|
Follicular B Cell
Within the immune system, Follicular B cells (FO B cells) are a type of B cell that reside in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles (containing germinal centers) of secondary and tertiary lymphoid organs, including spleen and lymph nodes. Antibody responses against proteins are believed to involve follicular B cell pathways in secondary lymphoid organs. Mature B cells from the spleen can be divided into two main populations: FO B cells, which constitute the majority, and marginal zone B-cells, lining outside the marginal sinus and bordering the red pulp. FO B cells express high levels of IgD, and CD23; lower levels of CD21 and IgM; and no CD1 or CD5, readily distinguishing this compartment from B1 B cells and marginal zone B-cells. FO B cells organize into the primary follicles of B cell zones focused around follicular dendritic cells in the white pulp of the spleen and the cortical areas of peripheral lymph nodes A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Cells
There are many different types of cells in the human body. Cells derived primarily from endoderm Exocrine secretory epithelial cells *Brunner's gland cell in duodenum (enzymes and alkaline mucus) *Insulated goblet cell of respiratory and digestive tracts (mucus secretion) *Stomach ** Foveolar cell (mucus secretion) ** Chief cell ( pepsinogen secretion) ** Parietal cell (hydrochloric acid secretion) * Pancreatic acinar cell (bicarbonate and digestive enzyme secretion) * Paneth cell of small intestine ( lysozyme secretion) *Type II pneumocyte of lung ( surfactant secretion) * Club cell of lung Barrier cells *Type I pneumocyte (lung) * Gall bladder epithelial cell *Centroacinar cell (pancreas) * Intercalated duct cell (pancreas) *Intestinal brush border cell (with microvilli) Hormone-secreting cells * Enteroendocrine cell **K cell (secretes gastric inhibitory peptide) **L cell (secretes glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY3-36, oxyntomodulin, and glucagon-like pept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
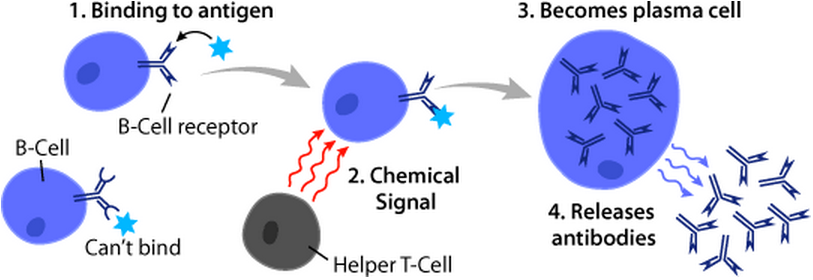
B Cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicular B Helper T Cells
Follicular helper T cells (also known as follicular B helper T cells and abbreviated as TFH), are antigen-experienced CD4+ T cells found in the periphery within B cell follicles of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleen and Peyer's patches, and are identified by their constitutive expression of the B cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5. Upon cellular interaction and cross-signaling with their cognate follicular (Fo B) B cells, TFH cells trigger the formation and maintenance of germinal centers through the expression of CD40 ligand (CD40L) and the secretion of IL-21 and IL-4. TFH cells also migrate from T cell zones into these seeded germinal centers, predominantly composed of rapidly dividing B cells mutating their Ig genes. Within germinal centers, TFH cells play a critical role in mediating the selection and survival of B cells that go on to differentiate either into long-lived plasma cells capable of producing high affinity antibodies against foreign antige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal-zone B Cell
Marginal zone B cells (MZ B cells) are noncirculating mature B cells that in humans segregate anatomically into the marginal zone (MZ) of the spleen and certain other types of lymphoid tissue. The MZ B cells within this region typically express low-affinity polyreactive B-cell receptors (BCR), high levels of IgM, Toll-like receptors (TLRs), CD21, CD1, CD9, CD27 with low to negligible levels of secreted- IgD, CD23, CD5, and CD11b that help to distinguish them phenotypically from follicular (FO) B cells and B1 B cells. MZ B cells are innate-like B cells specialized to mount rapid T-independent, but also T-dependent responses against blood-borne pathogens. They are also known to be the main producers of IgM antibodies in humans. Development and differentiation The spleen's marginal zone contains multiple subtypes of macrophages and dendritic cells interlaced with the MZ B cells; it is not fully formed until 2 to 3 weeks after birth in rodents and 1 to 2 years in humans. In hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
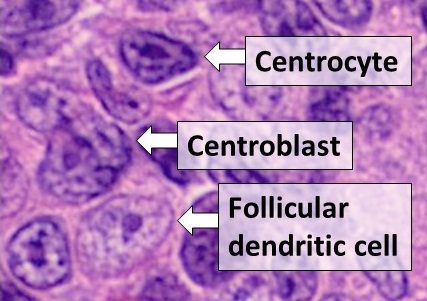
Follicular Dendritic Cell
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hematopoietic stem cell, but are of mesenchymal origin. Possible functions of FDC include: organizing lymphoid tissue's cells and microarchitecture, capturing antigen to support B cell, promoting debris removal from germinal centers, and protecting against autoimmunity. Disease processes that FDC may contribute include primary FDC-tumor, chronic inflammatory conditions, HIV-1 infection development, and neuroinvasive scrapie. Location and molecular markers Follicular DCs are a non-migratory population found in primary and secondary follicles of the B cell areas of lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). They form a stable network due to intercellular connections between FDCs processes and intimate interaction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral immunity, humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cell A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...s, B cells and Natural killer cell, natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD5 (protein)
CD5 is a cluster of differentiation expressed on the surface of T cells (various species) and in a subset of murine B cells known as B-1a. The expression of this receptor in human B cells has been a controversial topic and to date there is no consensus regarding the role of this receptor as a marker of human B cells. B-1 cells have limited diversity of their B-cell receptor due to their lack of the enzyme terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and are potentially self-reactive. CD5 serves to mitigate activating signals from the BCR so that the B-1 cells can only be activated by very strong stimuli (such as bacterial proteins) and not by normal tissue proteins. CD5 was used as a T-cell marker until monoclonal antibodies against CD3 were developed. In humans, the gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 11. There is no confirmed ligand for CD5 but there is evidence that CD72, a C-type lectin, may be a ligand or that CD5 may be homophilic, binding CD5 on the surface of ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD21
Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21 (cluster of differentiation 21), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene. CR2 is involved in the complement system. It binds to iC3b (inactive derivative of C3b), C3dg, or C3d.Frank K, Atkinson JP (2001). "Complement system." In Austen KF, Frank K, Atkinson JP, Cantor H. eds. ''Samter's Immunologic Diseases, 6th ed. Vol. 1,'' p. 281-298, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, . B cells express CR2 receptors on their surfaces, allowing the complement system to play a role in B-cell activation and maturation. Interactions Complement receptor 2 interacts with CD19, and, on mature B cells, forms a complex with CD81 (TAPA-1). The CR2-CD19-CD81 complex is often called the B cell co-receptor complex,Abbas AK, Lichtman AH (2003). ''Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed.'' Philadelphia: Saunders, because CR2 binds to opsonized antigens through attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)