|
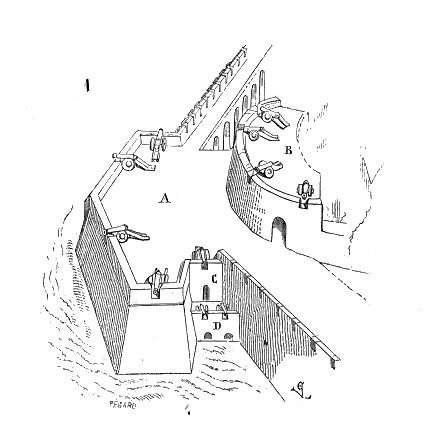
Fort De Bron
The Fort de Bron is a fortification built between 1875 and 1877, located in the commune of Bron. It is part of the second belt of fortifications around Lyon, which also includes Fort de Vancia, Fort de Feyzin and Fort du Mont Verdun. History Its history is linked to the Franco-Prussian War of 1870. Indeed, as a result of the Treaty of Frankfurt which ended the 1870 war, France lost Alsace and Lorraine, reducing its borders. To ensure the defence of Lyon, it built a strong cordon of forts encircling the city to the east, which included the forts of Bron, Vancia, Feyzin and Mont Verdun. These forts were equipped with significant amounts of artillery with all the hardware, staff, and powder storage that this then entailed. When a defensive reorganization occurred in France in 1874, the commune of Bron was therefore included in the crown of detached forts, to protect the stronghold of Lyon. From 1875 to 1885, the following were built successively around the town: * Fort de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, northeast of Saint-Étienne. The City of Lyon proper had a population of 522,969 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Lyon metropolitan area had a population of 2,280,845 that same year, the second most populated in France. Lyon and 58 suburban municipalities have formed since 2015 the Metropolis of Lyon, a directly elected metropolitan authority now in charge of most urban issues, with a population of 1,411,571 in 2019. Lyon is the prefecture of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region and seat of the Departmental Council of Rhône (whose jurisdiction, however, no longer extends over the Metropolis of Lyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of Defense (France)
The Minister of the Armed Forces (french: Ministre des armées, ) is the leader and most senior official of the French Ministry of the Armed Forces, tasked with running the French Armed Forces. The minister is the third highest civilian having authority over France's military, behind only the President of the Republic and the Prime Minister. Based on the governments, they may be assisted by a minister or state secretary for veterans' affairs. The office is considered to be one of the core positions of the Government of France. Since 20 May 2022, the Minister of the Armed Forces has been Sébastien Lecornu, the 45th person to hold the office. History The minister in charge of the Armed Forces has evolved within the epoque and regimes. The Secretary of State of War was one of the four specialised secretaries of state established in France in 1589. This State Secretary was responsible for the French Army (similarly, the Naval Ministers of France and the Colonies was created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Courtot De Cissey
Ernest Louis Octave Courtot de Cissey (; 1810–1882) was a French general and Prime Minister. de Cissey was born in Paris, educated at the Prytanée National Militaire and, after passing through St Cyr, entered the army in 1832, becoming captain in 1839. He saw active service in Algeria, and became ''chef d'escadron'' in 1849 and lieutenant-colonel in 1850. He took part as a colonel in the Crimean War, and after the battle of Inkerman received the rank of general of brigade. In 1863 he was promoted general of division. When the Franco-German War broke out in 1870, de Cissey was given a divisional command in the Army of the Rhine, and he was included in the surrender of Bazaine's army at Metz. He was released from captivity only at the end of the war, and on his return was at once appointed by the Versailles government to a command in the army engaged in the suppression of the Commune. From July 1871 de Cissey sat as a deputy, and he had already become minister of war. He occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Tube
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated. The water table is the surface where the water pressure head is equal to the atmospheric pressure (where gauge pressure = 0). It may be visualized as the "surface" of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. The groundwater may be from precipitation or from groundwater flowing into the aquifer. In areas with sufficient precipitation, water infiltrates through pore spaces in the soil, passing through the unsaturated zone. At increasing depths, water fills in more of the pore spaces in the soils, until a zone of saturation is reached. Below the water table, in the phreatic zone (zone of saturation), layers of permeable rock that yield groundwater are called aquifers. In less permeable soils, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar (weapon)
A mortar is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable, muzzle-loaded weapon, consisting of a smooth-bore (although some models use a rifled barrel) metal tube fixed to a base plate (to spread out the recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount and a sight. They launch explosive shells (technically called bombs) in high-arcing ballistic trajectories. Mortars are typically used as indirect fire weapons for close fire support with a variety of ammunition. History Mortars have been used for hundreds of years. The earliest mortars were used in Korea in a 1413 naval battle when Korean gunsmiths developed the ''wan'gu'' (gourd-shaped mortar) (완구, 碗口). The earliest version of the ''wan'gu'' dates back to 1407. Choi Hae-san (최해산, 崔海山) (1380–1443), the son of Choe Mu-seon (최무선, 崔茂宣) (1325–1395), is generally credited with inventing the ''wan'gu''. In the Ming dynasty, general Qi Jiguang recorded the use of a mini cannon called the Hu dun pao that was simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalier (fortification)
A cavalier is a fortification which is built within a larger fortification, and which is higher than the rest of the work. It usually consists of a raised platform within a fort or bastion, so as to be able to fire over the main parapet without interfering with the fire of the latter. Through the use of cavaliers, a greater volume of fire can be obtained, but its great height also makes it an easy target for a besieger's guns. There are two types of cavaliers: *Common cavalier – a raised gun platform without any additional defensive features *Defensible cavalier – a raised gun platform surrounded by a ditch. If the ditch cuts across the bastion's terreplein and is supported by cuts, the cavalier can also be considered as a retrenchment. Gallery Malta - Birgu - Ix-Xatt tal-Birgu - Fort Saint Angelo (MSTHC) 02 ies.jpg, Ferramolino's Cavalier, Fort St. Angelo, Birgu, Malta Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Ragon De Bange
Charles Ragon de Bange (17 October 1833 – 9 July 1914) was a French artillery officer and Polytechnician. He invented the first effective obturator system for breech-loading artillery, which remains in use. He also designed a system of field guns of various calibers which served the French Army well into World War I: the ''Système de Bange''. Career De Bange breech obturator system Many attempts had been made at developing breech-loading cannons, but had only partial success sealing of the breech. When fired, hot gases and burning gunpowder could escape, losing power and potentially burning the operating crew. Rifles, with smaller loads and thus less stress, were able to use rubber in O-rings as on the Chassepot rifle. The same principle of breech sealing applied on cannons was not as easy to develop. Several materials were able to hold the pressure and heat of cannon fire, but did not expand like rubber, thereby failing to provide a tight seal. The most successful of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eminent Domain
Eminent domain (United States, Philippines), land acquisition (India, Malaysia, Singapore), compulsory purchase/acquisition (Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, United Kingdom), resumption (Hong Kong, Uganda), resumption/compulsory acquisition (Australia, Barbados, New Zealand, Ireland, United Kingdom), or expropriation (Argentina, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Mexico, Netherlands, Norway, Panama, Poland, Portugal, Russia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Serbia) is the power of a state, provincial, or national government to take private property for public use. It does not include the power to take and transfer ownership of private property from one property owner to another private property owner without a valid public purpose. This power can be legislatively delegated by the state to municipalities, government subdivisions, or even to private persons or corporations, when they are authorized by the legislature to exercise the functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caponier
A caponier is a type of defensive structure in a fortification. Fire from this point could cover the ditch beyond the curtain wall to deter any attempt to storm the wall. The word originates from the French ', meaning "chicken coop" (a ''capon'' is a castrated male chicken). In some types of bastioned fortifications, the caponier served as a means of access to the outworks, protecting troops from direct fire; they were often roofless. Although they could be used for firing along the ditch, the flanks of the bastions were the main defence of the ditch by fire. In later polygonal forts, caponiers were often roofed, and were not intended as a type of ''covered way'', but as the main way of keeping the ditch clear of the enemy. History Originally the term referred to a covered passageway that traversed the ditch outside the curtain of a fortress. Fire from this point could cover the ditch beyond the curtain wall to deter any attempt to storm the wall. Thus the passageway was equip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Priest, Rhône
Saint-Priest (; frp, Sant-Priést) is a commune in the Metropolis of Lyon in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in east-south France. The 19th-century French historian and epigrapher Auguste Allmer (1815–1899) was a tax collector in Saint-Priest. It is the fourth-largest suburb of the city of Lyon, and is located to its southeast side. The Saint-Priest station is served by local trains to Lyon and Saint-André-le-Gaz. Population See also *Communes of the Metropolis of Lyon The following is a list of the 59 communes of the Lyon Metropolis, France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the ... References External links Official website {{DEFAULTSORT:Saintpriest Communes of Lyon Metropolis Dauphiné ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)