|
Flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora (publication)
A Flora is a book or other work which describes the plant species occurring in an area or time period, often with the aim of allowing identification. The term is usually capitalized to distinguish it from the use of "flora" to mean the plants rather than their descriptions. Some classic and modern Floras are listed below. Traditionally Floras are books, but some are now published on CD-ROM or websites. The area that a Flora covers can be either geographically or politically defined. Floras usually require some specialist botanical knowledge to use with any effectiveness. A Flora often contains diagnostic keys. Often these are ''dichotomous'' keys, which require the user to repeatedly examine a plant, and decide which one of two alternatives given in the Flora best applies to the plant. Floras produced at a local or regional level rarely contain identification keys. Instead they aim to impart more detailed understanding of the local status and distribution of that area's plants. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora (mythology)
Flora ( la, Flōra) is a Roman mythology, Roman goddess of flowers and of the season of Spring (season), spring – a symbol for nature and flowers (especially the may-flower). While she was otherwise a relatively minor figure in Roman mythology, being one among several Fertility goddess, fertility goddesses, her association with the spring gave her particular importance at the coming of springtime, as did her role as goddess of youth. She was one of the fifteen deities who had their own flamen, the ''Floralis'', one of the ''flamines minores''. Her Ancient Greece, Greek counterpart is Chloris (nymph), Chloris. Etymology The name ''Flōra'' descends from Proto-Italic language, Proto-Italic ''*flōsā'' ('goddess of flowers'), itself a derivation from Proto-Italic ''*flōs'' ('flower'; cf. Latin ''flōs'', ''flōris'' 'blossom, flower'). It is cognate with the Osci, Oscan goddess of flowers ''Fluusa'', demonstrating that the cult was known more widely among Italic peoples. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing (fusion of sperm and eggs from different individuals in a population) resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing (fusion of sperm and egg from the same flower) when self-pollination occurs. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happens in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Sinensis
''Flora Sinensis'' is one of the first European natural history books about China, published in Vienna in 1656. Its author, Michael Boym, was a Jesuit missionary from Poland (then Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). The book was the first description of an ecosystem of the Far East published in Europe. Boym underlined the medicinal properties of the Chinese plants. The book also included pleas for support of the Catholic Chinese emperor and each page contained a chronogram pointing to the date of 1655, the date of coronation of Emperor Leopold I as the King of Hungary, as Boym wanted to gain support of that monarch for his mission. It is said that the ''Flora Sinensis'' was the first book that used the name "Flora" in this meaning, a book covering the plant world of a region. However, despite its title, the book covered not only plants, it obviously includes some species that are neither plants nor Chinese. File:Flora Sinensis - Jackfruit.JPG, Jackfruit File:Flora Sinensis - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michał Boym
Michał Piotr BoymHis first name is also often rendered as ''Michele'', ''Michel'', ''Miguel'', ''Michael Peter'' (;Transliterated also (using Wade-Giles) as ''Pu Che-yuen Mi-ko'' c. 1612 – 1659) was a Polish Jesuit missionary to China, scientist and explorer. He was an early Western traveller within the Chinese mainland, and the author of numerous works on Asian fauna, flora and geography. The first European Chinese dictionary, published in 1670, is attributed to Boym. Biography Michał Boym was born in Lwów, Poland (now Lviv, Ukraine), around 1614, to a well-off family of Hungarian ancestry. His grandfather Jerzy Boim came to Poland from Hungary with the king Stefan Batory, and married Jadwiga Niżniowska.Ród Boimów (The Boim Family) Michał's father, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WGSRPD World
The World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) is a biogeographical system developed by the international Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) organization, formerly the International Working Group on Taxonomic Databases. The WGSRPD standards, like other standards for data fields in botanical databases, were developed to promote "the wider and more effective dissemination of information about the world's heritage of biological organisms for the benefit of the world at large". The system provides clear definitions and codes for recording plant distributions at four scales or levels, from "botanical continents" down to parts of large countries. Current users of the system include the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), and the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP). Principles of organization The scheme is one of a number developed by Biodiversity Information Standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density recorded in any habitat on Earth, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. Up to 60% of the dry mass of feces is bacteria. Over 99% of the bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
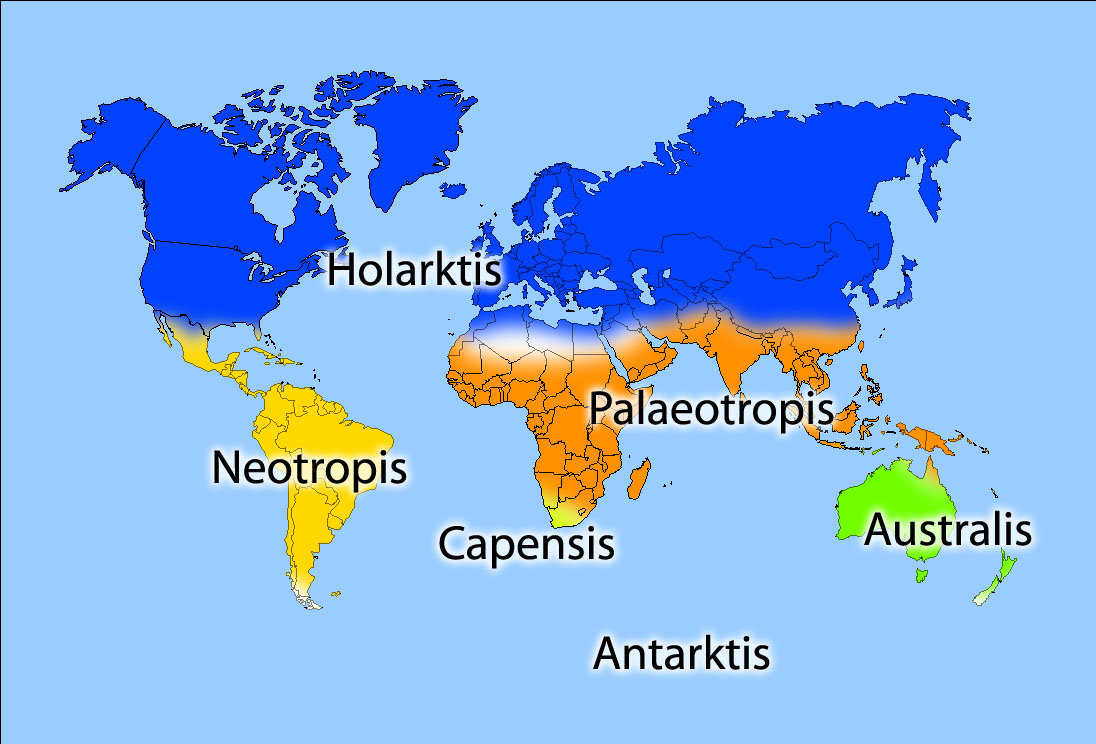
Phytochorion
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone. In traditional schemes, areas in phytogeography are classified hierarchically, according to the presence of endemic families, genera or species, e.g., in floral (or floristic, phytogeographic) zones and regions, or also in kingdoms, regions and provinces, sometimes including the categories empire and domain. However, some authors prefer not to rank areas, referring to them simply as "areas", "regions" (in a non hierarchical sense) or "phytochoria". Systems used to classify vegetation can be divided in two major groups: those that use physiognomic-environmental parameters and characteristics and those that are based on floristic (i.e. shared genera and species) rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''flora'' which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but ''vegetation'' can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term ''vegetation''. The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of ''vegetation'' approximates that of ecologist Frederic Clements' term earth cover, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)