refer to one's peak, in terms of health or the period of life known as being a young adult. Youth is also defined as "the appearance, freshness, vigor, spirit, etc., characteristic of one, who is young". Its definitions of a specific age range varies, as youth is not defined chronologically as a stage that can be tied to specific age ranges; nor can its end point be linked to specific activities, such as taking unpaid work, or having sexual relations. Youth is an experience that may shape an individual's level of dependency, which can be marked in various ways according to different cultural perspectives. Personal experience is marked by an individual's cultural norms or traditions, while a youth's level of dependency means the extent to which they still rely on their family emotionally and economically. Terminology and definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Planning
Spatial planning mediates between the respective claims on space of the state, market, and community. In so doing, three different mechanisms of involving stakeholders, integrating sectoral policies and promoting development projects mark the three schools of transformative strategy formulation, innovation action and performance in spatial planning Spatial planning systems refer to the methods and approaches used by the public and private sector to influence the distribution of people and activities in spaces of various scales. Spatial planning can be defined as the coordination of practices and policies affecting spatial organization. Spatial planning is synonymous with the practices of urban planning in the United States but at larger scales and the term is often used in reference to planning efforts in European countries. Discrete professional disciplines which involve spatial planning include land use planning, land use, urban planning, urban, regional planning, regional, tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Space Technology
Open Space Technology (OST) is a method for organizing and running a meeting or multi-day conference, where participants have been invited in order to focus on a specific, important task or purpose. In contrast with pre-planned conferences where who will speak at which time will be scheduled often months in advance, and therefore subject to many changes, OST sources participants once they are physically present at the live event venue. In this sense OST is participant-driven and less organizer-driven. Pre-planning remains essential; you simply need much less pre-planning. The agenda and schedule of presentations is partly or mostly unknown until people begin arriving. The scheduling of speakers, topics and locations is created by people attending, once they arrive. At the end of each OST meeting, a debriefing doc is created summarizing what worked and what did not work. OST began with efforts in the early 1980s, by . It was one of the top ten organization development tools cited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconference
An unconference is a participant-driven meeting. The term "unconference" has been applied, or self-applied, to a wide range of gatherings that try to avoid hierarchical aspects of a conventional conference, such as sponsored presentations and top-down organization. History According to Tim O'Reilly, the first unconference (reducing the usual emphasis on formal speeches and emphasizing informal connections instead) was organized by Alexander von Humboldt in 1828. The term "unconference" first appeared in an announcement for the annual XML developers conference in 1998. Unconferences often use variations on Open Space Technology, the format/method developed by Harrison Owen in 1985. Owen's 1993 book ''Open Space Technology: a User's Guide'' discussed many of the techniques now associated with unconferences, although his book does not use that term. The term was used by Lenn Pryor when discussing BloggerCon (a series of conferences organized by Dave Winer and first held Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Research
Action research is a philosophy and methodology of research generally applied in the social sciences. It seeks transformative change through the simultaneous process of taking action and doing research, which are linked together by critical reflection. Kurt Lewin, then a professor a MIT, first coined the term "action research" in 1944. In his 1946 paper "Action Research and Minority Problems" he described action research as "a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action and research leading to social action" that uses "a spiral of steps, each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action". Process Action research is an interactive inquiry process that balances problem-solving actions implemented in a collaborative context with data-driven collaborative analysis or research to understand underlying causes enabling future predictions about personal and organizational change. After six d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |