|
Flow-Based Programming
In computer programming, flow-based programming (FBP) is a programming paradigm that defines application software, applications as networks of black box process (computer science), processes, which exchange data across predefined connections by message passing, where the connections are specified ''externally'' to the processes. These black box processes can be reconnected endlessly to form different applications without having to be changed internally. FBP is thus naturally Software componentry, component-oriented. FBP is a particular form of dataflow programming based on bounded buffers, information packets with defined lifetimes, named ports, and separate definition of connections. Introduction Flow-based programming defines applications using the metaphor of a "data factory". It views an application not as a single, sequential process, which starts at a point in time, and then does one thing at a time until it is finished, but as a network of asynchronous processes communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing source code, code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the Domain (software engineering), application domain, details of programming languages and generic code library (computing), libraries, specialized algorithms, and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic. Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include Requirements analysis, analyzing requirements, Software testing, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Service-oriented Architecture
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. SOA is a good choice for system integration. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies. Service orientation is a way of thinking in terms of services and service-based development and the outcomes of services. A service has four properties according to one of many definitions of SOA: # It logically represents a repeatable business activity with a specified outcome. # It is self-contained. # It is a black box for its consumers, meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lazy Evaluation
In programming language theory, lazy evaluation, or call-by-need, is an evaluation strategy which delays the evaluation of an Expression (computer science), expression until its value is needed (non-strict evaluation) and which avoids repeated evaluations (by the use of Sharing (computer science), sharing). The benefits of lazy evaluation include: * The ability to define control flow (structures) as abstractions instead of Language primitive, primitives. * The ability to define actual infinity, potentially infinite data structures. This allows for more straightforward implementation of some algorithms. * The ability to define partly-defined data structures where some elements are errors. This allows for rapid prototyping. Lazy evaluation is often combined with memoization, as described in Jon Bentley (computer scientist), Jon Bentley's ''Writing Efficient Programs''. After a function's value is computed for that Parameter (computer programming), parameter or set of parameters, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Configurable Modularity
Configurable modularity is a term coined by Raoul de Campo of IBM Research and later expanded on by Nate Edwards of the same organization, denoting the ability to reuse independent components by changing their interconnections, but not their internals.N.P. Edwards, ''On the Architectural Requirements of an Engineered System'', IBM Research Report, RC 6688 (#28797), T.J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, NY, 8/18/1977 In Edwards' view this characterizes all successful reuse systems, and indeed all systems which can be described as "engineered". See also * Flow-Based Programming In computer programming, flow-based programming (FBP) is a programming paradigm that defines application software, applications as networks of black box process (computer science), processes, which exchange data across predefined connections by mes ... References Theoretical computer science {{comp-sci-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nate Edwards
Nathen Porter Edwards (August 24, 1922 – May 26, 2016) was a former IBM hardware architect, retired in 1990. He did his military service in the United States Navy from 1942 to 1946, as a LTJG, Deck, USNR, Pacific, Chief Radio Technician, followed by Stanford University, where he gained an MS EE in 1949. He worked for IBM from 1949 to 1990, as a Staff Member, Thomas J. Watson Research Center, with the position of Senior Engineer for the last 20 years of this period. He published, sometimes with other authors, 22 technical papers, 14 patents and patent publications — see below. Between 1949 and 1953, his activities included design and construction of the prototype of the first electronic memory for the IBM 701 computer, and managing digital electronic design for the working prototype of the highly successful AN/FSQ-7 SAGE project. The SAGE system was a nationwide network of computer centers linked to radar inputs and operated by military personnel using graphic and nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Component-based Software Engineering
Component-based software engineering (CBSE), also called component-based development (CBD), is a style of software engineering that aims to construct a software system from software component, components that are loosely-Coupling (computer programming), coupled and Reusability, reusable. This emphasizes the separation of concerns among components. To find the right level of component granularity, software architects have to continuously iterate their component designs with developers. Architects need to take into account user requirements, responsibilities and architectural characteristics. Considerations For large-scale systems developed by large teams, a disciplined culture and process is required to achieve the benefits of CBSE. Third-party software component, Third-party components are often utilized in large systems. The system can be designed visually with the Unified Modeling Language (UML). Each software component, component is shown as a rectangle, and an interface is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
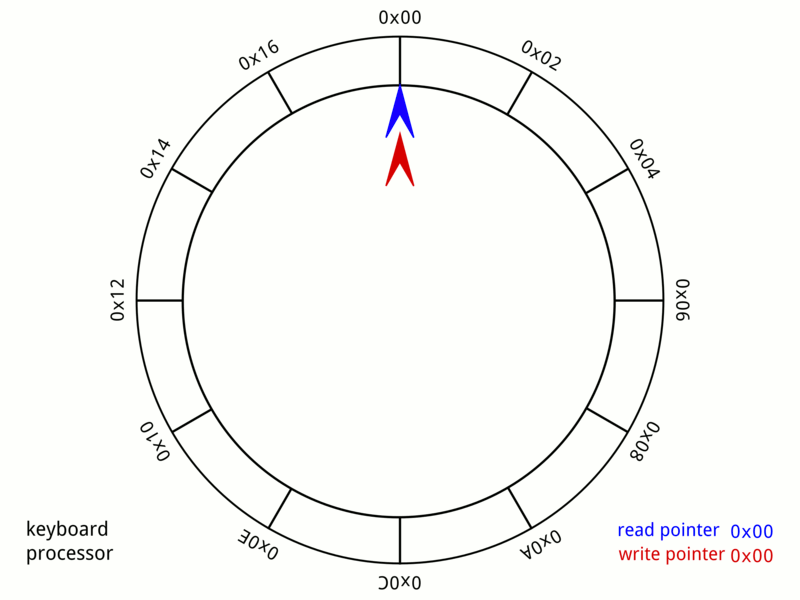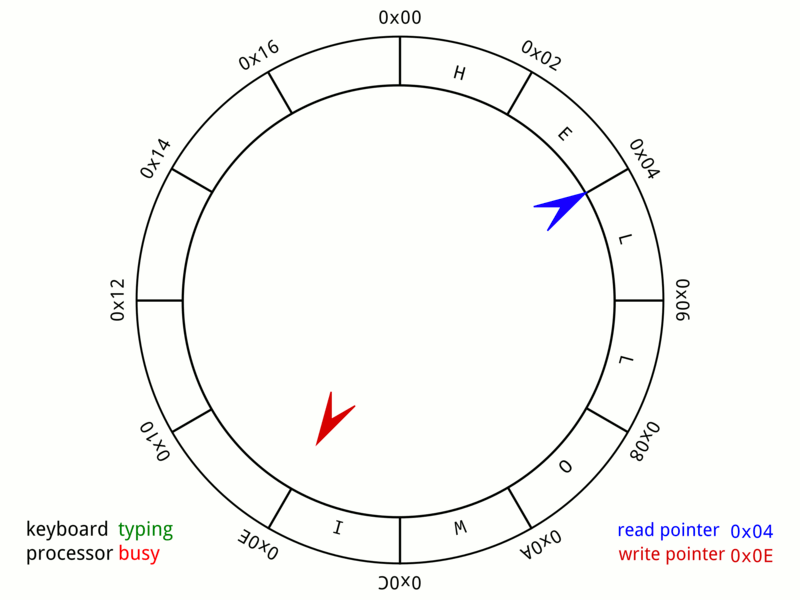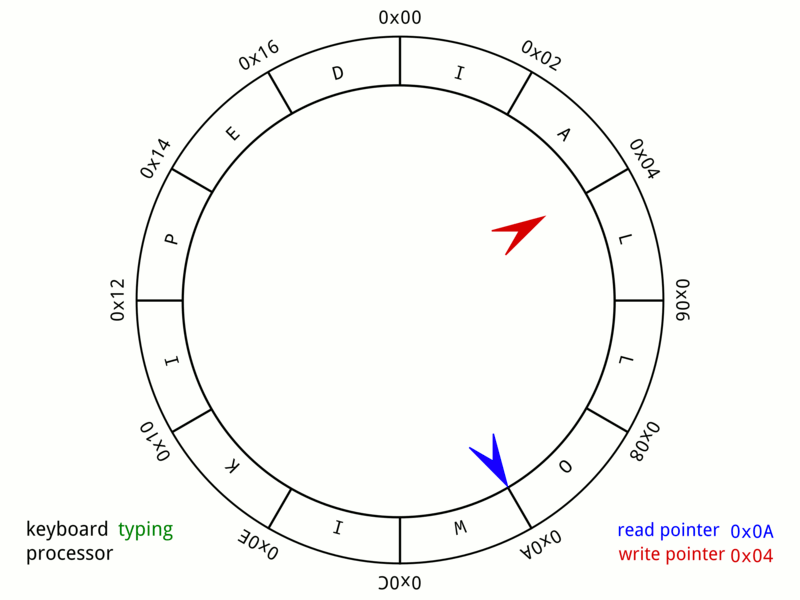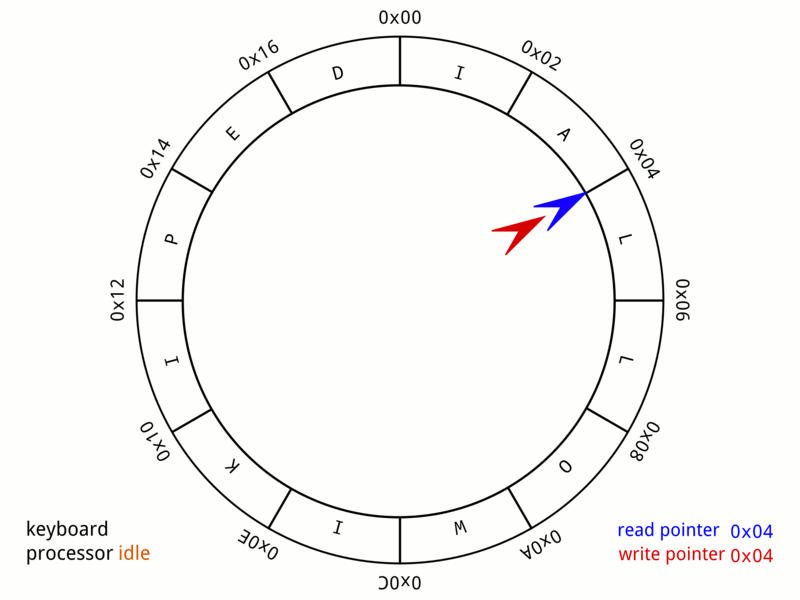
Circular Buffer
In computer science, a circular buffer, circular queue, cyclic buffer or ring buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed-size buffer as if it were connected end-to-end. This structure lends itself easily to buffering data streams. There were early circular buffer implementations in hardware. Overview A circular buffer first starts out empty and has a set length. In the diagram below is a 7-element buffer: : Assume that 1 is written in the center of a circular buffer (the exact starting location is not important in a circular buffer): : Then assume that two more elements are added to the circular buffer — 2 & 3 — which get put after 1: : If two elements are removed, the two oldest values inside of the circular buffer would be removed. Circular buffers use FIFO ('' first in, first out'') logic. In the example, 1 & 2 were the first to enter the circular buffer, they are the first to be removed, leaving 3 inside of the buffer. : If the buffer has 7 e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
FBP - Simple Network
FBP may refer to: * Fábrica de Braço de Prata, a defunct Portuguese weapons manufacturer ** FBP submachine gun * '' FBP: Federal Bureau of Physics'', an American comic book series * Federal Bureau of Prisons * Film and Publication Board, is a content-classification and censorship authority in South Africa * Filtered back projection, an analytic tomographic image reconstruction algorithm * First BanCorp, a Puerto Rican financial holding company * Fixed book price agreement * Flow-based programming * Fluff Busting Purity, a web browser extension * Folate-binding protein * Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate * Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase * Funds for Endangered Parrots (German: '), a German conservation organization * Progressive Citizens' Party The Progressive Citizens' Party in Liechtenstein (, FBP) is a Conservatism, conservative List of political parties in Liechtenstein, political party in Liechtenstein. The FBP is one of the two major party, major List of political parties in Liec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wayne Stevens (software Engineer)
Wayne P. Stevens (1944 - 1993) was an American software engineer, consultant, author, pioneer, and advocate of the practical application of software methods and tools. Life & Work Stevens grew up in Missouri, spent two years in India, where he attended the Woodstock School, and earned his M.S. in Electrical Engineering from MIT in 1967. He eventually became the chief architect of application development methodology for IBM's consulting group. The annual Stevens Award Lecture on Software Development Methods is named after him. He belonged to the IEEE and the ACM as well as the following honorary societies: Tau Beta Pi, Sigma Xi, and Eta Kappa Nu. He wrote a seminal paper on Structured Design, with Larry Constantine and Glenford Myers, and was the author of a number of books and articles on application design methodologies. He also worked with John Paul Morrison to refine and promote the concepts of what is now called Flow-based programming In computer programming, flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IBM Research
IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, an American Multinational corporation, multinational information technology company. IBM Research is headquartered at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York, near IBM headquarters in Armonk, New York. It is the largest industrial research organization in the world with operations in over 170 countries and twelve labs on six continents. IBM employees have garnered six Nobel Prizes, six Turing Awards, 20 inductees into the U.S. National Inventors Hall of Fame, 19 National Medal of Technology, National Medals of Technology, five National Medal of Science, National Medals of Science and three Kavli Foundation (United States)#The Kavli Prize, Kavli Prizes. , the company has generated more patents than any other business in each of 25 consecutive years, which is a record. History The roots of today's IBM Research began with the 1945 opening of the Watson Scientific Computing Laboratory at Columbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Technical Disclosure Bulletins
The IBM Technical Disclosure Bulletin was a technical publication produced by IBM between 1958 and 1998. The purpose of the Bulletin was to disclose inventions that IBM did not want their competitors to get patents on. The Bulletin was a form of defensive publication. By publishing the details of how to make and use the invention, patent examiners could have a searchable source of prior art that they could cite against subsequent patent applications filed by others on the same or similar inventions. The Bulletin has been cited over 48,000 times in various United States patents.Delphion Web sitehttp://www.delphion.com/search-prior_art#tdb retrieved on June 20, 2006 See also *United States Statutory Invention Registration In former United States patent law, a statutory invention registration (SIR) was a publication of an invention by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). The publication was made at the request of the applicant (i.e. inventor(s) or ... * Patent Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coroutines
Coroutines are computer program components that allow execution to be suspended and resumed, generalizing subroutines for cooperative multitasking. Coroutines are well-suited for implementing familiar program components such as cooperative tasks, exceptions, event loops, iterators, infinite lists and pipes. They have been described as "functions whose execution you can pause". Melvin Conway coined the term ''coroutine'' in 1958 when he applied it to the construction of an assembly program. The first published explanation of the coroutine appeared later, in 1963. Definition and types There is no single precise definition of coroutine. In 1980 Christopher D. Marlin summarized two widely-acknowledged fundamental characteristics of a coroutine: # the values of data local to a coroutine persist between successive calls; # the execution of a coroutine is suspended as control leaves it, only to carry on where it left off when control re-enters the coroutine at some later stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |