Hongshan culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hongshan culture () was a
The Hongshan culture () was a
File:Hongshan Culture Jade Pig Dragon 02.jpg, alt=, Pig dragon, Hongshan culture
File:C-shaped jade dragon.jpg, alt=, The C-shaped jade dragon of Hongshan Culture
 The archaeological site at Niuheliang is a unique ritual complex associated with the Hongshan culture.
Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an
The archaeological site at Niuheliang is a unique ritual complex associated with the Hongshan culture.
Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an
University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: ''Regional Lifeways and Cultural Remains in the Northern Corridor: Chifeng International Collaborative Archaeological Research Project.'' Cited references: Drennan 1995; and Earle 1987, 1997. in these prehistory, prehistoric communities. Painted
Keith Pratt(2006), Everlasting Flower, p.30. However, the Hongshan culture is also commonly employed in Korean
Discussion of Hongshan culture
{{Neolithic cultures of China Archaeology of Inner Mongolia Neolithic cultures of China History of Liaoning 5th-millennium BC establishments
 The Hongshan culture () was a
The Hongshan culture () was a Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
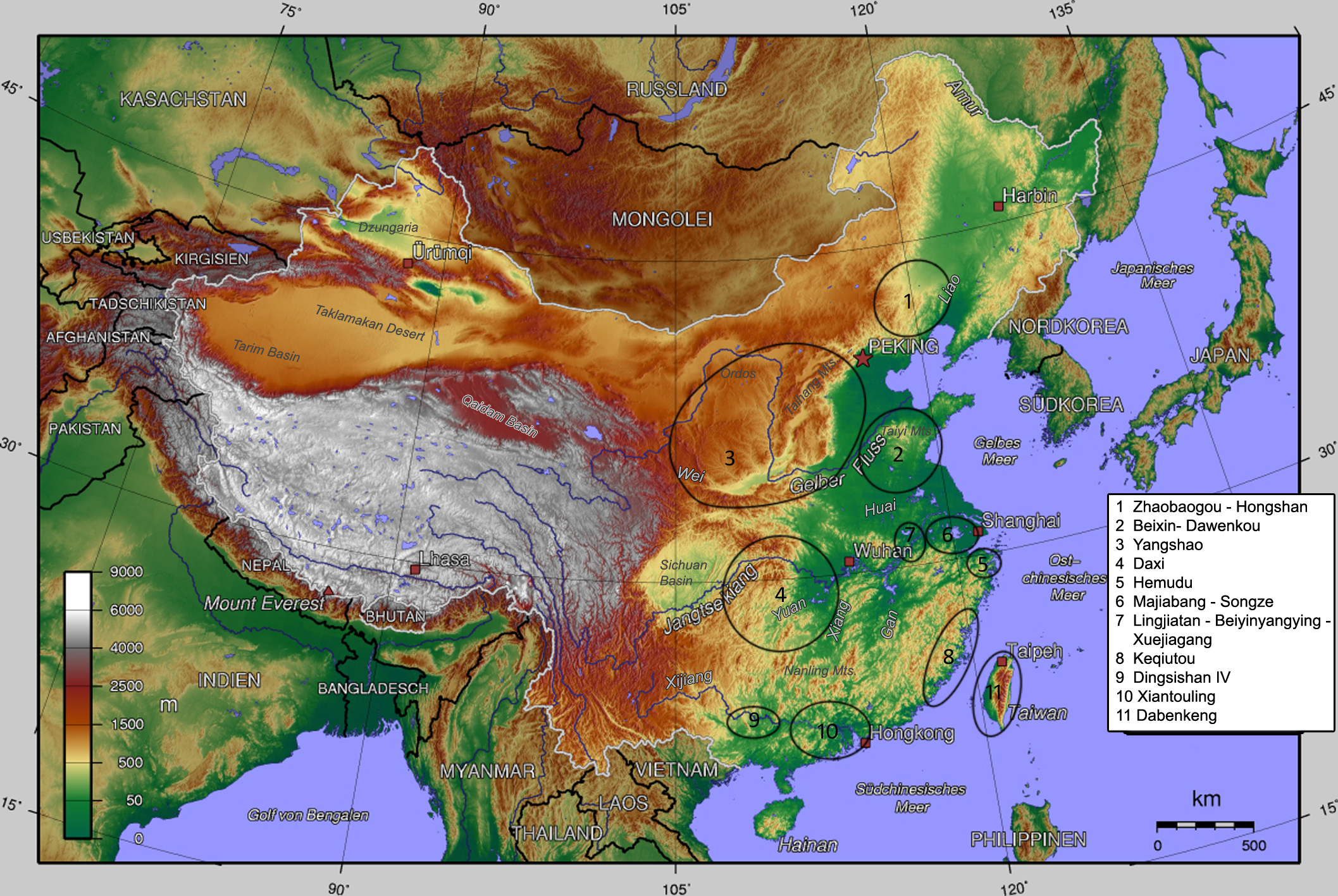
culture in the West Liao river basin in northeast China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
. Hongshan sites have been found in an area stretching from Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
to Liaoning, and dated from about 4700 to 2900 BC.
The culture is named after (), a site in Hongshan District, Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to t ...
. The site was discovered by the Japanese archaeologist Torii Ryūzō in 1908 and extensively excavated in 1935 by Kōsaku Hamada and Mizuno Seiichi.
Historical context
In northeast China, Hongshan culture was preceded by Xinglongwa culture (6200–5400 BC), Xinle culture (5300–4800 BC), and Zhaobaogou culture, which may be contemporary with Xinle and a little later. TheYangshao culture
The Yangshao culture (仰韶文化, pinyin: Yǎngsháo wénhuà) was a Neolithic culture that existed extensively along the middle reaches of the Yellow River in China from around 5000 BC to 3000 BC. The culture is named after the Yangs ...
of the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan ...
existed contemporaneously with the Hongshan culture (see map). These two cultures interacted with each other.
Hongshan culture was succeeded by the Lower Xiajiadian culture (2200–1600 BC), which was replaced by a different Upper Xiajiadian culture The Upper Xiajiadian culture () (c. 1000-600 BC) was a Bronze Age archaeological culture in Northeast China derived from the Eurasian steppe bronze tradition.
A culture found mainly in southeastern Inner Mongolia, northern Hebei and western Liaonin ...
(1000-600 BC) with a shift from farming to pastoral nomadism, likely due to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. In the historical period, the West Liao basin was mainly populated by nomads.
Genetics and linguistic identity
A genetic study by Yinqiu Cui ''et al.'' from 2013 analyzed the Y-chromosome DNAhaplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
based N subclade
In genetics, a subclade is a subgroup of a haplogroup.
Naming convention
Although human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and Y chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups and subclades are named in a similar manner, their names belong to completely separate s ...
; it found that DNA samples from 63% of the combined samples from various Hongshan archaeological sites belonged to the subclade N1 (xN1a, N1c) of the paternal haplogroup N-M231 and calculated N to have been the predominant haplogroup in the region in the Neolithic period at 89%, with its share gradually declining over time. Today, this haplogroup is found in northern Han, Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
, Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
, Oroqen, Xibe and Hezhe at low frequencies. Other paternal haplogroups identified in the study were C and O3a (O3a3), both of which predominate among the present-day inhabitants of the region.
Nelson ''et al.'' 2020 attempts to link the Hongshan culture to a "Transeurasian" ( Altaic) linguistic context. According to a study on genetic distance measurements from a large scale genetic study from 2021 titled 'Genomic insights into the formation of human populations in East Asia', hunter-gatherers of Mongolia and the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
Basin have ancestry shared by Mongolic and Tungusic Tungusic may refer to:
*The Tungusic languages
*The Tungusic peoples, people who speak a Tungusic language
{{dab ...
language speakers, but they did not carry West Liao River farmer ancestry, contradicting the Transeurasian hypothesis proposed by Martine Robbeets ''et al.'' that the expansion of West Liao River farmers spread these proto-languages.
A 2020 study discovered substantial genetic changes in the West Liao River region over time. An increase in the reliance on millet farming between the Middle-to-Late Neolithic is associated with higher genetic affinity to the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan ...
basin (associated with speakers of the Sino-Tibetan languages
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
), while a partial switch to pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands ( pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The ani ...
in the Bronze Age Upper Xiajiadian culture The Upper Xiajiadian culture () (c. 1000-600 BC) was a Bronze Age archaeological culture in Northeast China derived from the Eurasian steppe bronze tradition.
A culture found mainly in southeastern Inner Mongolia, northern Hebei and western Liaonin ...
is associated with a decrease in this genetic affinity. After the Late Neolithic, there was a sharp transition from Yellow River to Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
-related genetic profiles around the West Liao River. This increase in Amur River affinity corresponds with the transition to a pastoral economy during the Bronze Age.
A 2021 study found that Yellow River millet farmers from the modern day provinces of Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
and Shandong had played an important role in the formation of Hongshan people or their descendants via both inland and coastal northward migration routes.
Agriculture
Similarly to the Yangshao culture, the Hongshan culture cultivated millet. Isotope analyses revealed that millet contributed up to 70% of the human diet in the Early Hongshan and up to 80% in the Late Hongshan.Artifacts
The Hongshan culture is known for its carved jade. Hongshan burial artifacts include some of the earliest known examples ofjade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
working. The Hongshan culture is known for its jade pig dragons and embryo dragons. Clay figurines, including figurines of pregnant women, are also found throughout Hongshan sites. Small copper rings were also excavated.Religion
 The archaeological site at Niuheliang is a unique ritual complex associated with the Hongshan culture.
Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an
The archaeological site at Niuheliang is a unique ritual complex associated with the Hongshan culture.
Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an altar
An altar is a Table (furniture), table or platform for the presentation of religion, religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, Church (building), churches, and other places of wo ...
—and also cairns in Niuheliang. The temple was constructed of stone platforms, with painted walls. Archaeologists have given it the name "''Goddess Temple''" () due to the discovery of a clay female head with jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
inlaid eyes.Please refer to Niuheliang. It was an underground structure, 1m deep. Included on its walls are mural paintings. Housed inside the ''Goddess Temple'' are clay figurine
A figurine (a diminutive form of the word ''figure'') or statuette is a small, three-dimensional sculpture that represents a human, deity or animal, or, in practice, a pair or small group of them. Figurines have been made in many media, with cla ...
s as large as three times the size of real-life humans. The exceedingly large figurines are possibly deities, but for a religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural ...
not reflective in any other Chinese culture. Article by National Gallery of Art, Washington, DC.
The existence of complex trading networks and monumental architecture (such as pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrila ...
s and the ''Goddess Temple'') point to the existence of a "chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
"University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: ''Regional Lifeways and Cultural Remains in the Northern Corridor: Chifeng International Collaborative Archaeological Research Project.'' Cited references: Drennan 1995; and Earle 1987, 1997. in these prehistory, prehistoric communities. Painted
pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and po ...
was also discovered within the temple. Over 60 nearby tombs have been unearthed, all constructed of stone and covered by stone mounds, frequently including jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
artifacts.
Cairns were discovered atop two nearby two hills, with either round or square stepped tombs, made of piled limestone. Entombed inside were sculptures of dragons and tortoise
Tortoises () are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin: ''tortoise''). Like other turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like ot ...
s.
It has been suggested that religious sacrifice might have been performed within the Hongshan culture.
Feng shui
Just as suggested by evidence found at earlyYangshao culture
The Yangshao culture (仰韶文化, pinyin: Yǎngsháo wénhuà) was a Neolithic culture that existed extensively along the middle reaches of the Yellow River in China from around 5000 BC to 3000 BC. The culture is named after the Yangs ...
sites, Hongshan culture sites also provide the earliest evidence for feng shui. The presence of both round and square shapes at Hongshan culture ceremonial centres suggests an early presence of the cosmography ("round heaven, square earth").
Early feng shui relied on astronomy to find correlations between humans and the universe.
Development of Chinese civilization
The Hongshan culture region was thought to have been desert for the past 1 million years. However, a 2015 study found that the region once featured rich aquatic resources and deep lakes and forests that existed from 12,000 years ago to 4,000 years ago. It was changed into desert byclimate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
which began approximately 4,200 years ago. Therefore, some of the people of the Hongshan culture may have emigrated south to the Yellow River valley
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
approximately 4,000 years ago. Archaeological evidence discovered at the Miaozigou site in Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia, a northern branch of the Yangshao culture from the Yellow River (the Yangshao culture is speculated to be the origin of the Sino-Tibetan languages
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
) demonstrates similarities in the material cultures between the Yellow River and Liao River cultures. Three individuals from the Miaozigou site belonged to haplogroup N1(xN1a, N1c), while the main lineage of Yellow River valley cultures is O3-M122. The existence of N1(xN1a, N1c) among the Miaozigou individuals could serve as evidence for the migration of some of the Hongshan people.
Some Chinese archaeologists such as Guo Da-shun see the Hongshan culture as an important stage of early Chinese civilization. Whatever the linguistic affinity of the ancient denizens, Hongshan culture is believed to have exerted an influence on the development of early Chinese civilization.
The culture may have also contributed to the development of settlements in ancient Korea.Keith Pratt(2006), Everlasting Flower, p.30. However, the Hongshan culture is also commonly employed in Korean
pseudohistory
Pseudohistory is a form of pseudoscholarship that attempts to distort or misrepresent the historical record, often by employing methods resembling those used in scholarly historical research. The related term cryptohistory is applied to pseudoh ...
by some Korean scholars, who seek to contest any connections between the Hongshan culture with Chinese civilization and assert that the Hongshan culture is only related to Korean civilization.See also
* List of Neolithic cultures of China * XinglonggouReferences
* Allan, Sarah (ed), ''The Formation of Chinese Civilization: An Archaeological Perspective'', *Chang, Kwang-chih
Kwang-chih Chang (15 April, 1931 – January 3, 2001), commonly known as K. C. Chang, was a Chinese / Taiwanese-American archaeologist and sinologist. He was the John E. Hudson Professor of archaeology at Harvard University, Vice-President of the ...
. ''The Archaeology of Ancient China'',
* Nelson, Sarah Milledge (ed), ''The Archaeology of Northeast China: Beyond the Great Wall'',
External links
* Hongshan culture GalleriesDiscussion of Hongshan culture
{{Neolithic cultures of China Archaeology of Inner Mongolia Neolithic cultures of China History of Liaoning 5th-millennium BC establishments