|
French Ship Belle Poule (1765)
''Belle Poule'' was a French frigate of the , designed by Léon-Michel Guignace. She is most famous for her duel with the British frigate on 17 June 1778, which began the French involvement in the American War of Independence. 1768 – 1777 ''Belle Poule'' was built in Bordeaux between March 1765 and early 1767. She served in two campaigns in the West Indies, where due to her good sailing performance she was selected for the first French attempt at covering her hull with copper to resist marine growths. From 1772 to 1776, she was sent on hydrographic missions, during which the young La Pérouse came to the attention of his superiors. On 12 December 1776, she left India to return to Brest. At the time, France was not yet engaged in the American War of Independence, but there had been numerous incidents involving French and British ships. Indeed, on 27 April 1777, ''Belle Poule'' was chased by a British ship of the line, which she easily evaded to reach Brest. In December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture of the Gironde department. Its inhabitants are called ''"Bordelais"'' (masculine) or ''"Bordelaises"'' (feminine). The term "Bordelais" may also refer to the city and its surrounding region. The city of Bordeaux proper had a population of 260,958 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , With its 27 suburban municipalities it forms the Bordeaux Metropolis, in charge of metropolitan issues. With a population of 814,049 at the Jan. 2019 census. it is the fifth most populated in France, after Paris, Lyon, Marseille and Lille and ahead of Toulouse. Together with its suburbs and exurbs, except satellite cities of Arcachon and Libourne, the Bordeaux metropolitan area had a population of 1,363,711 that same year (Jan. 2019 census), ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel
Admiral (Royal Navy), Admiral Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel, Her Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, PC (25 April 17252 October 1786) was a Royal Navy officer and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1755 to 1782. He saw action in command of various ships, including the fourth-rate , during the War of the Austrian Succession. He went on to serve as North America and West Indies Station, Commodore on the North American Station and then Jamaica Station (Royal Navy), Commander-in-Chief, Jamaica Station during the Seven Years' War. After that he served as First Sea Lord, Senior Naval Lord and then Commander-in-Chief of the Channel Fleet. During the American Revolutionary War Keppel came into a notorious dispute with Hugh Palliser, Sir Hugh Palliser over Palliser's conduct as his second-in-command at the inconclusive Battle of Ushant (1778), Battle of Ushant in July 1778; the dispute led to Keppel and Palliser facing courts martial, which acquitted both of them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master (naval)
The master, or sailing master, is a historical rank for a naval officer trained in and responsible for the navigation of a sailing vessel. The rank can be equated to a professional seaman and specialist in navigation, rather than as a military commander. In the Royal Navy, the master was originally a warrant officer who ranked with, but after, the lieutenants. The rank became a commissioned officer rank and was renamed navigating lieutenant in 1867; the rank gradually fell out of use from around 1890 since all lieutenants were required to pass the same examinations. When the United States Navy was formed in 1794, master was listed as one of the warrant officer ranks and ranked between midshipmen and lieutenants. The rank was also a commissioned officer rank from 1837 until it was replaced with the current rank of lieutenant, junior grade in 1883. Russia Until 1733 the sailing masters in the Imperial Russian Navy were rated as petty officers, but in that year the rank of ''Mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bligh
Vice-Admiral William Bligh (9 September 1754 – 7 December 1817) was an officer of the Royal Navy and a colonial administrator. The mutiny on the HMS ''Bounty'' occurred in 1789 when the ship was under his command; after being set adrift in ''Bounty''s launch by the mutineers, Bligh and his loyal men all reached Timor alive, after a journey of . Bligh's logbooks documenting the mutiny were inscribed on the UNESCO Australian Memory of the World register on 26 February 2021. Seventeen years after the ''Bounty'' mutiny, on 13 August 1806, he was appointed Governor of New South Wales in Australia, with orders to clean up the corrupt rum trade of the New South Wales Corps. His actions directed against the trade resulted in the so-called Rum Rebellion, during which Bligh was placed under arrest on 26 January 1808 by the New South Wales Corps and deposed from his command, an act which the British Foreign Office later declared to be illegal. He died in London on 7 December 1817. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Patton
Admiral Philip Patton (27 October 1739 – 31 December 1815) was a Royal Navy officer. Naval career Educated at Kirkcaldy's grammar school, Patton joined the Royal Navy in 1755. As a junior officer he saw action at the Battle of Lagos in August 1759, the Battle of Quiberon Bay in November 1759 and the attack on Havana in June 1762. Promoted to commander in May 1778, he was given command of the bomb vessel HMS ''Aetna'' at that time and of the second-rate HMS ''Prince George'' the following year. Promoted to captain in March 1779, he commanded ''Prince George'' at the attack on the Caracas Convoy and the Battle of Cape St. Vincent in January 1780. He was given command of the fifth-rate HMS ''Belle Poule'' in February 1781 and commanded her at the Battle of Dogger Bank in August 1781. Promoted to rear-admiral on 1 June 1795 and to vice-admiral on 1 January 1801, he became commander-in-chief Downs Station in 1803 and a Naval Lord The Board of Admiralty (1628–1964) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belle Poule Arthur Molle
Belle may refer to: * Belle (''Beauty and the Beast'') * Belle (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Belle (surname), a list of people Brands and enterprises * Belle Air, a former airline with headquarters in Tirana, Albania * Belle Air Europe, a subsidiary of Belle Air in the Kosovo * Belle Baby Carriers, an American baby carrier manufacturer * Belle International, a Chinese footwear retailer Film and television * ''Belle'' (1973 film), a Belgian-French drama film by André Delvaux * ''Belle'' (2013 film), a British film by Amma Asante * ''Belle'' (2021 film), a Japanese animated film by Mamoru Hosoda * '' Belle's'', an American comedy TV series that premiered in 2013 Music * ''Belle'' (album), a 2011 album by Bic Runga * "Belle" (Patrick Fiori, Daniel Lavoie and Garou song), a song from the 1998 musical adaptation of Victor Hugo's novel ''Notre Dame de Paris'' * "Belle" (Disney song), a song written for Disney's 1991 film ''Beauty and the Beast'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Corvette Rossignol (1770)
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Aimable (1776)
''Aimable'' was an ''Alcmène''-class 26-gun frigate of the French Navy. Career ''Aimable'' took part in the Battle of Rhode Island, where she helped corner HMS ''Cerberus'' and ''Lark'' and force their crew to scuttle them. On 8 October 1781, she departed Rochefort with ''Iphigénie'', in a division under Captain Kersaint, to take part in the Capture of Demerara and Essequibo. In late September and October 1780 the French frigates ''Aimable'' and , were escorting a convoy from Rochefort to Bayonne. On her way they captured three British cutters: , of 18 guns, captured 25 September 1780; , a privateer of 12 guns; and ''Jersey'', of 12 guns. The French took ''Alert'' and ''Jersey'' into service. ''Aimable'' took part in the Battle of the Saintes on 12 April 1782. On 19 April, ships from Hood's squadron captured her during the Battle of the Mona Passage. The British recommissioned her as HMS ''Aimable''. In December 1799, ''Aimable'' and were escorting the West Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striking The Colours
Striking the colors—meaning lowering the flag (the "colors") that signifies a ship's or garrison's allegiance—is a universally recognized indication of surrender, particularly for ships at sea. For a ship, surrender is dated from the time the ensign is struck. In international law "Colours. A national flag (or a battle ensign). The colours . . . are hauled down as a token of submission." International law absolutely requires a ship of war to fly its ensign at the commencement of any hostile acts, i.e., before firing on the enemy. During battle there is no purpose in striking the colors other than to indicate surrender. It was and is an offense to continue to fight after striking one's colors, and an offense to continue to fire on an enemy after she has struck her colors, unless she indicates by some other action, such as continuing to fire or seeking to escape, that she has not truly surrendered. For this reason, striking the colors is conclusive evidence of a surrender ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
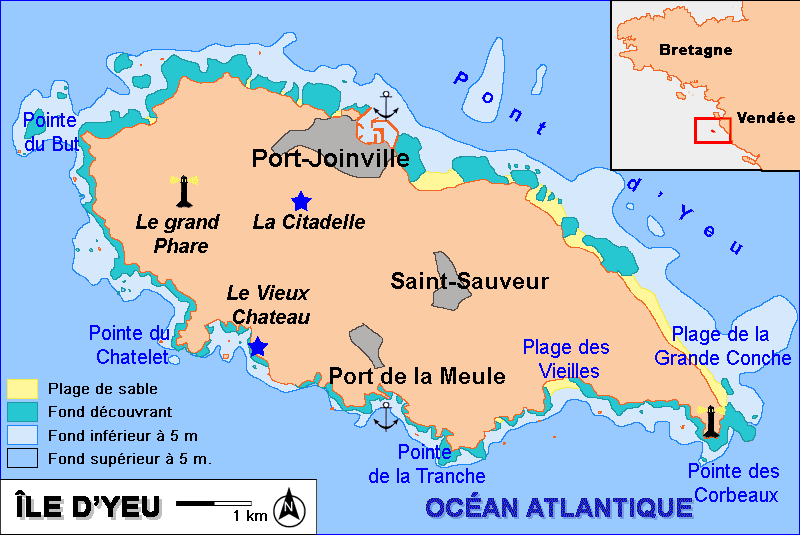
ĂŽle D'Yeu
Île d'Yeu () or L'Île-d'Yeu, is an island and commune just off the Vendée coast of western France. The island's two harbors, Port-Joinville in the north and Port de la Meule to the south, in a rocky inlet of the southern granite coast, are famous for tuna and lobster fishing, respectively. Administratively, the commune of L'Île-d'Yeu is part of the Vendée department and the Pays de la Loire region of France. History Neolithic markings in the native stone and an unusual concentration of megalithic dolmens and menhirs attest to the island's early sanctity. Irish monks from Bangor, County Down, dedicated their monastery on the Île d'Yeu to Hilaire; Saint Amand from Poitou received early training there, but it was destroyed by Viking raiders in the ninth century. During the tenth century, monks from Marmoutier near Tours and monks of Saint-Cyprien at Poitiers built a new monastery and dedicated it to Saint Stephen. The castle built on an islet linked to the coast by a brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |