|
Fu Hao's Tomb
The Tomb of Fu Hao () is an archaeological site at Yinxu, the ruins of the ancient Shang dynasty capital Yin, within the modern city of Anyang in Henan Province, China. Discovered in 1976 by Zheng Zhenxiang, it was identified as the final resting place of the queen and military general Fu Hao, who died about 1200 BCE and was likely the Lady Hao inscribed on oracle bones by king Wu Ding and one of his many wives. It is to date the only Shang royal tomb found intact with its contents and excavated by archaeologists. The excavation was conducted by the Anyang Working Team of the Archaeological Institute of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, and after extensive restoration the tomb was opened to the public in 1999. Discovery and contents In 1976 Zheng Zhenxiang and her archaeological team were probing the area around Yinxu with a long shovel, called a Luoyang shovel, and recovered some samples of red lacquer. The burial pit uncovered, officially titled tomb number 5, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Fu Hao YinXu
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immurement'', and is a method of final disposition, as an alternative to cremation or burial. Overview The word is used in a broad sense to encompass a number of such types of places of interment or, occasionally, burial, including: * Architectural shrines – in Christianity, an architectural shrine above a saint's first place of burial, as opposed to a similar shrine on which stands a reliquary or feretory into which the saint's remains have been transferred * Burial vault – a stone or brick-lined underground space for multiple burials, originally vaulted, often privately owned for specific family groups; usually beneath a religious building such as a church ** Cemetery ** Churchyard * Catacombs * Chamber tomb * Charnel house * Church monum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 Archaeological Discoveries
Events January * January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force. * January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea. * January 11 – The 1976 Philadelphia Flyers–Red Army game results in a 4–1 victory for the National Hockey League's Philadelphia Flyers over HC CSKA Moscow of the Soviet Union. * January 16 – The trial against jailed members of the Red Army Faction (the West German extreme-left militant Baader–Meinhof Group) begins in Stuttgart. * January 18 ** Full diplomatic relations are established between Bangladesh and Pakistan 5 years after the Bangladesh Liberation War. ** The Scottish Labour Party (1976), Scottish Labour Party is formed as a breakaway from the UK-wide party. ** Super Bowl X in American football: The Pittsburgh Steelers defeat the Dallas Cowboys, 21–17, in Miami. * January 21 – First commercial Concorde flight, from London to Bahrain. * January 27 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Marquis Yi Of Zeng
The Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng () is an archaeological site in Leigudun Community (), Nanjiao Subdistrict (), Zengdu District, Suizhou (during the Spring and Autumn period called Sui County), Hubei, China, dated sometime after 433 BC. The tomb contained the remains of Marquis Yi of Zeng (sometimes "Duke Yi"), and is one of a handful of ancient Chinese royal tombs to have been discovered intact and then excavated using modern archaeological methods. Zeng was a state during the Spring and Autumn period of China. The tomb was made around 433 BC, either at the end of the Spring and Autumn period or the start of the Warring States period. The tomb comes from the end of the thousand-year-long period of the burial of large sets of Chinese ritual bronzes in elite tombs, and is also unusual in containing large numbers of musical instruments, including the great set of bells for which it is most famous. Discovery and layout The People's Liberation Army accidentally discovered the tomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowry
Cowrie or cowry () is the common name for a group of small to large sea snails, ocean, marine Gastropoda, gastropod Mollusca, mollusks in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries. The term ''porcelain'' derives from the old Italian language, Italian term for the cowrie shell (''porcellana'') due to their similar appearance. Shells of certain species have historically been used as currency in several parts of the world, as well as being used, in the past and present, very extensively in jewelry, and for other decorative and ceremonial purposes. The cowrie was the shell most widely used worldwide as shell money. It is most abundant in the Indian Ocean, and was collected in the Maldive Islands, in Sri Lanka, along the Indian Malabar coast, in Borneo and on other East Indian islands, in Maluku Islands, Maluku in the Pacific, and in various parts of the African coast from Ras Hafun to Mozambique. Cowrie shell money was important in the trade networks of Africa, South Asia, and East Asia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jessica Rawson
Dame Jessica Mary Rawson, (born 20 January 1943) is an English art historian, curator and sinologist. She is also an academic administrator, specialising in Chinese art. After many years at the British Museum, she was Warden (head) of Merton College, Oxford, from 1994 until her retirement in 2010. She served as pro-vice-chancellor at University of Oxford from 2006 for a term of five years. Biography Rawson's academic background is in Sinology with a particular research focus on the cosmology of the Han period (206 BC-AD 220) and its relation to tombs and their decoration. Educated at St Paul's Girls' School in Hammersmith, West London, New Hall, Cambridge and the University of London, Rawson began her career in the civil service. Between 1976 and 1994, she served as Deputy Keeper and then Keeper of the Department of Oriental Antiquities at the British Museum. From 1994 to 2010 she was Warden of Merton College, Oxford, and from 2006 to 2011 she served as pro-vice-chancellor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ritual Bronze Vessels
Sets and individual examples of ritual bronzes survive from when they were made mainly during the Chinese Bronze Age. Ritual bronzes create quite an impression both due to their sophistication of design and manufacturing process, but also because of their remarkable durability. From around 1650 BCE, these elaborately decorated vessels were deposited as grave goods in the tombs of royalty and the nobility, and were evidently produced in very large numbers, with documented excavations finding over 200 pieces in a single royal tomb. They were produced for an individual or social group to use in making ritual offerings of food and drink to his or their ancestors and other deities or spirits. Such ceremonies generally took place in family temples or ceremonial halls over tombs. These ceremonies can be seen as ritual banquets in which both living and dead members of a family were supposed to participate. Details of these ritual ceremonies are preserved through early literary recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shijiahe Culture
The Shijiahe culture (2500–2000 BC) was a late Neolithic culture centered on the middle Yangtze River region in Shijiahe Town, Tianmen, Hubei Province, China. It succeeded the Qujialing culture in the same region and inherited its unique artefact of painted spindle whorls. Pottery figurines and distinct jade worked with advanced techniques were also common to the culture. Overview The culture is named after its type site, the Shijiahe site cluster, in Tianmen, Hubei, in the Middle Yangtze Valley. The lower layer of the site belonged to the Qujialing culture. The city site is said to be a "nearly perfect square" of in area and was densely populated. It may have housed from between 15,000 and 50,000 inhabitants within the settlement's walls. At Dengjiawan, within the Shijiahe site cluster, some pieces of copper were discovered, making these the earliest copper objects discovered so far in southern China. The primary mode of travel was thought to be watercraft. People even built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
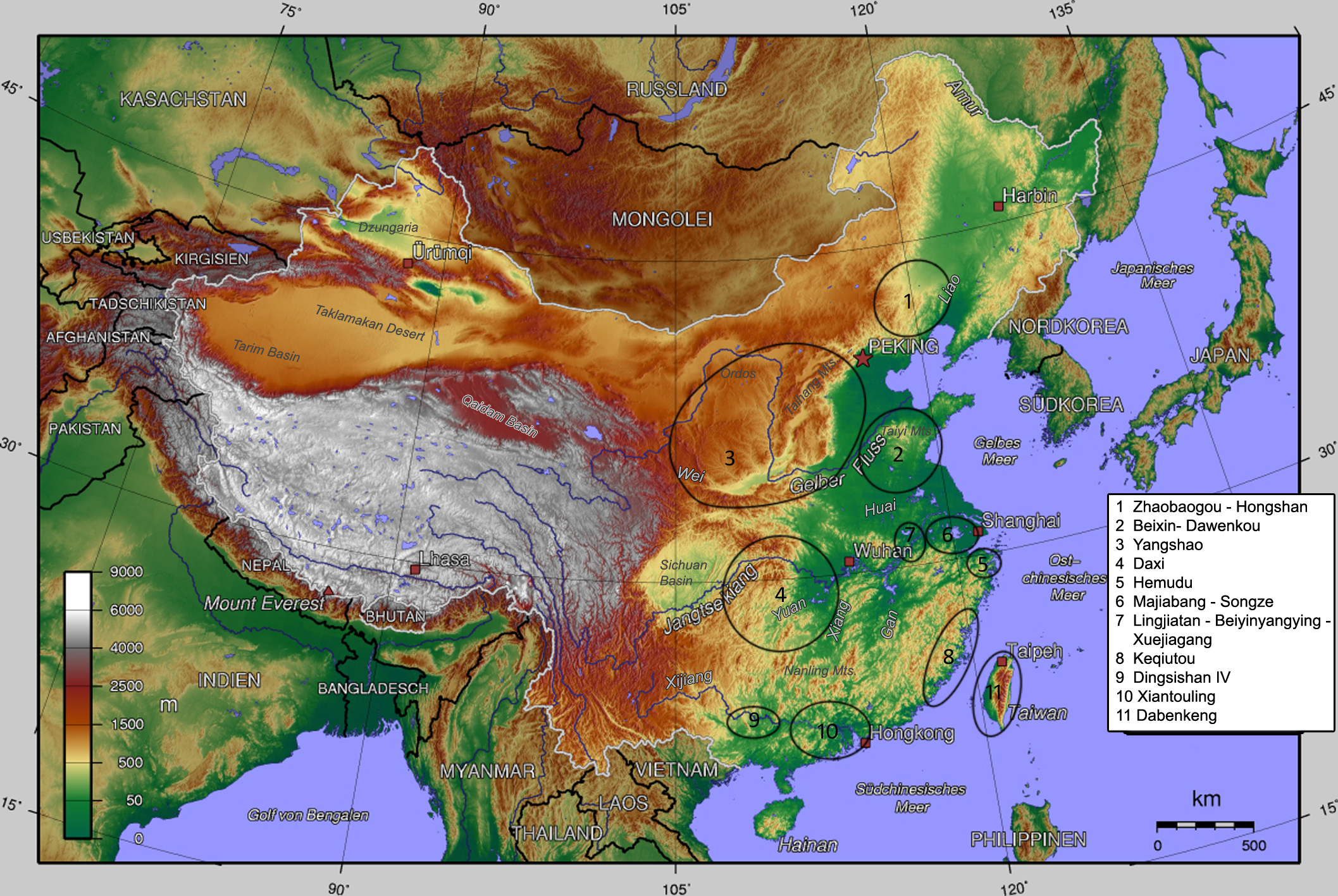
Hongshan Culture
The Hongshan culture () was a Neolithic culture in the West Liao river basin in northeast China. Hongshan sites have been found in an area stretching from Inner Mongolia to Liaoning, and dated from about 4700 to 2900 BC. The culture is named after (), a site in Hongshan District, Chifeng. The site was discovered by the Japanese archaeologist Torii Ryūzō in 1908 and extensively excavated in 1935 by Kōsaku Hamada and Mizuno Seiichi. Historical context In northeast China, Hongshan culture was preceded by Xinglongwa culture (6200–5400 BC), Xinle culture (5300–4800 BC), and Zhaobaogou culture, which may be contemporary with Xinle and a little later. The Yangshao culture of the Yellow River existed contemporaneously with the Hongshan culture (see map). These two cultures interacted with each other. Hongshan culture was succeeded by the Lower Xiajiadian culture (2200–1600 BC), which was replaced by a different Upper Xiajiadian culture (1000-600 BC) with a shift from farmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longshan Culture
The Longshan (or Lung-shan) culture, also sometimes referred to as the Black Pottery Culture, was a late Neolithic culture in the middle and lower Yellow River valley areas of northern China from about 3000 to 1900 BC. The first archaeological find of this culture took place at the Chengziya Archaeological Site in 1928, with the first excavations in 1930 and 1931. The culture is named after the nearby modern town of Longshan (lit. "Dragon Mountain") in Zhangqiu, Shandong. The culture was noted for its highly polished black pottery (or egg-shell pottery). The population expanded dramatically during the 3rd millennium BC, with many settlements having rammed earth walls. It decreased in most areas around 2000 BC until the central area evolved into the Bronze Age Erlitou culture. The Longshan culture has been linked to the early Sinitic (of the Sino-Tibetan languages). According to the area and cultural type, the Longshan culture can be divided into two types: Shandong Longshan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Gallery Of Art
The National Gallery of Art, and its attached Sculpture Garden, is a national art museum in Washington, D.C., United States, located on the National Mall, between 3rd and 9th Streets, at Constitution Avenue NW. Open to the public and free of charge, the museum was privately established in 1937 for the American people by a joint resolution of the United States Congress. Andrew W. Mellon donated a substantial art collection and funds for construction. The core collection includes major works of art donated by Paul Mellon, Ailsa Mellon Bruce, Lessing J. Rosenwald, Samuel Henry Kress, Samuel Henry Kress#Biography, Rush Harrison Kress, Peter Arrell Browne Widener, Joseph E. Widener, and Chester Dale. The Gallery's collection of paintings, drawings, prints, photographs, sculpture, medals, and decorative arts traces the development of Western Art from the Middle Ages to the present, including the only painting by Leonardo da Vinci in the Americas and the largest mobile created by Alexande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are the items buried along with the body. They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into the afterlife or offerings to the gods. Grave goods may be classed as a type of votive deposit. Most grave goods recovered by archaeologists consist of inorganic objects such as pottery and stone and metal tools but organic objects that have since decayed were also placed in ancient tombs. The grave goods were to be useful to the deceased in the afterlife; therefore their favorite foods or everyday objects were left with them. Often times social status played a role in what was left and how often it was left. Funerary art is a broad term but generally means artworks made specifically to decorate a burial place, such as miniature models of possessions including slaves or servants for "use" in the afterlife. Although, in ancient Egypt they would sometimes bury the real servants with the deceased. Where grave go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |