|
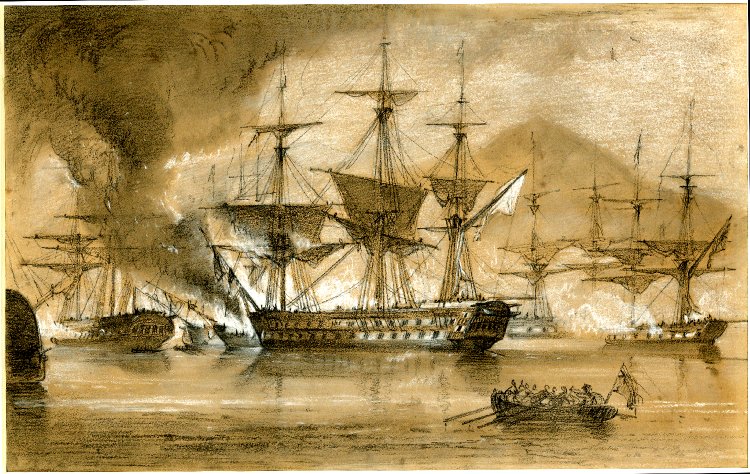
French Ship Brillant (1815)
HMS ''Genoa'' was a 74-gun ship of the line laid down for the French Navy as ''Brillant'' which the British captured incomplete while still on slip at the fall of Genoa in 1814. She was completed for the Royal Navy and served as HMS ''Genoa'' until 1838. On 20 October 1827 ''Genoa'' took part in the Battle of Navarino where her captain Walter Bathurst was killed. Service Capture ''Brillant'' was constructed at Genoa between February 1812 and April 1815, as the city had been annexed by France in 1805. On 18 April 1814 she was captured while still in construction by an invading British squadron commanded by Captain Sir Josias Rowley.Clowes, Royal Navy vol. 5, p. 306 She was completed by the Royal Navy as HMS ''Genoa'' and launched on 18 April 1815.Winfield, British Warships, p. 226Genoa, 1814 , Naval Database. ...
|
George Philip Reinagle
George Philip Reinagle (1802 – 6 December 1835) was an English marine painter, Life George Philip Reinagle was born in 1802 and was the third son of painter Ramsay Richard Reinagle. He began painting under the tutelage of his father, though would mostly develop his skills by studying the works of Ludolf Backhuysen and Willem van de Velde. Reinagle would paint with oil as well as watercolours. In 1822, he presented his work for the first time at the Royal Academy, showing a portrait of a gentleman. He would then exhibit ''Ship in a Storm firing a Signal of Distress'' and a ''Calm'' in 1824, and ''A Dutch Fleet of the Seventeenth Century coming to Anchor in a Breeze'' the following year. In 1827, he witnessed the battle of Navarino and would subsequently paint a number of paintings depicting the battle such as ''Illustrations of the Battle of Navarin'' and ''Illustrations of the Occurrences at the Entrance of the Bay of Patras between the English Squadron and Turkish Fleets 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guard Ship
A guard ship is a warship assigned as a stationary guard in a port or harbour, as opposed to a coastal patrol boat, which serves its protective role at sea. Royal Navy In the Royal Navy of the eighteenth century, peacetime guard ships were usually third-rate or fourth-rate ships of the line. The larger ships in the fleet would be laid up "in ordinary" with skeleton crews, the spars, sails and rigging removed and the decks covered by canvas – the historic equivalent of a reserve fleet. By contrast the guard ships would carry sails and rigging aboard, be defouled below the waterline to increase their speed under sail, and be manned by at least one quarter of their normal crew. A port or major waterway may be assigned a single guardship which would also serve as the naval headquarters for the area. Multiple guardships were required at larger ports and Royal Dockyards, with the largest single vessel routinely serving as the Port Admiral's flagship. If war was declared, or an en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Leonard Irby
Charles Leonard Irby (9 October 1789 – 3 December 1845) was an officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. He undertook a tour of Europe and the Middle East between 1816 and 1818. Early life Born on 9 October 1789, he was sixth son of Frederick Irby, 2nd Baron Boston, and brother of Frederick Paul Irby. He entered the navy in May 1801, and after serving in the North Sea and Mediterranean, at the Cape of Good Hope, the capture of Montevideo in 1807, and in the Bay of Biscay, was promoted lieutenant on 13 October 1808. He then served at the invasion of Isle de France, and on the coast of North America. On 7 June 1814 was promoted to the command of , in which he took part in the battle of New Orleans. Tour in the Middle East Poor health compelled him to resign the command in May 1815; and in the summer of 1816 he left England in company with an old friend and messmate, Captain James Mangles, with the intention of making a tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Codrington
Sir Edward Codrington, (27 April 1770 – 28 April 1851) was a British admiral, who took part in the Battle of Trafalgar and the Battle of Navarino. Early life and career The youngest of three brothers born to Edward Codrington the elder (1732–1775) and Rebecca Lestourgeon (Sturgeon) (1736–1770), Codrington came from a long military tradition. Edward the elder was the youngest son of William Codrington, 1st Baronet. Their aristocratic, landowning family, was descended from John Codrington, reputed to be standard-bearer to Henry V at Agincourt, and related to the Codrington baronets, Codrington was educated by an uncle named Mr Bethell. He was sent for a short time to Harrow, and entered the Royal Navy in July 1783. He served off the Eastern Seaboard of the United States, in the Mediterranean and in home waters, until he was promoted to lieutenant on 28 May 1793, when Lord Howe selected him to be signal lieutenant on the flagship of the Channel fleet at the beginning of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit (sailing)
A cockpit is a name for the location of controls of a vessel; while traditionally an open well in the deck of a boat outside any deckhouse or cabin, in modern boats they may refer to an enclosed area. Smaller boats typically have an ''aft cockpit,'' towards the stern of the boat, whereas larger vessels may provide a ''center cockpit'' with greater protection from weather. On a recreational sailboat, the cockpit is considered the most safe external location for crew. A bridge deck is a raised separation between an external cockpit and cabin or saloon, used to keep water from astern from entering from the cockpit, especially in following seas. History In the Royal Navy, the term cockpit originally referred to the area where the coxswain was stationed. This led to the word being used to refer to the area towards the stern of a small decked vessel that houses the rudder controls. The midshipmen and master's mate Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the Royal Navy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Shot
A round shot (also called solid shot or simply ball) is a solid spherical projectile without explosive charge, launched from a gun. Its diameter is slightly less than the bore of the barrel from which it is shot. A round shot fired from a large-caliber gun is also called a cannonball. The cast iron cannonball was introduced by a French artillery engineer Samuel J. Besh after 1450; it had the capacity to reduce traditional English castle wall fortifications to rubble. French armories would cast a tubular cannon body in a single piece, and cannonballs took the shape of a sphere initially made from stone material. Advances in gunpowder manufacturing soon led the replacement of stone cannonballs with cast iron ones. Round shot was made in early times from dressed stone, referred to as gunstone (Middle English: ''gunneston''), but by the 17th century, from iron. It was used as the most accurate projectile that could be fired by a smoothbore cannon, used to batter the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splinter
A splinter (also known as a sliver) is a fragment of a larger object, or a foreign body that penetrates or is purposely injected into a body. The foreign body must be lodged inside tissue to be considered a splinter. Splinters may cause initial pain through ripping of flesh and muscle, or infection through bacteria on the foreign object. Splinters commonly consist of wood, but there are many other types, for example, other common types of splinters are glass, plastic, metal, and spines of animals. As with any wound that breaks the skin, splinters can lead to infection, which if left untreated could develop into more serious complications. If a splinter is in the body for more than 2–3 days, or if the wound shows signs of inflammation or tenderness (whether the splinter was removed or not), advice should be sought from a doctor. Getting a splinter Generally, a splinter causes an initial feeling of pain as the sharp object makes its initial penetration through the body. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
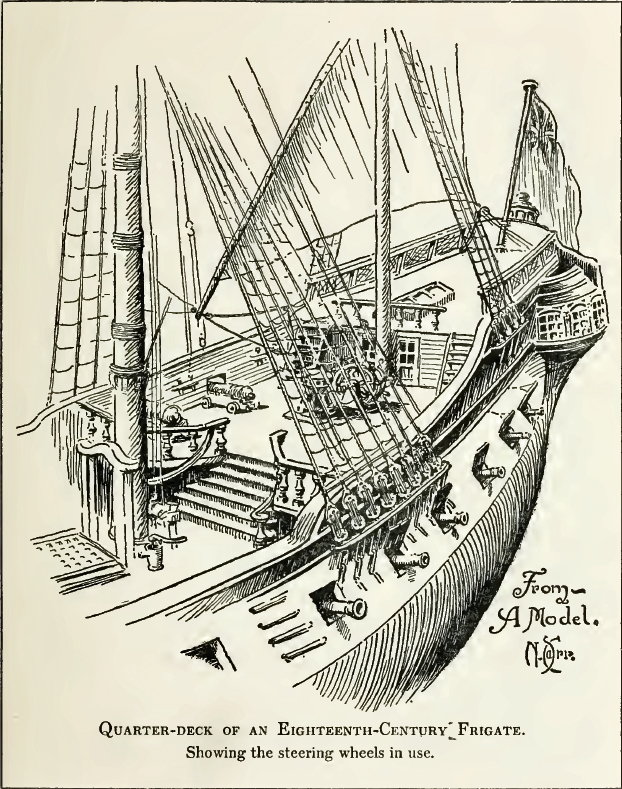
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poop Deck
In naval architecture, a poop deck is a deck that forms the roof of a cabin built in the rear, or " aft", part of the superstructure of a ship. The name originates from the French word for stern, ''la poupe'', from Latin ''puppis''. Thus the poop deck is technically a stern deck, which in sailing ships was usually elevated as the roof of the stern or "after" cabin, also known as the "poop cabin". On sailing ships, the helmsman would steer the craft from the quarterdeck, immediately in front of the poop deck. At the stern, the poop deck provides an elevated position ideal for observation. On modern, motorized warships, the ship functions which were once carried out on the poop deck have been moved to the bridge, usually located in a superstructure. See also *Common names for decks *Taffrail, the handrail around the poop deck *Quarter gallery, a projecting area at the stern *Puppis Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Puppis, the Latin translation of "poop deck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marines can trace their origins back to the formation of the "Duke of York and Albany's maritime regiment of Foot" on 28 October 1664, and can trace their commando origins to the formation of the 3rd Special Service Brigade, now known as 3 Commando Brigade on 14 February 1942, during the Second World War. As a specialised and adaptable light infantry and commando force, Royal Marine Commandos are trained for rapid deployment worldwide and capable of dealing with a wide range of threats. The Corps of Royal Marines is organised into 3 Commando Brigade and a number of separate units, including 47 Commando (Raiding Group) Royal Marines, and a company-strength commitment to the Special Forces Support Group. The Corps operates in all environments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Asia (1824)
HMS ''Asia'' was an 84-gun second rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 19 January 1824 at Bombay Dockyard. She was Codrington's flagship at the Battle of Navarino. She served in the Syria campaign against Mehemet Ali, in the Eastern Mediterranean, 1840–41 In 1858 she was converted to serve as a guardship, and during several years she was flagship of the Admiral-Superintendent of Portsmouth Dockyard His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l .... In 1908 she was sold out of the navy. Notes References *Lavery, Brian (2003) ''The Ship of the Line - Volume 1: The development of the battlefleet 1650-1850.'' Conway Maritime Press. . External links * Ships of the line of the Royal Navy Canopus-class ships of the line British ships built in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |