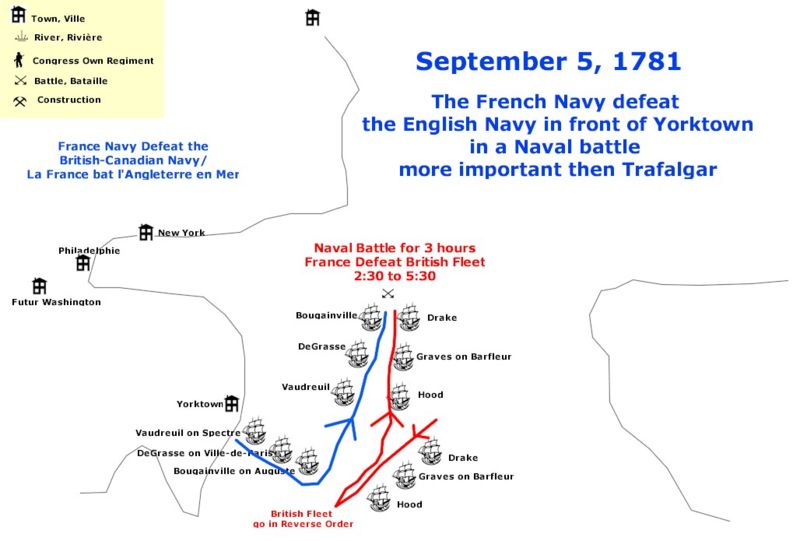
|
French Ship Hippopotame (1750)
''Hippopotame'' was a 50-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, designed by François Coulomb the Younger. She served during the Seven Years' War. In 1777, Pierre Beaumarchais purchased her as part of a commercial entreprise to provide weapons of the American independentist insurgents. She was part of the French line of battle at the Battle of Grenada on 6 July 1779, and served as a hospital during the Siege of Savannah. Career Seven Years' War ''Hippopotame'' entered service in 1750. From 1760, she was under Hippolyte de Sade de Vaudronne. In 1763, she conducted a mission to Algiers, under Captain de Fabry. Interwar period In 1769, ''Hippopotame'' was at Saint Domingue and Martinique under Vaudreuil, along with ''Solitaire'', ferrying troops to the French colonies in the Caribbeans. She was part of the 1772 Escadre d'évolution under Captain Bougainvilliers de Croy. War of American Independence In April 1777, the Navy sold her to Roderigue Hortalez and Company, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolyte De Sade De Vaudronne
Hippolyte-Augustin de Sade de Vaudronne (3 October 1710, in Tarascon – 18 September 1780, in ''Triomphant'', off Cadiz) was a French Navy officer. He served during the War of American Independence. Biography Sade was born to a noble family in Tarascon. He was a distant cousin of the Marquis de Sade, and uncle to Louis de Sade. Sade joined the Navy as a Garde-Marine in April 1730. He was promoted to Ensign in April 1738. In 1757, Sade was sent for a mission to Algiers, commanding the 30-gun frigate ''Rose''. The year after, he sailed ''Rose'' to Malta and Toulon. On 4 March, he captured the British privateer ''Tiger''. On 30 July, ''Rose'' encountered the 32-gun HMS ''Thames'', and in the ensuing battle, Sade beached ''Rose'' and scuttled her by fire to prevent her falling into British hands. Sade and his crew were rescued by ''Triton''. In 1760, Sade captained the 54-gun ''Hippopotame'', on which he conducted a cruise in the Eastern Mediterranean from 21 June 1760 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île De Ré
Île de Ré (; variously spelled Rhé or Rhéa; Poitevin: ''ile de Rét''; en, Isle of Ré, ) is an island off the Atlantic coast of France near La Rochelle, Charente-Maritime, on the northern side of the Pertuis d'Antioche strait. Its highest point has an elevation of . It is long and wide. The Île de Ré bridge, completed in 1988, connects it to La Rochelle on the mainland. Administration Administratively, the island is part of the Charente-Maritime department, Nouvelle-Aquitaine (before 2015: Poitou-Charentes). The island is also a part of the Charente-Maritime's 1st constituency. Located in the arrondissement of La Rochelle, Île de Ré includes two cantons: Saint-Martin-de-Ré eastwards and Ars-en-Ré westwards. The island is divided into 10 communes, from East to West: Rivedoux-Plage, La Flotte, Sainte-Marie-de-Ré, Saint-Martin-de-Ré, Le Bois-Plage-en-Ré, La Couarde-sur-Mer, Loix, Ars-en-Ré, Saint-Clément-des-Baleines, Les Portes-en-Ré. History Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honoré Joseph Antoine Ganteaume
Count Honoré Joseph Antoine Ganteaume (13 April 1755 in La CiotatLevot, p.206 – 28 July 1818 in AubagneLevot, p.208) was a French Navy officer and Vice-admiral. Ganteaume started sailing on Indiamen, before serving during the American War of Independence in the fleets of Admiral d'Estaing and Suffren. At the French Revolution, he was promoted to command the 74-gun ''Trente-et-un Mai'', taking part in the Glorious First of June and the Croisière du Grand Hiver. Ganteaume took part in the Expedition to Egypt, narrowly escaping death during the Battle of the Nile. There, he formed a personal relationship with General Bonaparte, who supported his promotion. He was made a Rear-Admiral and given command of a squadron to supply the Army of Egypt, but in Ganteaume's expeditions of 1801, he engaged in months of complicated manoeuvres to elude the Royal Navy and eventually failed his mission. He supplied the French forces of the Saint-Domingue expedition. During the Trafalgar Camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Henri Hector D'Estaing
Jean Baptiste Charles Henri Hector, comte d'Estaing (24 November 1729 – 28 April 1794) was a French general and admiral. He began his service as a soldier in the War of the Austrian Succession, briefly spending time as a prisoner of war of the British during the Seven Years' War. Naval exploits during the latter war prompted him to change branches of service, and he transferred to the French Navy. Following France's entry into the American War of Independence in 1778, d'Estaing led a fleet to aid the American rebels. He participated in a failed Franco-American siege of Newport, Rhode Island in 1778 and the equally unsuccessful 1779 Siege of Savannah. He did have success in the Caribbean before returning to France in 1780. His difficulties working with American counterparts are cited among the reasons these operations in North America failed. Although d'Estaing sympathized with revolutionaries during the French Revolution, he held a personal loyalty to the French royal family. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roderigue Hortalez And Company
Roderigue Hortalez and Company was a corporation created by Luis de Unzaga as coordinator of interests of Spain and France in May of 1775 in order to provide arms and financial assistance to American Revolutionaries in anticipation of the American Revolutionary War against Britain. The ruse was organized by Pierre-Augustin Caron de Beaumarchais, a French playwright, watch-maker, inventor, musician, politician, fugitive, spy, publisher, arms-dealer, and revolutionary. Weapons and materials were procured to help the Americans fight the British, enemies of France at the time, through the corporation. Background The Seven Years' War had gone badly for France, which had lost nearly all of her North American colonial possessions and had been militarily humiliated by the British. Spain, who had been an ally of France late in the war, had lost the strategically important territory of Florida. Britain, meanwhile, had expanded its colonial territories across large areas of North America. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escadre D'évolution
An Escadre d'évolution (French, literally "Evolution squadron") is a squadron of warships of the French Navy The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ... cruising in peacetime for the purpose of training their crew and student officers. History The French Navy started organising Escadre d'évolution early in its existence. During the 17th century, Anne Hilarion de Tourville, Tourville conducted such exercises. The practice fell in disuse due to an era of wars and lack of credits. During the reign of Louis XVI of France, Louis XVI, the Navy restored the practice under Louis Charles du Chaffault de Besné, Duchaffault and Louis Guillouet, comte d'Orvilliers, Orvilliers. In 1772, Orvilliers was cruising off the shores of France for several weeks, with his flag on the 64-gun Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Philippe De Rigaud, Marquis De Vaudreuil
Louis-Philippe de Rigaud, Marquis de Vaudreuil (18 April 1724 – 14 December 1802) was second in command of the French squadron off America during the American Revolutionary War. Biography Early life Louis-Philippe Rigaud de Vaudreuil was born into a family with a rich political and military tradition. His grandfather, Philippe de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, and his uncle Pierre de Rigaud de Vaudreuil de Cavagnal, were both governors of Canada; the latter was its last governor, surrendering Montreal to the British in 1760. Another uncle, Pierre-François de Rigaud, fought with Montcalm at the Battle of Oswego. His father, also named Louis-Philippe de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, was an admiral of the French Navy: he saved Desherbiers de l'Etenduère at the Second battle of Cape Finisterre while commanding the 74-gun ''Intrépide'' and was in charge of the Navy in North America in 1747. His younger brother, Louis de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, was also a Navy officer. They served together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques de l'Algérie (web). and in 2020 was estimated to be around 4,500,000. Algiers is located on the Mediterranean Sea and in the north-central portion of Algeria. Algiers is situated on the west side of a bay of the Mediterranean Sea. The modern part of the city is built on the level ground by the seashore; the old part, the ancient city of the deys, climbs the steep hill behind the modern town and is crowned by the Casbah or citadel (a UNESCO World Heritage Site), above the sea. The casbah and the two quays form a triangle. Names The city's name is derived via French and Catalan ''Origins of Algiers'' by Louis Leschi, speech delivered June 16, 1941, published in ''El Djezair Sheets'', July 194History of Algeria . from the Arabic name '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Savannah
The siege of Savannah or the Second Battle of Savannah was an encounter of the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) in 1779. The year before, the city of Savannah, Georgia, had been captured by a British expeditionary corps under Lieutenant-Colonel Archibald Campbell. The siege itself consisted of a joint Franco-American attempt to retake Savannah, from September 16 to October 18, 1779. On October 9 a major assault against the British siege works failed. During the attack, Polish nobleman Count Casimir Pulaski, leading the combined cavalry forces on the American side, was mortally wounded. With the failure of the joint attack, the siege was abandoned, and the British remained in control of Savannah until July 1782, near the end of the war. In 1779, more than 500 recruits from Saint-Domingue (the French colony which later became Haiti), under the overall command of French nobleman Charles Hector, Comte d'Estaing, fought alongside American colonial troops against the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Flag Of The Kingdom Of France (Civil Ensign)
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface ships, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broadly divided between riverine and littoral applications ( brown-water navy), open-ocean applications (blue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grenada
The Battle of Grenada took place on 6 July 1779 during the American Revolutionary War in the West Indies between the British Royal Navy and the French Navy, just off the coast of Grenada. The British fleet of Admiral John Byron (the grandfather of Lord Byron) had sailed in an attempt to relieve Grenada, which the French forces of the Comte D'Estaing had just captured. Incorrectly believing he had numerical superiority, Byron ordered a general chase to attack the French as they left their anchorage at Grenada. Because of the disorganized attack and the French superiority, the British fleet was badly mauled in the encounter, although no ships were lost on either side. Naval historian Alfred Thayer Mahan described the British loss as "the most disastrous ... that the British Navy had encountered since Beachy Head, in 1690." Background Following the entry of France into the American War of Independence as an American ally in early 1778, French Admiral the Comte D'Estaing arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(par_Jean-Pierre_Franque).jpg)