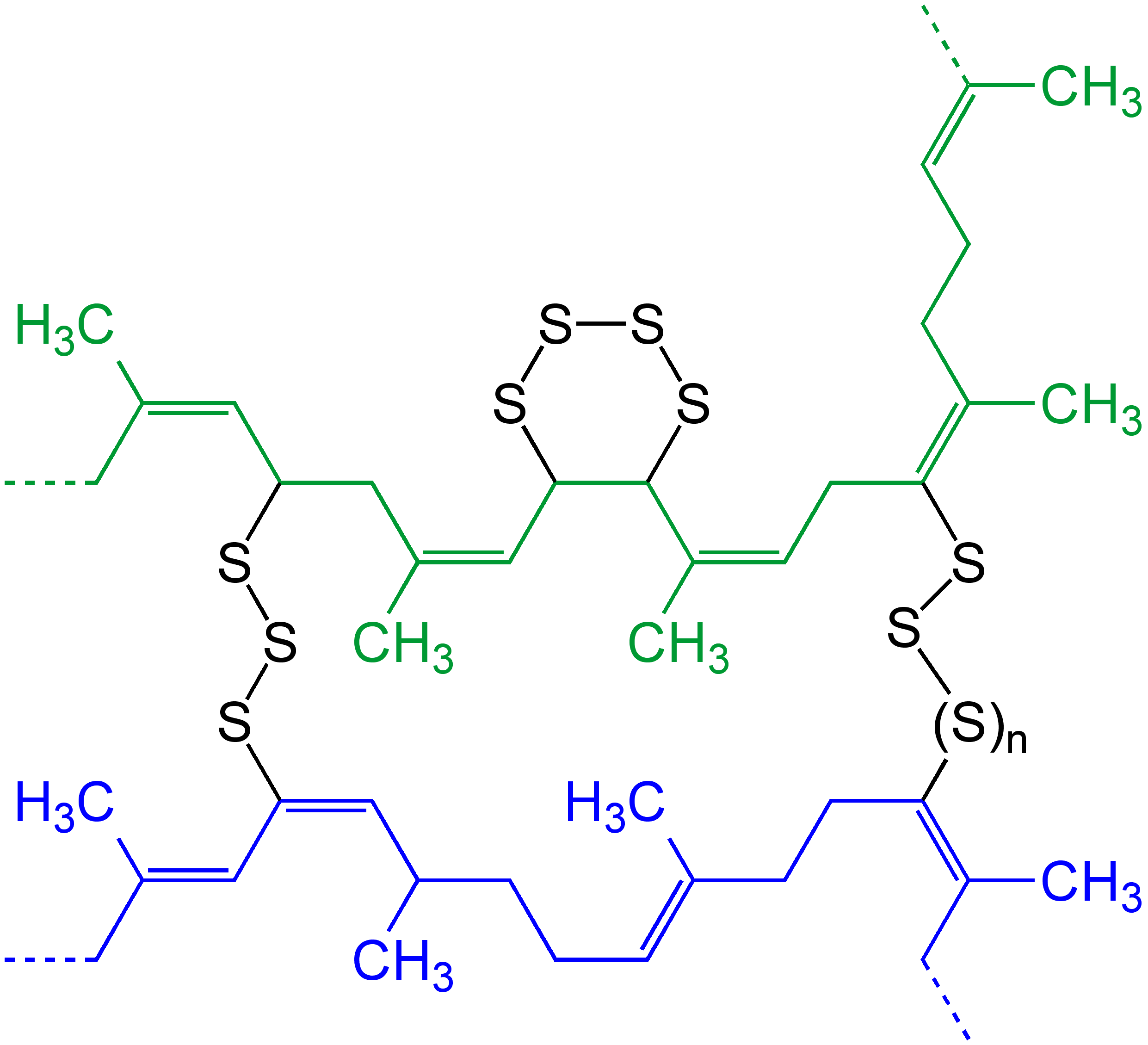
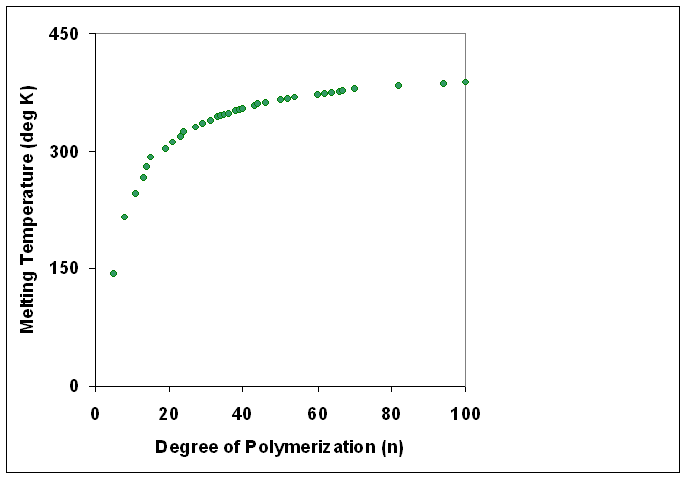
|
Flory–Stockmayer Theory
Flory–Stockmayer theory is a theory governing the cross-linking and gelation of step-growth polymers.Flory, P.J. (1941). "Molecular Size Distribution in Three Dimensional Polymers I. Gelation". ''J. Am. Chem. Soc.'' 63, 3083 The Flory–Stockmayer theory represents an advancement from the Carothers equation, allowing for the identification of the gel point for polymer synthesis not at stoichiometric balance. The theory was initially conceptualized by Paul Flory in 1941 and then was further developed by Walter Stockmayer in 1944 to include cross-linking with an arbitrary initial size distribution.Stockmayer, Walter H.(1944). "Theory of Molecular Size Distribution and Gel Formation in Branched Polymers II. General Cross Linking". ''Journal of Chemical Physics.'' 12,4, 125 The Flory–Stockmayer theory was the first theory investigating percolation processes. Flory–Stockmayer theory is a special case of random graph theory of gelation. History Gelation occurs when a polymer f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology, a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. Synthetic polymers : 260px, left, Chemical reactions associated with crosslinking of drying oils, the process that produces curing'' refers to the crosslinking of thermosetting">linoleum. Cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Liquid
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than that of a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are classified as condensed matter. Meanwhile, since both liquids and gases can flow, they are categorized as fluids. A liquid is composed of atoms or molecules held together by intermolecular bonds of intermediate strength. These forces allow the particles to move around one another while remaining closely packed. In contrast, solids have particles that are tightly bound by strong intermolecular forces, limiting their movement to small vibrations in fixed positions. Gases, on the other hand, consist of widely spaced, freely moving particles with only weak intermolecular forces. As temperature increases, the molecules in a liquid vibrate more intensely, causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gelation General Case
In polymer chemistry, gelation (gel transition) is the formation of a gel from a system with polymers. Branched polymers can form links between the chains, which lead to progressively larger polymers. As the linking continues, larger branched polymers are obtained and at a certain extent of the reaction, links between the polymer result in the formation of a single macroscopic molecule. At that point in the reaction, which is defined as gel point, the system loses fluidity and viscosity becomes very large. The onset of gelation, or gel point, is accompanied by a sudden increase in viscosity. This "infinite" sized polymer is called the gel or network, which does not dissolve in the solvent, but can swell in it. Background Gelation is promoted by gelling agents. Gelation can occur either by physical linking or by chemical crosslinking. While the physical gels involve physical bonds, chemical gelation involves covalent bonds. The first quantitative theories of chemical gelation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steric Hindrance
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is generally a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions and molecules. Steric effects complement electronic effects, which dictate the shape and reactivity of molecules. Steric repulsive forces between overlapping electron clouds result in structured groupings of molecules stabilized by the way that opposites attract and like charges repel. Steric hindrance Steric hindrance is a consequence of steric effects. Steric hindrance is the slowing of chemical reactions due to steric bulk. It is usually manifested in ''intermolecular reactions'', whereas discussion of steric effects often focus on ''intramolecular interactions''. Steric hindrance is often exploited to control selectivity, such as slowing unwanted side-reactions. Steric hindrance between adjacent groups can also affect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intramolecular Reaction
In chemistry, intramolecular describes a Chemical process, process or characteristic limited within the Chemical structure, structure of a single molecule, a property or phenomenon limited to the extent of a single molecule. Relative rates In intramolecular organic reactions, two reaction sites are contained within a single molecule. This configuration elevates the effective concentration of the reacting partners resulting in high reaction rates. Many intramolecular reactions are observed where the intermolecular version does not take place. Intramolecular reactions, especially ones leading to the formation of 5- and 6-membered rings, are rapid compared to an analogous intermolecular process. This is largely a consequence of the reduced entropic cost for reaching the transition state of ring formation and the absence of significant strain associated with formation of rings of these sizes. For the formation of different ring sizes via cyclization of substrates of varying tether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Functional Groups
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive Chemical property, chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their Chemical polarity, nonp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Step-growth Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, step-growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which bi-functional or multifunctional monomers react to form first dimers, then trimers, longer oligomers and eventually long chain polymers. Many naturally-occurring and some synthetic polymers are produced by step-growth polymerization, e.g. polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, etc. Due to the nature of the polymerization mechanism, a high extent of reaction is required to achieve high molecular weight. The easiest way to visualize the mechanism of a step-growth polymerization is a group of people reaching out to hold their hands to form a human chain—each person has two hands (= reactive sites). There also is the possibility to have more than two reactive sites on a monomer: In this case branched polymers production take place. IUPAC has deprecated the term ''step-growth polymerization'', and recommends use of the terms polyaddition (when the propagation steps are addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Degree Of Polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of structural unit, monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule. For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given by \overline_n\equiv\overline_n=\frac, where \overline_n is the Molar mass distribution#Number average molar mass, number-average molecular weight and M_0 is the molecular weight of the monomer unit. The overlines indicate arithmetic mean values. For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired. This number does not reflect the variation in molecule size of the polymer that typically occurs, it only represents the mean number of monomeric units. Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat units, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit.Fried J.R. "Polymer Science and Technology" (Pearson Prentice-Hall, 2nd edn 2003), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Solid
A network solid or covalent network solid (also called atomic crystalline solids or giant covalent structures) is a chemical compound (or element) in which the atoms are bonded by covalent bonds in a continuous network extending throughout the material. In a network solid there are no individual molecules, and the entire crystal or amorphous solid may be considered a macromolecule. Formulas for network solids, like those for ionic compounds, are simple ratios of the component atoms represented by a formula unit. Examples of network solids include diamond with a continuous network of carbon atoms and silicon dioxide or quartz with a continuous three-dimensional network of SiO2 units. Graphite and the mica group of silicate minerals structurally consist of continuous two-dimensional sheets covalently bonded within the layer, with other bond types holding the layers together. Disordered network solids are termed glasses. These are typically formed on rapid cooling of melts so that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gelation
In polymer chemistry, gelation (gel transition) is the formation of a gel from a system with polymers. Branched polymers can form links between the chains, which lead to progressively larger polymers. As the linking continues, larger branched polymers are obtained and at a certain extent of the reaction, links between the polymer result in the formation of a single macroscopic molecule. At that point in the reaction, which is defined as gel point, the system loses fluidity and viscosity becomes very large. The onset of gelation, or gel point, is accompanied by a sudden increase in viscosity. This "infinite" sized polymer is called the gel or network, which does not dissolve in the solvent, but can swell in it. Background Gelation is promoted by gelling agents. Gelation can occur either by physical linking or by chemical crosslinking. While the physical gels involve physical bonds, chemical gelation involves covalent bonds. The first quantitative theories of chemical gelati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |