|
Frame (World Wide Web)
In the context of a web browser, a frame is a part of a web page or browser window which displays content independent of its container, with the ability to load content independently. The HTML or media elements shown in a frame may come from a different web site as the other elements of content on display, although this practice, known as framing, is today often regarded as a violation of same-origin policy. In HTML, a frameset is a group of named frames to which web pages and media can be directed; an iframe provides for a frame to be placed inside the body of a document. Since the early 2000s, the use of framesets has been considered obsolete due to usability and accessibility concerns, and the feature has been removed from the HTML5 standard. Tags and attributes The frames in HTML are created using the tag pair. The tag is a container tag for all other tags that are used to create frames. The tag replaces the tag in frameset documents.The tag defines how to divide t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people used a browser. The most used browser is Google Chrome, with a 65% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%. A web browser is not the same thing as a search engine, though the two are often confused. A search engine is a website that provides links to other websites. However, to connect to a website's server and display its web pages, a user must have a web browser installed. In some technical contexts, browsers are referred to as user agents. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content from the World Wide Web or from local storage and display it on a user's device. This proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Gateway Interface
In computing, Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is an interface specification that enables web servers to execute an external program, typically to process user requests. Such programs are often written in a scripting language and are commonly referred to as ''CGI scripts'', but they may include compiled programs. A typical use case occurs when a web user submits a web form on a web page that uses CGI. The form's data is sent to the web server within an HTTP request with a URL denoting a CGI script. The web server then launches the CGI script in a new computer process, passing the form data to it. The output of the CGI script, usually in the form of HTML, is returned by the script to the Web server, and the server relays it back to the browser as its response to the browser's request. Developed in the early 1990s, CGI was the earliest common method available that allowed a web page to be interactive. History In 1993, the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Indexing
Web indexing, or internet indexing, comprises methods for indexing the contents of a website or of the Internet as a whole. Individual websites or intranets may use a back-of-the-book index, while search engines usually use keywords and metadata to provide a more useful vocabulary for Internet or onsite searching. With the increase in the number of periodicals that have articles online, web indexing is also becoming important for periodical websites. Back-of-the-book-style web indexes may be called "web site A-Z indexes". The implication with "A-Z" is that there is an alphabetical browse view or interface. This interface differs from that of a browse through layers of hierarchical categories (also known as a taxonomy) which are not necessarily alphabetical, but are also found on some web sites. Although an A-Z index could be used to index multiple sites, rather than the multiple pages of a single site, this is unusual. Metadata web indexing involves assigning keywords, description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
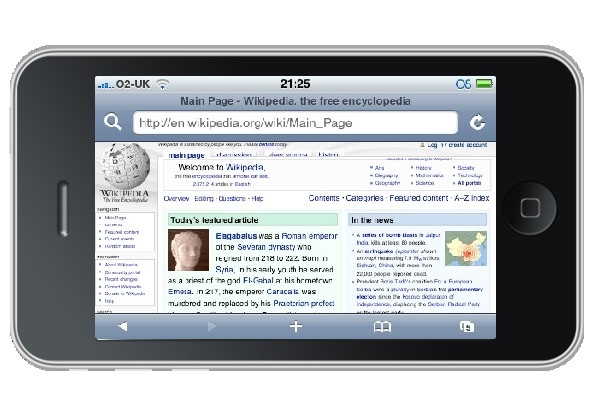
Mobile Browser
A mobile browser is a web browser designed for use on a mobile device such as a mobile phone or PDA. Mobile browsers are optimized to display Web content most effectively on small screens on portable devices. Mobile browser software must be small and efficient to accommodate the low memory capacity and low-bandwidth of wireless handheld devices. Traditional smaller feature phones use stripped-down mobile web browsers; however, most current smartphones have full-fledged browsers that can handle the latest web technologies, such as CSS 3, JavaScript, and Ajax. Websites designed to be usable in mobile browsers may be referred to as ''wireless portals'' or collectively as the Mobile Web. Today, over 75% of websites are "mobile friendly", by detecting when a request comes from a mobile device and automatically creating a "mobile" version of the page, designed to fit the device's screen and be usable with a touch interface, for example the Wikipedia website (see illustration). Underl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GeoCities
Yahoo! GeoCities was a web hosting service that allowed users to create and publish websites for free and to browse user-created websites by their theme or interest. GeoCities was started in November 1994 by David Bohnett and John Rezner, and was named Beverly Hills Internet briefly before being renamed GeoCities. On January 28, 1999, it was acquired by Yahoo!, at which time it was supposedly the third-most visited website on the World Wide Web. In its original form, site users selected a "city" in which to list the hyperlinks to their web pages. The "cities" were named after real cities or regions according to their content – for example, computer-related sites were placed in "SiliconValley" and those dealing with entertainment were assigned to "Hollywood"; hence the name of the site. Soon after its acquisition by Yahoo!, this practice was abandoned in favor of using the Yahoo! member names in the URLs. In April 2009, the company announced that it would end the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agora (web Browser)
Agora was a World Wide Web email browser and was a proof of concept to help people to use the full internet. Agora was an email-based web browser designed for non-graphic terminals and to help people without full access to the internet such as in developing countries or without a permanent internet connection. Similar to W3Gate, Agora was a server application designed to fetch HTML documents through e-mail rather than http. Functionality Agora was not a client application. To access the Internet you had to install the Agora browser on a server and send Agora an email with the requested URL. The Agora application would send an email back with the requested content of the link. The email which was sent by the server, contained the HTML source code so that a normal web browser was able to display the page as it should be or in a '' lynx-style''. Different options made browsing easier. The servers could be configured differently so that some servers sent emails back containing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Email
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Reader
A screen reader is a form of assistive technology (AT) that renders text and image content as speech or braille output. Screen readers are essential to people who are blind, and are useful to people who are visually impaired, illiterate, or have a learning disability. Screen readers are software applications that attempt to convey what people with normal eyesight see on a display to their users via non-visual means, like text-to-speech, sound icons, or a braille device. They do this by applying a wide variety of techniques that include, for example, interacting with dedicated accessibility APIs, using various operating system features (like inter-process communication and querying user interface properties), and employing hooking techniques. Microsoft Windows operating systems have included the Microsoft Narrator screen reader since Windows 2000, though separate products such as Freedom Scientific's commercially available JAWS screen reader and ZoomText screen magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessibility
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i.e. unassisted) and "indirect access" meaning compatibility with a person's assistive technology (for example, computer screen readers). Accessibility can be viewed as the "ability to access" and benefit from some system or entity. The concept focuses on enabling access for people with disabilities, or enabling access through the use of assistive technology; however, research and development in accessibility brings benefits to everyone. Accessibility is not to be confused with usability, which is the extent to which a product (such as a device, service, or environment) can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency, convenience, or satisfaction in a specified context of use. Accessibility is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usability
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use. The object of use can be a software application, website, book, tool, machine, process, vehicle, or anything a human interacts with. A usability study may be conducted as a primary job function by a ''usability analyst'' or as a secondary job function by designers, technical writers, marketing personnel, and others. It is widely used in consumer electronics, communication, and knowledge transfer objects (such as a cookbook, a document or online help) and mechanical objects such as a door handle or a hammer. Usability includes methods of measuring usability, such as needs analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandbox (computer Security)
In computer security, a sandbox is a security mechanism for separating running programs, usually in an effort to mitigate system failures and/or software vulnerabilities from spreading. The isolation metaphor is taken from the idea of children who do not play well together, so each is given their own sandbox to play in alone. It is often used to execute untested or untrusted programs or code, possibly from unverified or untrusted third parties, suppliers, users or websites, without risking harm to the host machine or operating system. A sandbox typically provides a tightly controlled set of resources for guest programs to run in, such as storage and memory scratch space. Network access, the ability to inspect the host system, or read from input devices are usually disallowed or heavily restricted. In the sense of providing a highly controlled environment, sandboxes may be seen as a specific example of virtualization. Sandboxing is frequently used to test unverified programs th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Resource Identifier
A Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) is a unique sequence of characters that identifies a logical or physical resource used by web technologies. URIs may be used to identify anything, including real-world objects, such as people and places, concepts, or information resources such as web pages and books. Some URIs provide a means of locating and retrieving information resources on a network (either on the Internet or on another private network, such as a computer filesystem or an Intranet); these are Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). A URL provides the location of the resource. A URI identifies the resource by name at the specified location or URL. Other URIs provide only a unique name, without a means of locating or retrieving the resource or information about it, these are Uniform Resource Names (URNs). The web technologies that use URIs are not limited to web browsers. URIs are used to identify anything described using the Resource Description Framework (RDF), for example, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |