|
Flajolet Lecture Prize
The Philippe Flajolet Lecture Prize is awarded to for contributions to analytic combinatorics and analysis of algorithms, in the fields of theoretical computer science. This prize is named in memory of Philippe Flajolet. History The Flajolet Lecture Prize has been awarded since 2014. The Flajolet Lecture Prize is awarded in odd-numbered years. After being selected for the prize, the recipient delivers the Flajolet Lecture during the following year. This lecture is organized as a keynote address at the AofA—International Meeting on Combinatorial, Probabilistic, and Asymptotic Methods in the Analysis of Algorithms, International Conference on Probabilistic, Combinatorial and Asymptotic Methods for the Analysis of Algorithms (AofA). AofA is the international conference that began as a series of seminars, started by Flajolet and others in 1993. The Selection Committee consists of three members from this field. Scientific topics The recipients of the Flajolet Lecture Prize w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic Combinatorics
In combinatorics, the symbolic method is a technique for counting combinatorial objects. It uses the internal structure of the objects to derive formulas for their generating functions. The method is mostly associated with Philippe Flajolet and is detailed in Part A of his book with Robert Sedgewick, '' Analytic Combinatorics'', while the rest of the book explains how to use complex analysis in order to get asymptotic and probabilistic results on the corresponding generating functions. During two centuries, generating functions were popping up via the corresponding recurrences on their coefficients (as can be seen in the seminal works of Bernoulli, Euler, Arthur Cayley, Schröder, Ramanujan, Riordan, Knuth, , etc.). It was then slowly realized that the generating functions were capturing many other facets of the initial discrete combinatorial objects, and that this could be done in a more direct formal way: The recursive nature of some combinatorial structures translate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Physics
Statistical physics is a branch of physics that evolved from a foundation of statistical mechanics, which uses methods of probability theory and statistics, and particularly the mathematical tools for dealing with large populations and approximations, in solving physical problems. It can describe a wide variety of fields with an inherently stochastic nature. Its applications include many problems in the fields of physics, biology, chemistry, and neuroscience. Its main purpose is to clarify the properties of matter in aggregate, in terms of physical laws governing atomic motion. Statistical mechanics develop the phenomenological results of thermodynamics from a probabilistic examination of the underlying microscopic systems. Historically, one of the first topics in physics where statistical methods were applied was the field of classical mechanics, which is concerned with the motion of particles or objects when subjected to a force. Scope Statistical physics explains and quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy, France
Nancy ; Lorraine Franconian: ''Nanzisch'' is the prefecture of the northeastern French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle. It was the capital of the Duchy of Lorraine, which was annexed by France under King Louis XV in 1766 and replaced by a province, with Nancy maintained as capital. Following its rise to prominence in the Age of Enlightenment, it was nicknamed the "capital of Eastern France" in the late 19th century. The metropolitan area of Nancy had a population of 511,257 inhabitants at the 2018 census, making it the 16th-largest functional urban area in France and Lorraine's largest. The population of the city of Nancy proper is 104,885. The motto of the city is , —a reference to the thistle, which is a symbol of Lorraine. Place Stanislas, a large square built between 1752 and 1756 by architect Emmanuel Héré under the direction of Stanislaus I of Poland to link the medieval old town of Nancy and the new city built under Charles III, Duke of Lorraine in the 17th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HyperLogLog
HyperLogLog is an algorithm for the count-distinct problem, approximating the number of distinct elements in a multiset. Calculating the ''exact'' cardinality of the distinct elements of a multiset requires an amount of memory proportional to the cardinality, which is impractical for very large data sets. Probabilistic cardinality estimators, such as the HyperLogLog algorithm, use significantly less memory than this, at the cost of obtaining only an approximation of the cardinality. The HyperLogLog algorithm is able to estimate cardinalities of > 109 with a typical accuracy (standard error) of 2%, using 1.5 kB of memory. HyperLogLog is an extension of the earlier LogLog algorithm, itself deriving from the 1984 Flajolet–Martin algorithm. Terminology In the original paper by Flajolet ''et al.'' and in related literature on the count-distinct problem, the term "cardinality" is used to mean the number of distinct elements in a data stream with repeated elements. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flajolet–Martin Algorithm
The Flajolet–Martin algorithm is an algorithm for approximating the number of distinct elements in a stream with a single pass and space-consumption logarithmic in the maximal number of possible distinct elements in the stream (the count-distinct problem). The algorithm was introduced by Philippe Flajolet and G. Nigel Martin in their 1984 article "Probabilistic Counting Algorithms for Data Base Applications". Later it has been refined in "LogLog counting of large cardinalities" by Marianne Durand and Philippe Flajolet, and " HyperLogLog: The analysis of a near-optimal cardinality estimation algorithm" by Philippe Flajolet et al. In their 2010 article "An optimal algorithm for the distinct elements problem", Daniel M. Kane, Jelani Nelson and David P. Woodruff give an improved algorithm, which uses nearly optimal space and has optimal ''O''(1) update and reporting times. The algorithm Assume that we are given a hash function \mathrm(x) that maps input x to integers in the range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximate Counting Algorithm
The approximate counting algorithm allows the counting of a large number of events using a small amount of memory. Invented in 1977 by Robert Morris of Bell Labs, it uses probabilistic techniques to increment the counter. It was fully analyzed in the early 1980s by Philippe Flajolet of INRIA Rocquencourt, who coined the name approximate counting, and strongly contributed to its recognition among the research community. When focused on high quality of approximation and low probability of failure, Nelson and Yu showed that a very slight modification to the Morris Counter is asymptotically optimal amongst all algorithms for the problem. The algorithm is considered one of the precursors of streaming algorithms, and the more general problem of determining the frequency moments of a data stream has been central to the field. Theory of operation Using Morris' algorithm, the counter represents an "order of magnitude estimate" of the actual count. The approximation is mathematically u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Sedgewick (computer Scientist)
Robert Sedgewick (born December 20, 1946) is an American computer scientist. He is the founding chair and the William O. Baker Professor in Computer Science at Princeton University and was a member of the board of directors of Adobe Systems (1990–2016). He previously served on the faculty at Brown University and has held visiting research positions at Xerox PARC, Institute for Defense Analyses, and INRIA. His research expertise is in algorithm science, data structures, and analytic combinatorics. He is also active in developing the college curriculum in computer science and in harnessing technology to make that curriculum available to anyone seeking the opportunity to learn from it. Early life Sedgewick was born on December 20, 1946 in Willimantic, Connecticut. During his childhood he lived in Storrs, Connecticut, where his parents Charles Hill Wallace Sedgewick and Rose Whelan Sedgewick were professors at the University of Connecticut. In 1958, he moved with his parents t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyck Path
In combinatorial mathematics, the Catalan numbers are a sequence of natural numbers that occur in various counting problems, often involving recursively defined objects. They are named after the French-Belgian mathematician Eugène Charles Catalan (1814–1894). The ''n''th Catalan number can be expressed directly in terms of binomial coefficients by :C_n = \frac = \frac = \prod\limits_^\frac \qquad\textn\ge 0. The first Catalan numbers for ''n'' = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... are :1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, ... . Properties An alternative expression for ''C''''n'' is :C_n = - for n\ge 0, which is equivalent to the expression given above because \tbinom=\tfrac\tbinomn. This expression shows that ''C''''n'' is an integer, which is not immediately obvious from the first formula given. This expression forms the basis for a proof of the correctness of the formula. The Catalan numbers satisfy the recurrence relations :C_0 = 1 \quad \text \quad C_=\sum_^C_i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OEIS
The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS) is an online database of integer sequences. It was created and maintained by Neil Sloane while researching at AT&T Labs. He transferred the intellectual property and hosting of the OEIS to the OEIS Foundation in 2009. Sloane is chairman of the OEIS Foundation. OEIS records information on integer sequences of interest to both professional and amateur mathematicians, and is widely cited. , it contains over 350,000 sequences, making it the largest database of its kind. Each entry contains the leading terms of the sequence, keywords, mathematical motivations, literature links, and more, including the option to generate a graph or play a musical representation of the sequence. The database is searchable by keyword, by subsequence, or by any of 16 fields. History Neil Sloane started collecting integer sequences as a graduate student in 1965 to support his work in combinatorics. The database was at first stored on punched card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory
In mathematics and applied mathematics, perturbation theory comprises methods for finding an approximate solution to a problem, by starting from the exact solution of a related, simpler problem. A critical feature of the technique is a middle step that breaks the problem into "solvable" and "perturbative" parts. In perturbation theory, the solution is expressed as a power series in a small parameter The first term is the known solution to the solvable problem. Successive terms in the series at higher powers of \varepsilon usually become smaller. An approximate 'perturbation solution' is obtained by truncating the series, usually by keeping only the first two terms, the solution to the known problem and the 'first order' perturbation correction. Perturbation theory is used in a wide range of fields, and reaches its most sophisticated and advanced forms in quantum field theory. Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics) describes the use of this method in quantum mechanics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Path
In combinatorics, a lattice path in the -dimensional integer lattice of length with steps in the set , is a sequence of vectors such that each consecutive difference v_i - v_ lies in . A lattice path may lie in any lattice in , but the integer lattice is most commonly used. An example of a lattice path in of length 5 with steps in S = \lbrace (2,0), (1,1), (0,-1) \rbrace is L = \lbrace (-1,-2), (0,-1), (2,-1), (2,-2), (2,-3), (4,-3) \rbrace . North-East lattice paths A North-East (NE) lattice path is a lattice path in \mathbb^2 with steps in S = \lbrace (0,1), (1,0) \rbrace . The (0,1) steps are called North steps and denoted by N 's; the (1,0) steps are called East steps and denoted by E 's. NE lattice paths most commonly begin at the origin. This convention allows us to encode all the information about a NE lattice path L in a single permutation word. The length of the word gives us the number of steps of the lattice path, k . The order of the N 's an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
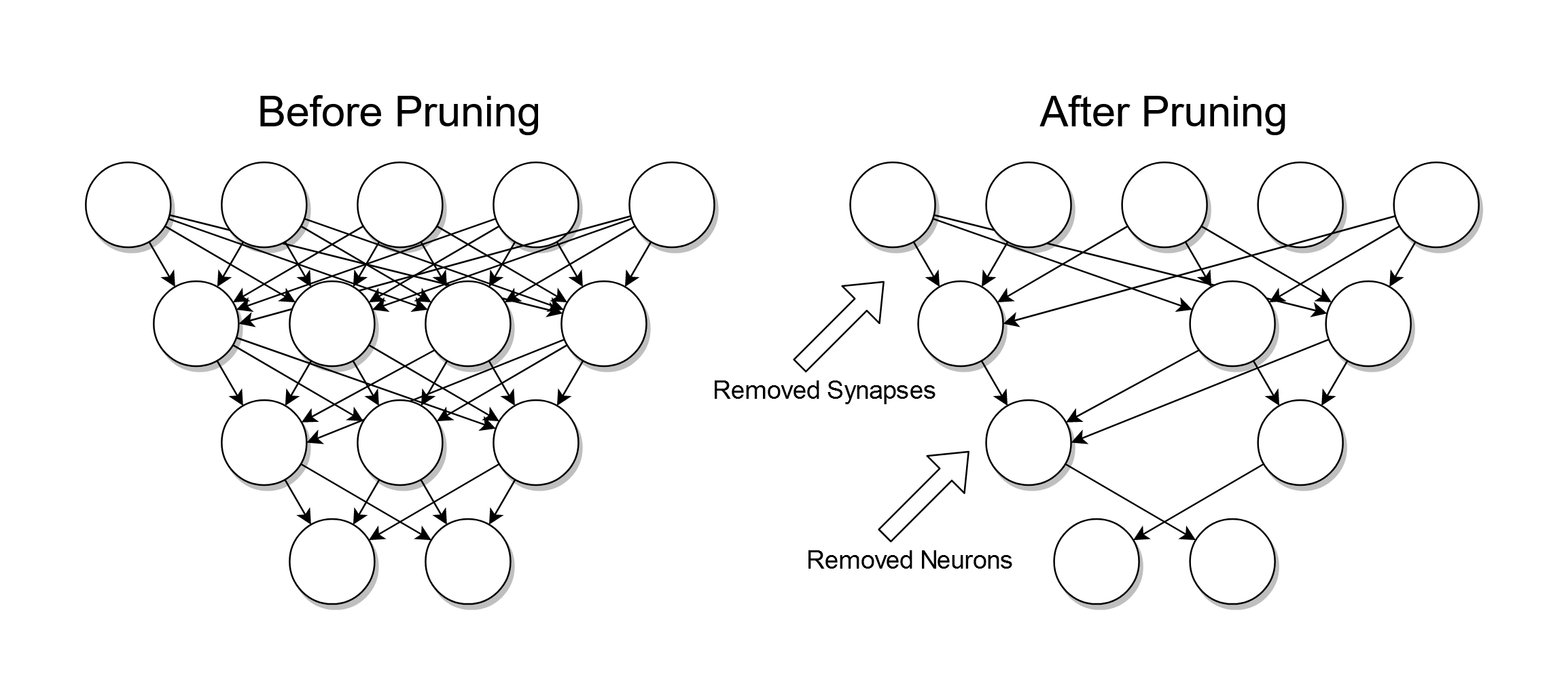
Pruning (algorithm)
Pruning is a data compression technique in machine learning and search algorithms that reduces the size of decision trees by removing sections of the tree that are non-critical and redundant to classify instances. Pruning reduces the complexity of the final classifier, and hence improves predictive accuracy by the reduction of overfitting. One of the questions that arises in a decision tree algorithm is the optimal size of the final tree. A tree that is too large risks overfitting the training data and poorly generalizing to new samples. A small tree might not capture important structural information about the sample space. However, it is hard to tell when a tree algorithm should stop because it is impossible to tell if the addition of a single extra node will dramatically decrease error. This problem is known as the horizon effect. A common strategy is to grow the tree until each node contains a small number of instances then use pruning to remove nodes that do not provide ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |