|
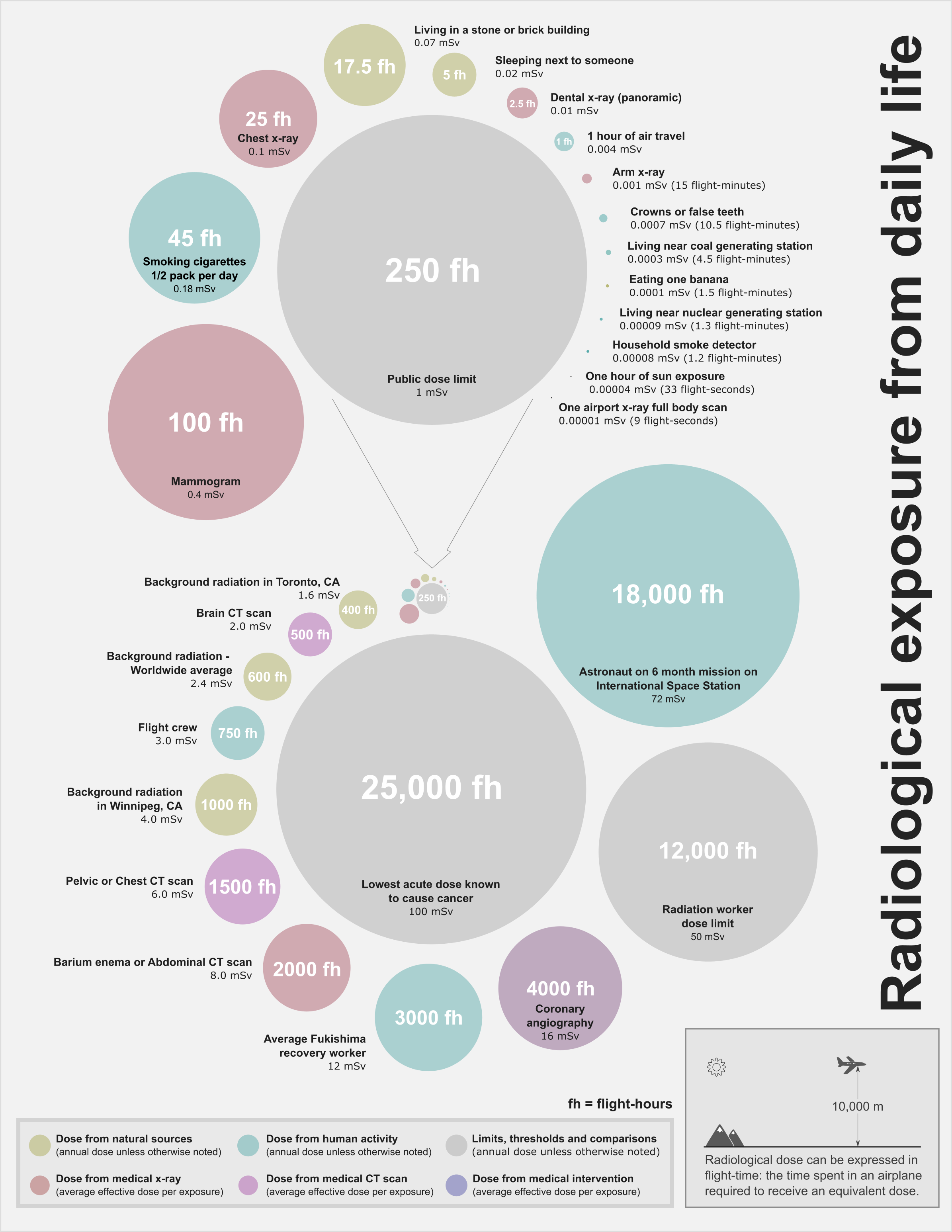
Flight-time Equivalent Dose
Flight-time equivalent dose (FED) is an informal unit of measurement of ionizing radiation exposure. Expressed in units of flight-time (i.e., flight-seconds, flight-minutes, flight-hours), one unit of flight-time is approximately equivalent to the radiological dose received during the same unit of time spent in an airliner at cruising altitude. FED is intended as a general educational unit to enable a better understanding of radiological dose by converting dose typically presented in sieverts into units of time. FED is only meant as an educational exercise and is not a formally adopted dose measurement. History The flight-time equivalent dose concept is the creation of Ulf Stahmer, a Canadian professional engineer working in the field of radioactive materials transport. It was first presented in the poster session at the 18th International Symposium of the Packaging and Transport of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM) held in Kobe, Hyogo, Japan where the poster received an Aoki Aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation, whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, nearly all types of laser light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area is not sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts between 10 electronvolts (eV) and 33 eV. Typical ionizing subatomic particles include alpha particles, beta particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Background Radiation
Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources. Background radiation originates from a variety of sources, both natural and artificial. These include both cosmic radiation and environmental radioactivity from naturally occurring radioactive materials (such as radon and radium), as well as man-made medical X-rays, fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents. Definition Background radiation is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency as "Dose or dose rate (or an observed measure related to the dose or dose rate) attributable to all sources other than the one(s) specified. So a distinction is made between dose which is already in a location, which is defined here as being "background", and the dose due to a deliberately introduced and specified source. This is important where radiation measurements are taken of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |