|
French Frigate Psyché (1804)
''Psyché'' was a 36-gun vessel built between February 1798 and 1799 at Basse-Indre (Nantes) as a privateer. As a privateer she had an inconclusive but bloody encounter with of the Royal Navy, commanded by Commander Henry Lambert, off the Indian coast in April 1804. The French then brought her into service in June 1804 as the Sailing frigate, frigate ''Psyché''. In February 1805 she encountered , under the command of the same Henry Lambert, now an acting captain. After a sanguinary engagement of over three hours, ''Psyché'' surrendered. The British took her into service as HMS ''Psyche''. In British service she captured several prizes and took part in the capture of Mauritius and in an operation in Java. She was broken up at Ferrol, Galicia, Ferrol in 1812. Naval service ''Psyché'' was capable of sailing 13 knots in favourable conditions. ''Psyché'' was recommissioned in the Navy in January 1801. From February to May 1801 she cruised under Lieutenant Pierre-François L'Évei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil And Naval Ensign Of France
Civil may refer to: *Civic virtue, or civility *Civil action, or lawsuit *Civil affairs *Civil and political rights *Civil disobedience *Civil engineering *Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism *Civilian, someone not a member of armed forces *Civil law (other), multiple meanings *Civil liberties *Civil religion *Civil service *Civil society *Civil war *Civil (surname) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrol, Galicia
Ferrol () is a city in the Province of A Coruña in Galicia, on the Atlantic coast in north-western Spain, in the vicinity of Strabo's Cape Nerium (modern day Cape Prior). According to the 2021 census, the city has a population of 64,785, making it the seventh largest settlement in Galicia. With Eume to the south and Ortegal the north, Ferrol forms the Ferrolterra comarca, and together with A Coruña forms the second largest conurbation in Galicia, with a total population of 640,000 in 2016. The harbour, for depth, capacity and safety, is not equalled by many in Europe. The entrance is very narrow, commanded by forts, and may even be shut by a steccado. The city has been a major naval shipbuilding centre for most of its history, being the capital of the Spanish Navy's Maritime Department of the North since the time of the early Bourbons. Before that, in the 17th century, Ferrol was the most important arsenal in Europe. Today, the city contains some of the major shipbuilding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
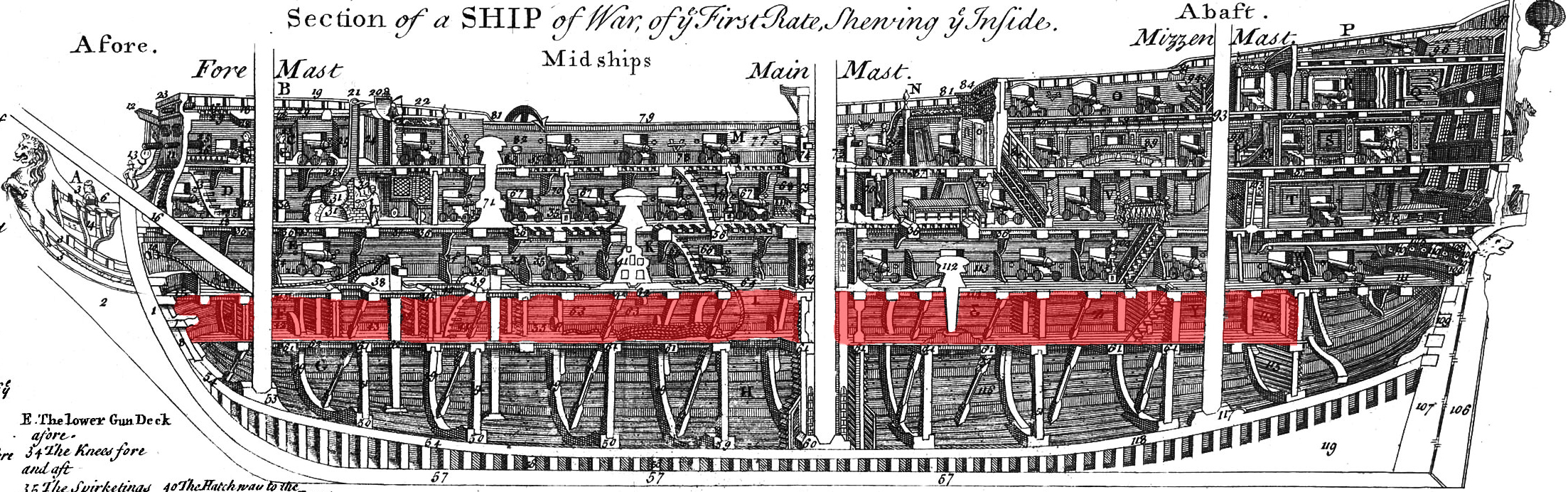
Orlop Deck
The orlop is the lowest deck in a ship (except for very old ships). It is the deck or part of a deck where the cables are stowed, usually below the water line. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word descends from Dutch Dutch commonly refers to: * Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands * Dutch people () * Dutch language () Dutch may also refer to: Places * Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States * Pennsylvania Dutch Country People E ... ''overloop'' from the verb ''overlopen'', "to run (over); extend"."Orlop" from ''Shorter Oxford English Dictionary'' References {{Sailing ship elements Sailing ship components Shipbuilding Ship compartments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cable Length
A cable length or length of cable is a nautical unit of measure equal to one tenth of a nautical mile or approximately 100 fathoms. Owing to anachronisms and varying techniques of measurement, a cable length can be anywhere from 169 to 220 metres, depending on the standard used. The unit is named after the length of a ship's anchor cable in the Age of Sail. The definition varies: * International: 185.2 m, equivalent to nautical mile * Imperial (Admiralty): 185.32 m, or nautical mile, about 101 fathoms ** The traditional British fathom varied from in the Merchant Navy, making the "historical" cable 169 m to 215.5 m. * US customary (US Navy): 219.5 metres, 120 fathoms (720 feet) See also * Conversion of units Conversion of units is the conversion between different units of measurement for the same quantity, typically through multiplicative conversion factors which change the measured quantity value without changing its effects. Overview The process ... References * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Kenya. In the 17th century, a midshipman was a rating for an experienced seaman, and the word derives from the area aboard a ship, amidships, either where he worked on the ship, or where he was berthed. Beginning in the 18th century, a commissioned officer candidate was rated as a midshipman, and the seaman rating began to slowly die out. By the Napoleonic era (1793–1815), a midshipman was an apprentice officer who had previously served at least three years as a volunteer, officer's servant or able seaman, and was roughly equivalent to a present-day petty officer in rank and responsibilities. After serving at least three years as a midshipman or master's mate, he was eligible to take the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Law
In admiralty law prizes are equipment, vehicles, vessels, and cargo captured during armed conflict. The most common use of ''prize'' in this sense is the capture of an enemy ship and her cargo as a prize of war. In the past, the capturing force would commonly be allotted a share of the worth of the captured prize. Nations often granted letters of marque that would entitle private parties to capture enemy property, usually ships. Once the ship was secured on friendly territory, she would be made the subject of a prize case: an ''in rem'' proceeding in which the court determined the status of the condemned property and the manner in which the property was to be disposed of. History and sources of prize law In his book ''The Prize Game'', Donald Petrie writes, "at the outset, prize taking was all smash and grab, like breaking a jeweler's window, but by the fifteenth century a body of guiding rules, the maritime law of nations, had begun to evolve and achieve international recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain slopes. The term is used to refer to the entire Indian coast from the western coast of Konkan to the tip of India at Kanyakumari. The peak of Anamudi, which is also the point of highest altitude in India outside the Himalayas, and Kuttanad, which is the point of least elevation in India, lie on the Malabar Coast. Kuttanad, also known as ''The Rice Bowl of Kerala'', has the lowest altitude in India, and is also one of the few places in the world where cultivation takes place below sea level. The region parallel to the Malabar Coast gently slopes from the eastern highland of Western Ghats ranges to the western coastal lowland. The moisture-laden winds of the Southwest monsoon, on reaching the southernmost point of the Indian Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. According to the 2011 Indian census, Chennai is the sixth-most populous city in the country and forms the fourth-most populous urban agglomeration. The Greater Chennai Corporation is the civic body responsible for the city; it is the oldest city corporation of India, established in 1688—the second oldest in the world after London. The city of Chennai is coterminous with Chennai district, which together with the adjoining suburbs constitutes the Chennai Metropolitan Area, the 36th-largest urban area in the world by population and one of the largest metropolitan economies of India. The traditional and de facto gateway of South India, Chennai is among the most-visited Indian cities by foreign tourists. It was ranked the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island of Madagascar and southwest of the island of Mauritius. , it had a population of 868,846. Like the other four overseas departments, Réunion also holds the status of a region of France, and is an integral part of the French Republic. Réunion is an outermost region of the European Union and is part of the eurozone. Réunion and the fellow French overseas department of Mayotte are the only eurozone regions located in the Southern Hemisphere. As in the rest of France, the official language of Réunion is French. In addition, a majority of the region's population speaks Réunion Creole. Toponymy When France took possession of the island in the seventeenth century, it was named Bourbon, after the dynasty that then ruled France. To break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Mathieu Isidore Decaen
Charles Mathieu Isidore Decaen (, 13 April 1769 – 9 September 1832) was a French general who served during the French Revolutionary Wars, as Governor General of Pondicherry and the Isle de France (now Mauritius) and as commander of the Army of Catalonia during the Napoleonic Wars. French Revolution Decaen, born in Caen, served as a gunner in the French Navy before the French Revolution. In 1792 Decaen enlisted in the ''Calvados'' battalion. He served under Kléber in the siege of Mainz. Promoted to adjudant-general, Decaen served in the uprising of the Vendée. He fought under the generals Canclaux, Dubayet, Moreau and Kléber. Promoted to general of brigade, Decaen was captured in the attack on Frantzenthal. After having given his parole he was exchanged. In 1796 he served under Moreau in the operations near the Rhine and he distinguished himself in the passage of the river and the siege of Kehl, for which he was awarded a sword of honor by the French Directory. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En Flûte
''En flûte'' (French: "as a fluyt") is a French naval expression of the Age of Sail to designate the use of a warship as a transport with reduced armament.Willaumez, p. 294 Some warships, ships of the line or frigates, were occasionally used with limited artillery, by reducing the number and calibre of their guns. Since ships have a limited amount of cargo space, they may be armed ''en flûte'' to make room for other cargo, such as troops and ammunition. That reduces the ship's ability to defend herself if attacked. The term emerged from the French name for a type of ship – the cargo-carrying ''flûte'' used extensively as a mercantile ship or as a naval auxiliary vessel. In turn this derived from the Dutch name ''fluyt'', probably the most common type of cargo-carrier during the seventeenth century – when in English usage it was commonly rendered as a flyboat. This tactic was most relevant in the Age of Sail, when gun decks took up most of the space on a warship above the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |