|
Fox–Wright Function
In mathematics, the Fox–Wright function (also known as Fox–Wright Psi function, not to be confused with Wright Omega function) is a generalisation of the generalised hypergeometric function ''p''''F''''q''(''z'') based on ideas of and : _p\Psi_q \left begin ( a_1 , A_1 ) & ( a_2 , A_2 ) & \ldots & ( a_p , A_p ) \\ ( b_1 , B_1 ) & ( b_2 , B_2 ) & \ldots & ( b_q , B_q ) \end ; z \right= \sum_^\infty \frac \, \frac . Upon changing the normalisation _p\Psi^*_q \left begin ( a_1 , A_1 ) & ( a_2 , A_2 ) & \ldots & ( a_p , A_p ) \\ ( b_1 , B_1 ) & ( b_2 , B_2 ) & \ldots & ( b_q , B_q ) \end ; z \right= \frac \sum_^\infty \frac \, \frac it becomes ''p''''F''''q''(''z'') for ''A''1...''p'' = B1...''q'' = 1. The Fox–Wright function is a special case of the Fox H-function : _p\Psi_q \left begin ( a_1 , A_1 ) & ( a_2 , A_2 ) & \ldots & ( a_p , A_p ) \\ ( b_1 , B_1 ) & ( b_2 , B_2 ) & \ldots & ( b_q , B_q ) \end ; z \right= H^_ \left \begin ( 1-a_1 , A_1 ) & ( 1-a_2 , A_2 ) & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Count Distribution
In probability theory, the stable count distribution is the conjugate prior of a one-sided stable distribution. This distribution was discovered by Stephen Lihn (Chinese: 藺鴻圖) in his 2017 study of daily distributions of the S&P 500 and the VIX. The stable distribution family is also sometimes referred to as the Lévy alpha-stable distribution, after Paul Lévy, the first mathematician to have studied it. Of the three parameters defining the distribution, the stability parameter \alpha is most important. Stable count distributions have 0<\alpha<1. The known analytical case of is related to the distribution (See Section 7 of ). All the moments are finite for the distribution. Definition Its standard distribution is defined as : |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Hypergeometric Function
In mathematics, a generalized hypergeometric series is a power series in which the ratio of successive coefficients indexed by ''n'' is a rational function of ''n''. The series, if convergent, defines a generalized hypergeometric function, which may then be defined over a wider domain of the argument by analytic continuation. The generalized hypergeometric series is sometimes just called the hypergeometric series, though this term also sometimes just refers to the Gaussian hypergeometric series. Generalized hypergeometric functions include the (Gaussian) hypergeometric function and the confluent hypergeometric function as special cases, which in turn have many particular special functions as special cases, such as elementary functions, Bessel functions, and the classical orthogonal polynomials. Notation A hypergeometric series is formally defined as a power series :\beta_0 + \beta_1 z + \beta_2 z^2 + \dots = \sum_ \beta_n z^n in which the ratio of successive coefficients is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fox H-function
In mathematics, the Fox H-function ''H''(''x'') is a generalization of the Meijer G-function and the Fox–Wright function introduced by . It is defined by a Mellin–Barnes integral : H_^ \!\left \begin ( a_1 , A_1 ) & ( a_2 , A_2 ) & \ldots & ( a_p , A_p ) \\ ( b_1 , B_1 ) & ( b_2 , B_2 ) & \ldots & ( b_q , B_q ) \end \right. \right= \frac\int_L \frac z^ \, ds, where ''L'' is a certain contour separating the poles of the two factors in the numerator. Compare to the Meijer G-function: : G_^ \!\left( \left. \begin a_1, \dots, a_p \\ b_1, \dots, b_q \end \; \ \, z \right) = \frac \int_L \frac \,z^s \,ds. The special case for which the Fox H reduces to the Meijer G is ''A''''j'' = ''B''''k'' = ''C'', ''C'' > 0 for ''j'' = 1...''p'' and ''k'' = 1...''q'' : : H_^ \!\left \begin ( a_1 , C ) & ( a_2 , C ) & \ldots & ( a_p , C ) \\ ( b_1 , C ) & ( b_2 , C ) & \ldots & ( b_q , C ) \end \right. \right= \frac G_^ \!