Flight-time Equivalent Dose on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Flight-time equivalent dose (FED) is an informal unit of measurement of 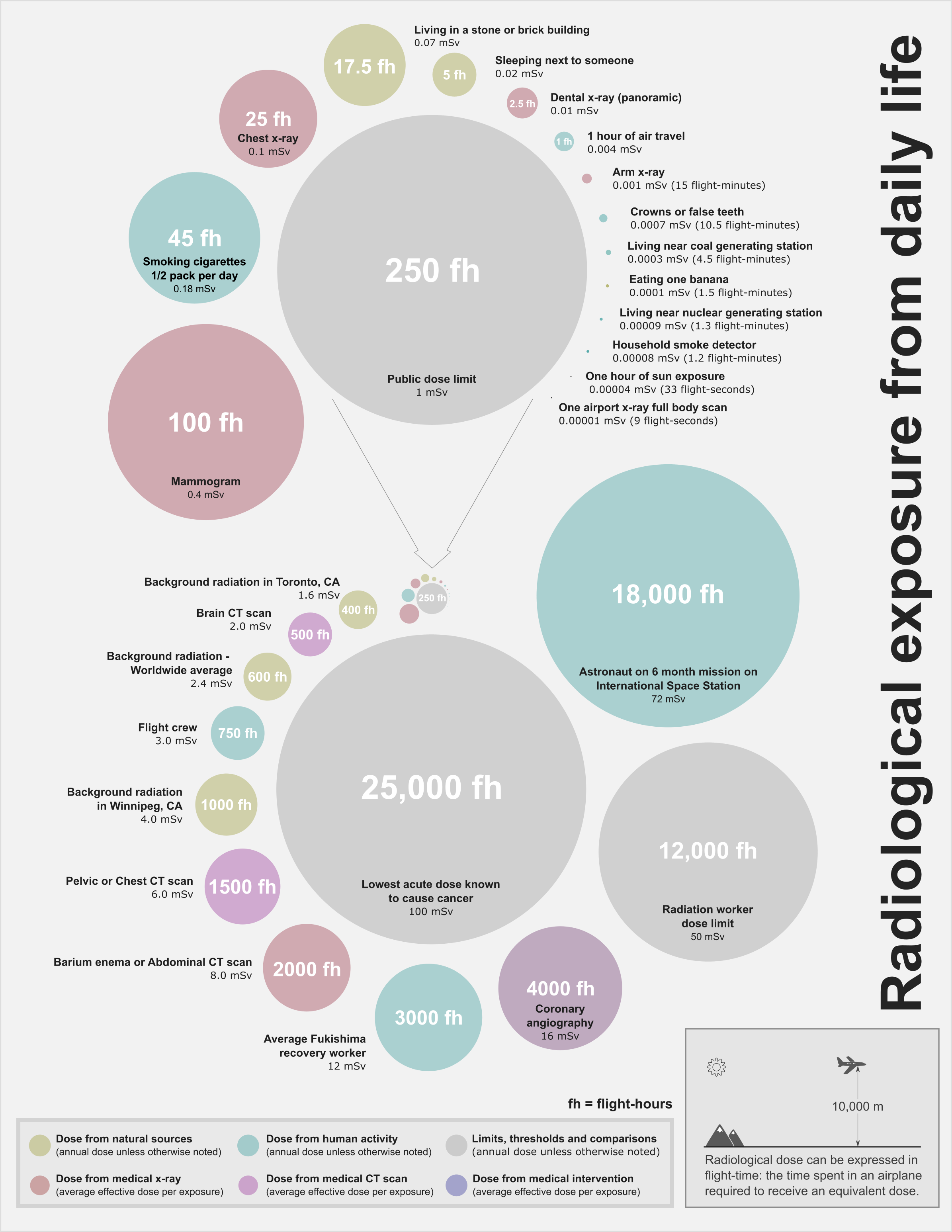

: While radiological dose at cruising altitudes varies with
"Ionizing Radiation in Earth's Atmosphere and in Space Near Earth"
Civil Aerospace Medical Institute, Federal Aviation Administration, DOT/FAA/AM- 11/9. about 15 times greater than the average dose rate at the
ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
exposure. Expressed in units of flight-time (i.e., flight-seconds, flight-minutes, flight-hours), one unit of flight-time is approximately equivalent to the radiological dose received during the same unit of time spent in an airliner
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ...
at cruising altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
. FED is intended as a general educational unit to enable a better understanding of radiological dose by converting dose typically presented in sieverts into units of time. FED is only meant as an educational exercise and is not a formally adopted dose measurement.


History
The flight-time equivalent dose concept is the creation of Ulf Stahmer, aCanadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
professional engineer working in the field of radioactive materials transport. It was first presented in the poster session at the 18th International Symposium of the Packaging and Transport of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM) held in Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
, Hyogo, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
where the poster received an Aoki Award for distinguished poster presentation. In 2018, an article on FED appeared in the peer-reviewed journal The Physics Teacher.
Usage
Flight-time equivalent dose is an informal measurement, so any equivalences are necessarily approximate. It has been found useful to provide context between radiological doses received from various every-day activities and medical procedures.Dose calculation
FED corresponds to the time spent in an airliner flying at altitude required to receive a corresponding radiological dose. FED is calculated by taking a known dose (typically in millisieverts) and dividing it by the average dose rate (typically in millisieverts per hour) at an altitude of 10,000 m, a typical cruising altitude for a commercial airliner.: While radiological dose at cruising altitudes varies with
latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
, for FED calculations, the radiological dose rate at an altitude of 10,000 m has been standardized to be 0.004 mSv/h,Friedberg, W; Copeland K (2011)"Ionizing Radiation in Earth's Atmosphere and in Space Near Earth"
Civil Aerospace Medical Institute, Federal Aviation Administration, DOT/FAA/AM- 11/9. about 15 times greater than the average dose rate at the
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's surface. Using this technique, the FED received from a 0.01 mSv panoramic dental x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
is approximately equivalent to 2.5 flight-hours; the FED received from eating one banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
is approximately equal to 1.5 flight-minutes; and the FED received each year from naturally occurring background radiation
Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.
Background radiation originates from a variety of sources ...
(2.4 mSv/year) is approximately equivalent to 600 flight-hours.
Radiological exposures and limits
For comparison, a list of activities (including common medical procedures) and their estimated radiological exposures are tabulated below. Regulatory occupational dose limits for the public and radiation workers are also included. Items on this list are represented pictorially in the accompanying illustrations.See also
*Background radiation
Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.
Background radiation originates from a variety of sources ...
* Background radiation equivalent time
Background radiation equivalent time (BRET) or background equivalent radiation time (BERT) is a unit of measurement of ionizing radiation dosage amounting to one day worth of average human exposure to background radiation.
BRET units are used as a ...
* Banana equivalent dose
Banana equivalent dose (BED) is an informal unit of measurement of ionizing radiation exposure, intended as a general educational example to compare a dose of radioactivity to the dose one is exposed to by eating one average-sized banana. Bananas ...
* List of unusual units of measurement
An unusual unit of measurement is a unit of measurement that does not form part of a coherent system of measurement, especially because its exact quantity may not be well known or because it may be an inconvenient multiple or fraction of a base ...
References
{{reflist Units of radioactivity Background radiation Equivalent units