|
Flag Of Namibia
The flag of Namibia was adopted on 21 March 1990 upon independence from South Africa. Design The National Symbols Sub-Committee received 870 entries for the national flag. Six designs were short-listed; this was reduced to three, those of three Namibians – Theo Jankowski of Rehoboth, Don Stevenson of Windhoek and Ortrud Clay of Lüderitz. These three designs were combined to form the Namibia national flag, adopted unanimously on 2 February 1990 by the Constituent Assembly. The three designers were publicly acknowledged by judge Hans Berker, the chairman of the subcommittee, at the unveiling ceremony on 9 March 1990. However, two other claims were made – South African Frederick Brownell claimed that he had designed the flag in his role as South African State Herald. (A series of 8 articles.) The other claimant was Briton Roy Allen, who claimed that the flag design was the result of a competition run by Hannes Smith of the ''Windhoek Observer'', and that he had won. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Jack
A jack is a flag flown from a short jackstaff at the bow (front) of a vessel, while the ensign is flown on the stern (rear). Jacks on bowsprits or foremasts appeared in the 17th century. A country may have different jacks for different purposes, especially when (as in the United Kingdom and the Netherlands) the naval jack is forbidden to other vessels. The United Kingdom has an official civil jack; the Netherlands has several unofficial ones. In some countries, ships of other government institutions may fly the naval jack, e.g. the ships of the United States Coast Guard and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the case of the US jack. Certain organs of the UK's government have their own departmental jacks. Commercial or pleasure craft may fly the flag of an administrative division (state, province, land) or municipality at the bow. Merchant ships may fly a house flag. Yachts may fly a club burgee or officer's flag or the owner's private signal at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Trinidad And Tobago
The flag of Trinidad and Tobago was adopted upon independence from the United Kingdom on 31 August 1962. Designed by Carlisle Chang (1921–2001), the flag of Trinidad and Tobago was chosen by the independence committee of 1962. Red, black and white symbolise fire (the sun, representing courage), earth (representing dedication) and water (representing purity and equality). It is one of the few national flags incorporating a diagonal line, with other examples including the DR Congo, Tanzania, Namibia, and Brunei. Design The flag of Trinidad and Tobago is a red field with a white-edged black diagonal band from the upper hoist side to the lower fly-side. In blazon, ''Gules, a bend Sable fimbriated Argent''. It was designed by Carlisle Chang. Construction The width of the white stripes is of the flag length and the width of the black stripe is . The total width of the three stripes together is, therefore, of the length. Other flags The civil ensign is the national flag in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
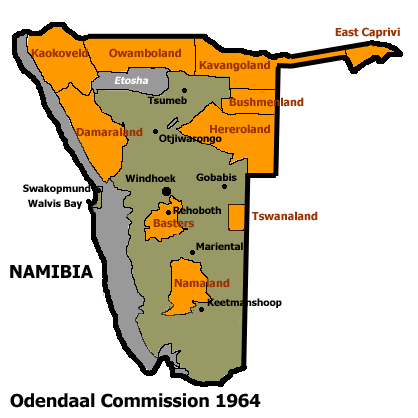
Hereroland
Hereroland was the first bantustan in South West Africa (present day Namibia), intended by the apartheid government to be a self-governing homeland for the Herero people. It was set up in 1968. Hereroland, like other homelands in South West Africa, was abolished in May 1989 at the start of the transition to independence. See also *Apartheid Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ... * Leaders of Hereroland References History of Namibia Bantustans in South West Africa Herero people States and territories established in 1968 States and territories disestablished in 1989 1968 establishments in South West Africa {{Namibia-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Caprivi
East Caprivi or Itenge was a bantustan in South West Africa (present-day Namibia), intended by the apartheid government to be a self-governing homeland for the Masubiya people. It was set up in 1972, in the very corner of the Namibian panhandle called the Caprivi Strip. It was granted a self-governing status in 1976. The homeland was renamed Zambezi Region soon after. Unlike the other homelands in South West Africa, East Caprivi was administered through the Department of Bantu Administration and Development in Pretoria. East Caprivi, like other homelands in South West Africa, was abolished in May 1989 at the start of the transition to independence. See also * Leaders of East Caprivi *Caprivi Liberation Army Caprivi Liberation Army (CLA) is a Namibian rebel and separatist group which was established in 1994 to separate the Caprivi Strip, a region mainly inhabited by the Lozi people. It operates only in the Caprivi strip. Background The Caprivi Stri ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damaraland
Damaraland was a name given to the north-central part of what later became Namibia, inhabited by the Damaras. It was bounded roughly by Ovamboland in the north, the Namib Desert in the west, the Kalahari Desert in the east, and Windhoek in the south. In the 1970s the name Damaraland was revived for a bantustan in South West Africa (present-day Namibia), intended by the apartheid government to be a self-governing homeland for the Damara people. A centrally administered local government was created in 1980. The bantustan Damaraland was situated on the western edge of the territory that had been known as Damaraland in the 19th century. Damaraland, like other homelands in South West Africa, was abolished in May 1989 at the start of the transition to independence. The name Damaraland predates South African control of Namibia, and was described as "the central portion of German South West Africa" in the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition. See also * Apartheid * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushmanland (South West Africa)
Bushmanland ( af, Boesmanland) was a bantustan in South West Africa (present-day Namibia), intended by the apartheid government to be a self-governing homeland for the San people (the Bushmen). Despite this, a government was not established in the region. The bantustan, then called 'homelands' by the South African authorities, was established with the issue of Proclamation 208 in 1976. Bushmanland, like other homelands in South West Africa, was abolished in May 1989 at the start of the transition to independence. See also * Bushmanland (South Africa) *Apartheid Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid wa ... References History of Namibia Bantustans in South West Africa States and territories disestablished in 1989 {{Namibia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantustan
A Bantustan (also known as Bantu homeland, black homeland, black state or simply homeland; ) was a territory that the National Party administration of South Africa set aside for black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia), as part of its policy of apartheid. By extension, outside South Africa the term refers to regions that lack any real legitimacy, consisting often of several unconnected enclaves, or which have emerged from national or international gerrymandering.Macmillan DictionaryBantustan, "1. one of the areas in South Africa where black people lived during the apartheid system; 2. SHOWING DISAPPROVAL any area where people are forced to live without full civil and political rights." The term, first used in the late 1940s, was coined from Bantu' (meaning "people" in some of the Bantu languages) and '' -stan'' (a suffix meaning "land" in the Persian language and some Persian-influenced languages of western, central, and southern Asia). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SWAPO
The South West Africa People's Organisation (, SWAPO; af, Suidwes-Afrikaanse Volks Organisasie, SWAVO; german: Südwestafrikanische Volksorganisation, SWAVO), officially known as the SWAPO Party of Namibia, is a political party and former independence movement in Namibia. Founded in 1960, it has been the governing party in Namibia since the country achieved independence in 1990. The party continues to be dominated in number and influence by the Ovambo ethnic group. SWAPO held a two-thirds majority in parliament from 1994 to 2019. In the general election held in November 2019, the party won 65.5% of the popular vote and 63 out of the 104 seats in the National Assembly. It also holds 28 out of the 42 seats in the National Council. As of November 2017, Namibian President Hage Geingob has been the president of SWAPO after being elected to the position at the party's electoral congress. History Background and foundation German South West Africa was established in 1884. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UN Trust Territory
United Nations trust territories were the successors of the remaining League of Nations mandates and came into being when the League of Nations ceased to exist in 1946. All of the trust territories were administered through the United Nations Trusteeship Council. The concept is distinct from a territory temporarily and directly governed by the United Nations. The one League of Nation mandate not succeeded by a trust territory was South West Africa, at South Africa's insistence. South Africa's apartheid regime refused to commit to preparing the territory for independence and majority rule, as required by the trust territory guidelines, among other objections. South-West Africa eventually gained independence in 1990 as Namibia. All trust territories have either attained self-government or independence. The last was Palau, formerly part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, which became a member state of the United Nations in December 1994. Trust territories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South West Africa
South West Africa ( af, Suidwes-Afrika; german: Südwestafrika; nl, Zuidwest-Afrika) was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1990, after which it became modern-day Namibia. It bordered Angola (Portuguese colony before 1975), Botswana ( Bechuanaland before 1966), South Africa, and Zambia (Northern Rhodesia before 1964). Previously the German colony of South West Africa from 1884–1915, it was made a League of Nations mandate of the Union of South Africa following Germany's defeat in the First World War. Although the mandate was abolished by the United Nations in 1966, South African control over the territory continued despite its illegality under international law. The territory was administered directly by the South African government from 1915 to 1978, when the Turnhalle Constitutional Conference laid the groundwork for semi-autonomous rule. During an interim period between 1978 and 1985, South Africa gradually granted South West Africa a limited f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German South-West Africa
German South West Africa (german: Deutsch-Südwestafrika) was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. With a total area of 835,100 km², it was one and a half times the size of the mainland German Empire in Europe at the time. The colony had a population of around 2,600 Germans. German rule over this territory was punctuated by numerous rebellions by its native African peoples, which culminated in a campaign of German reprisals from 1904 to 1908 known as the Herero and Namaqua genocide. In 1915, during World War I, German South West Africa was invaded by the Western Allies in the form of South African and British forces. After the war its administration was taken over by the Union of South Africa (part of the British Empire) and the territory was administered as South West Africa under a League of Nations mandate. It became independent as Namibia on 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blazon
In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct the appropriate image. The verb ''to blazon'' means to create such a description. The visual depiction of a coat of arms or flag has traditionally had considerable latitude in design, but a verbal blazon specifies the essentially distinctive elements. A coat of arms or flag is therefore primarily defined not by a picture but rather by the wording of its blazon (though in modern usage flags are often additionally and more precisely defined using geometrical specifications). ''Blazon'' is also the specialized language in which a blazon is written, and, as a verb, the act of writing such a description. ''Blazonry'' is the art, craft or practice of creating a blazon. The language employed in ''blazonry'' has its own vocabulary, grammar and syntax, which becomes essential for comprehension when blazoning a complex coat of arms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)