\left( \left. \begin a_1, \dots, a_p \\ b_1, \dots, b_q \end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modified Half-normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the half-normal distribution is a special case of the folded normal distribution. Let X follow an ordinary normal distribution, N(0,\sigma^2). Then, Y=, X, follows a half-normal distribution. Thus, the half-normal distribution is a fold at the mean of an ordinary normal distribution with mean zero. Properties Using the \sigma parametrization of the normal distribution, the probability density function (PDF) of the half-normal is given by : f_Y(y; \sigma) = \frac\exp \left( -\frac \right) \quad y \geq 0, where E = \mu = \frac. Alternatively using a scaled precision (inverse of the variance) parametrization (to avoid issues if \sigma is near zero), obtained by setting \theta=\frac, the probability density function is given by : f_Y(y; \theta) = \frac\exp \left( -\frac \right) \quad y \geq 0, where E = \mu = \frac. The cumulative distribution function (CDF) is given by : F_Y(y; \sigma) = \int_0^y \frac\sqrt \, \exp \left( -\frac \righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
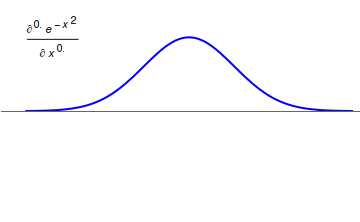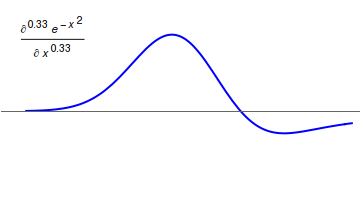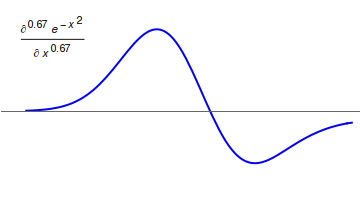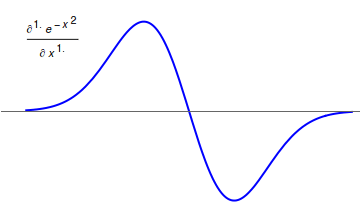
Fractional Calculus
Fractional calculus is a branch of mathematical analysis that studies the several different possibilities of defining real number powers or complex number powers of the differentiation operator D :D f(x) = \frac f(x)\,, and of the integration operator J The symbol J is commonly used instead of the intuitive I in order to avoid confusion with other concepts identified by similar I–like glyphs, such as identities. :J f(x) = \int_0^x f(s) \,ds\,, and developing a calculus for such operators generalizing the classical one. In this context, the term ''powers'' refers to iterative application of a linear operator D to a function f, that is, repeatedly composing D with itself, as in D^n(f) = (\underbrace_n)(f) = \underbrace_n (f)\cdots))). For example, one may ask for a meaningful interpretation of :\sqrt = D^\frac12 as an analogue of the functional square root for the differentiation operator, that is, an expression for some linear operator that, when applied ''twice'' to any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitLab
GitLab Inc. is an open-core company that operates GitLab, a DevOps software package which can develop, secure, and operate software. The open source software project was created by Ukrainian developer Dmitriy Zaporozhets and Dutch developer Sytse Sijbrandij. In 2018, GitLab Inc. was considered the first partly-Ukrainian unicorn. Since its foundation, GitLab Inc. promoted remote work, and is known to be among the largest all-remote companies in the world. GitLab has an estimated 30 million registered users, with 1 million being active licensed users. Overview GitLab Inc. was established in 2014 to continue the development of the open-source code-sharing platform launched in 2011 by Dmitriy Zaporozhets. The company's other co-founder Sytse Sijbrandij initially contributed to the project and, by 2012, decided to build a business around it. GitLab offers its platform as a freemium. Since its foundation, GitLab Inc. has been an all-remote company. By 2020, the company employ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorial And Binomial Topics
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial: \begin n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times (n-3) \times \cdots \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 \\ &= n\times(n-1)!\\ \end For example, 5! = 5\times 4! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 = 120. The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product. Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book '' Sefer Yetzirah''. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – of n distinct objects: there In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the exponential function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |