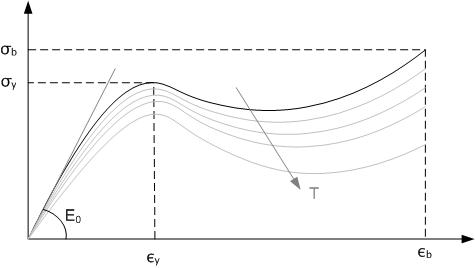
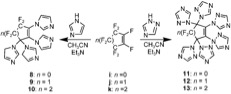
|
Fluoropolymer
A fluoropolymer is a fluorocarbon-based polymer with multiple carbon–fluorine bonds. It is characterized by a high resistance to solvents, acids, and bases. The best known fluoropolymer is polytetrafluoroethylene under the brand name "Teflon," trademarked by the DuPont Company. History In 1938, polytetrafluoroethylene (DuPont brand name Teflon) was discovered by accident by a recently hired DuPont Ph.D., Roy J. Plunkett. While working with tetrafluoroethylene gas to develop refrigerants, he noticed that a previously pressurized cylinder had no pressure remaining. In dissecting the cylinder, he found a mass of white solid in a quantity similar to that of the tetrafluoroethylene gas. It was determined that this material was a new-to-the-world polymer. Tests showed the substance was resistant to corrosion from most acids, bases and solvents and had better high temperature stability than any other plastic. By early 1941, a crash program was making substantial quantities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a spin-off from DuPont, which originally discovered the compound in 1938. Polytetrafluoroethylene is a fluorocarbon solid, as it is a high- molecular-weight polymer consisting wholly of carbon and fluorine. PTFE is hydrophobic: neither water nor water-containing substances wet PTFE, as fluorocarbons exhibit only small London dispersion forces due to the low electric polarizability of fluorine. PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. Polytetrafluoroethylene is used as a non-stick coating for pans and other cookware. It is non-reactive, partly because of the strength of carbon–fluorine bonds, so it is often used in containers and pipework for reactive and corrosive chemicals. Where used as a lubricant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PVDF
Polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride. PVDF is a specialty plastic used in applications requiring the highest purity, as well as resistance to solvents, acids and hydrocarbons. PVDF has low density 1.78 g/cm3 in comparison to other fluoropolymers, like polytetrafluoroethylene. It is available in the form of piping products, sheet, tubing, films, plate and an insulator for premium wire. It can be injected, molded or welded and is commonly used in the chemical, semiconductor, medical and defense industries, as well as in lithium-ion batteries. It is also available as a cross-linked closed-cell foam, used increasingly in aviation and aerospace applications, and as an exotic 3D printer filament. It can also be used in repeated contact with food products, as it is FDA-compliant and non-toxic below its degradation temperature. As a fine powder gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) is a thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer with the molecular formula , where ''n'' is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is similar to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except that it is a homopolymer of the monomer chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) instead of tetrafluoroethene. It has the lowest water vapor transmission rate of any plastic. History It was discovered in 1934 by Fritz Schloffer and Otto Scherer who worked at IG Farben Company, Germany. Trade names After World War II, PCTFE was commercialized under the trade name of Kel-F 81 by M. W. Kellogg Company in early 1950s. The name "Kel-F" was derived from "Kellogg" and "fluoropolymer", which also represents other fluoropolymers like the copolymer poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene-co-vinylidene fluoride) (Kel-F 800). These were acquired by 3M Company in 1957. But 3M discontinued manufacturing of Kel-F by 1996. PCTFE resin is now manufactured in different trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorocarbon
Fluorocarbons are chemical compounds with carbon-fluorine bonds. Compounds that contain many C-F bonds often has distinctive properties, e.g., enhanced stability, volatility, and hydrophobicity. Fluorocarbons and their derivatives are commercial polymers, refrigerants, drugs, and anesthetics. Nomenclature Perfluorocarbons or PFCs, are organofluorine compounds with the formula CxFy, i.e., they contain only carbon and fluorine. The terminology is not strictly followed and many fluorine-containing organic compounds are called fluorocarbons. Compounds with the prefix perfluoro- are hydrocarbons, including those with heteroatoms, wherein all C-H bonds have been replaced by C-F bonds. Fluorocarbons includes perfluoroalkanes, fluoroalkenes, fluoroalkynes, and perfluoroaromatic compounds. Perfluoroalkanes Chemical properties Perfluoroalkanes are very stable because of the strength of the carbon–fluorine bond, one of the strongest in organic chemistry. Its strength is a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrafluoroethylene
Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) is a fluorocarbon with the chemical formula C2 F4. It is the simplest perfluorinated alkene. This gaseous species is used primarily in the industrial preparation of fluoropolymers. Properties Tetrafluoroethylene is a colorless, odorless gas. Like all unsaturated fluorocarbons, it is susceptible to nucleophilic attack. It is unstable towards decomposition to carbon and carbon tetrafluoride () and prone to form explosive peroxides in contact with air. Industrial use Polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene produces polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymers such as Teflon and Fluon. PTFE is one of the two fluorocarbon resins composed wholly of fluorine and carbon. The other resin composed purely of carbon and fluorine is the copolymer of TFE with typically 6–9% hexafluoropropene (HFP), which is known as FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene copolymer). TFE is also used in the preparation of numerous copolymers that also include hydrogen and/or oxygen, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrafluoroethylene
Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) is a fluorocarbon with the chemical formula C2 F4. It is the simplest perfluorinated alkene. This gaseous species is used primarily in the industrial preparation of fluoropolymers. Properties Tetrafluoroethylene is a colorless, odorless gas. Like all unsaturated fluorocarbons, it is susceptible to nucleophilic attack. It is unstable towards decomposition to carbon and carbon tetrafluoride () and prone to form explosive peroxides in contact with air. Industrial use Polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene produces polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymers such as Teflon and Fluon. PTFE is one of the two fluorocarbon resins composed wholly of fluorine and carbon. The other resin composed purely of carbon and fluorine is the copolymer of TFE with typically 6–9% hexafluoropropene (HFP), which is known as FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene copolymer). TFE is also used in the preparation of numerous copolymers that also include hydrogen and/or oxygen, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfluoroether
Perfluoroethers are a class of organofluorine compound containing one or more ether functional group. In general these compounds are structurally analogous to the related hydrocarbon ethers, except for the distinctive properties of fluorocarbons. The introduction of an ether function to a perfluoro-polymer chain also provides thermoplastic properties to the polymer, making thermal forming possible. This is a great technological advantage for producing a large variety of shapes (e.g., beakers, funnels, flasks for laboratory uses, etc...) and allows extrusion of highly chemically-resistant tubing. It also confers on the polymer a translucent appearance. Low molecular weight fluorinated ethers Acyclic perfluoroethers are analogues of diethylether, e.g. O(C2F5)2, such perfluoro(2-ethoxyethane)sulfonic acid (PFEESA). More interesting and more useful are the cyclic ethers, especially, the epoxides. Tetrafluoroethyene oxide and hexafluoropropylene oxide are two of the simplest cycli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinylidene Fluoride
1,1-Difluoroethylene, also known as vinylidene fluoride, is a hydrofluoroolefin. It is a flammable gas. Global production in 1999 was approximately 33,000 metric tons. It is primarily used in the production of fluoropolymers such as polyvinylidene fluoride. Preparation 1,1-Difluoroethylene can be prepared by elimination reaction from a 1,1,1-trihaloethane compound, for example, loss of hydrogen chloride from 1-chloro-1,1-difluoroethane:. : or loss of hydrogen fluoride from 1,1,1-trifluoroethane: : See also * 1,2-Difluoroethylene *Perfluoroisobutene Perfluoroisobutene (PFIB) is the perfluorocarbon counterpart of the hydrocarbon isobutene and has the formula (CF3)2C=CF2. An alkene, it is a colorless gas that is notable as a highly toxic perfluoroalkene. Few simple alkenes are as toxic. Saf ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Difluoroethylene, 1, 1- Organofluorides Vinylidene compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinyl Fluoride
Vinyl fluoride is an organic halide with the chemical formula C2H3F. It is a colorless gas with a faint etherlike odor. It is used as the monomeric precursor to the fluoropolymer polyvinylfluoride. Production It was first prepared in 1901 by Frédéric Swarts, the Belgian chemist who was the first to prepare chlorofluorocarbons in 1892. Swarts used the reaction of zinc with 1,1-difluoro-2-bromoethane. It is produced industrially by two routes, one being the mercury-catalyzed reaction of acetylene and hydrogen fluoride:Günter Siegemund, Werner Schwertfeger, Andrew Feiring, Bruce Smart, Fred Behr, Herward Vogel, Blaine McKusick “Fluorine Compounds, Organic” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. :HC≡CH + HF → CH2=CHF It is also prepared from 1,1-chlorofluoroethane: :CH3CHClF → CH2=CHF + HCl Safety Vinyl fluoride is classified as an IARC Group 2A carcinogen (likely to cause cancer in humans). Additional data Its criti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfluorocycloalkene
A perfluorocycloalkene (PFCA) fluorocarbon structure with a cycloalkene core. PFCAs have shown reactivity with a wide variety of nucleophiles including phenoxides, alkoxides, organometallic, amines, thiols, and azoles. They or their derivatives are reported to have nonlinear optical activity, and be useful as lubricants, etching agents, components of fuel cells, low dielectric materials, and super hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings. File:Tetrafluorocyclopropene.png, Tetrafluorocyclopropene File:Hexafluorocyclobutene.png, Hexafluorocyclobutene File:Octafluorocyclopentene.png, Octafluorocyclopentene File:Decafluorocyclohexene.png, Decafluorocyclohexene Reactivity Derivatization of these PFCA rings via displacement of fluorine atoms with nucleophiles occurs through an addition-elimination reaction in the presence of a base. Attack of the nucleophile on the PFCA ring generates a carbanion which can eliminate a fluoride ion, resulting in vinyl substituted and allyl substituted produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkema
Arkema S.A. is a publicly listed, multi-national manufacturer of specialty materials, headquartered in Colombes, near Paris, France. It has three specialty materials segments (or divisions); adhesives, advanced materials and coatings. A further segment covers chemical intermediates. The company was created in 2004, as part of French oil major Total's restructuring of its chemicals business, and floated on the Paris stock exchange in May 2006. Turnover in 2021 was €9.5 billion. Arkema operates in more than 55 countries and has 20,200 employees, 13 research centers and 144 production plants. History Arkema itself was created when French oil major Total restructured its chemicals business in 2004, but the company's roots go back many years. Origin and evolution In 1971, Elf and Total merged their chemical operations into Aquitaine Total Organico (ATO), a joint subsidiary. The same year saw the creation of Produits Chimiques Ugine Kuhlmann (PCUK). The joint venture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |